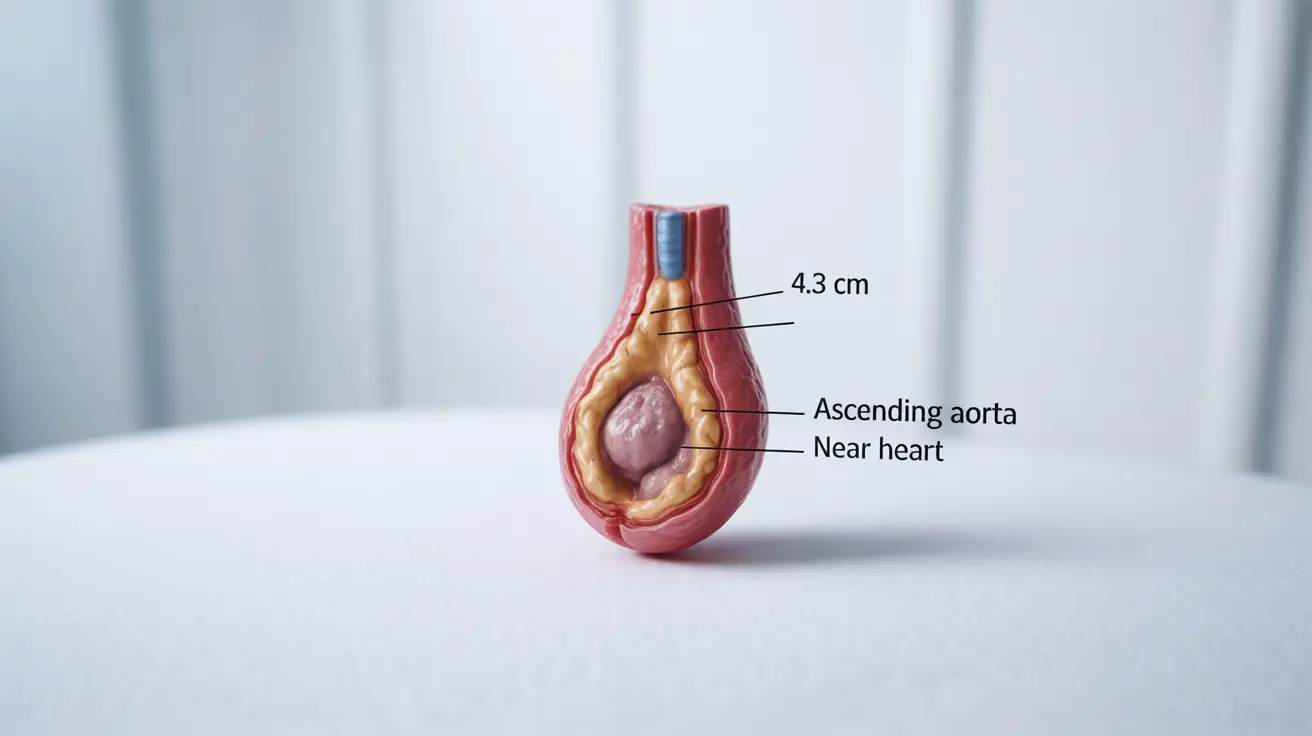
An ascending aortic aneurysm measuring 4.3 centimeters represents a significant cardiovascular condition that requires careful attention and monitoring. This enlargement of the aorta, while concerning, can be effectively managed with proper medical supervision and lifestyle modifications.
Understanding the implications of a 4.3 cm ascending aortic aneurysm is crucial for making informed decisions about your health care. This comprehensive guide will explore the risks, monitoring requirements, and management strategies associated with this condition.
Understanding the Risks of a 4.3 cm Ascending Aortic Aneurysm
At 4.3 centimeters, an ascending aortic aneurysm is considered moderate in size. The risk of rupture at this stage is relatively low, typically less than 1% per year. However, the location in the ascending aorta makes careful monitoring essential due to its proximity to the heart and other vital structures.
Several factors can influence the risk level, including:
- Family history of aortic conditions
- High blood pressure
- Smoking status
- Presence of genetic conditions like Marfan syndrome
- Overall cardiovascular health
Monitoring Requirements and Imaging Tests
Regular medical surveillance is crucial for tracking the progression of a 4.3 cm ascending aortic aneurysm. Your healthcare provider will typically recommend:
- Initial comprehensive imaging evaluation
- Regular follow-up scans every 6-12 months
- More frequent monitoring if growth is detected
- Additional testing if new symptoms develop
Types of Imaging Tests
Several imaging modalities may be used to monitor your aneurysm:
- CT (computed tomography) scans
- MRI (magnetic resonance imaging)
- Echocardiogram
- Chest X-rays (for general monitoring)
Lifestyle Modifications and Risk Management
While medical monitoring is essential, certain lifestyle changes can help manage your condition:
- Maintaining optimal blood pressure control
- Quitting smoking
- Engaging in appropriate physical activity
- Managing weight
- Reducing stress
- Following a heart-healthy diet
Exercise Guidelines
Physical activity should be approached carefully with a 4.3 cm ascending aortic aneurysm. Generally recommended activities include:
- Light to moderate aerobic exercise
- Controlled breathing exercises
- Gentle stretching
- Walking at a comfortable pace
Medical Intervention and Surgical Considerations
At 4.3 cm, surgical intervention is not typically recommended unless certain risk factors are present. However, your healthcare team will carefully evaluate factors such as:
- Rate of aneurysm growth
- Presence of symptoms
- Overall health status
- Family history
- Genetic conditions
Warning Signs and Emergency Symptoms
Knowing when to seek immediate medical attention is crucial. Watch for:
- Sudden, severe chest or back pain
- Difficulty breathing
- Sudden weakness or dizziness
- Loss of consciousness
- Difficulty speaking or vision changes
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the risks of having a 4.3 cm ascending aortic aneurysm and how likely is it to rupture? A 4.3 cm ascending aortic aneurysm carries a relatively low annual rupture risk of less than 1%. However, regular monitoring is essential as the risk increases if the aneurysm grows or if other risk factors are present.
How often should a 4.3 cm ascending aortic aneurysm be monitored with imaging tests like ultrasound or CT? Most healthcare providers recommend imaging every 6-12 months for a 4.3 cm ascending aortic aneurysm. The frequency may increase if growth is detected or if you have additional risk factors.
What lifestyle changes can help reduce the risk of aortic aneurysm growth or complications at this size? Key lifestyle modifications include maintaining normal blood pressure, quitting smoking, engaging in appropriate exercise, managing weight, reducing stress, and following a heart-healthy diet.
When does a 4.3 cm ascending aortic aneurysm typically require surgery or other medical intervention? Surgery is not typically recommended at 4.3 cm unless there are complicating factors such as rapid growth, genetic conditions, or significant symptoms. The decision for intervention is individualized based on multiple risk factors.
What symptoms should prompt immediate medical attention if I have a 4.3 cm ascending aortic aneurysm? Seek immediate medical care if you experience sudden severe chest or back pain, difficulty breathing, sudden weakness or dizziness, loss of consciousness, or changes in vision or speech.