Abnormal posturing is a serious medical condition that indicates significant brain dysfunction or injury. When someone exhibits abnormal posturing, their body assumes unusual positions involuntarily, often signaling a severe neurological emergency that requires immediate medical attention.
Healthcare professionals consider abnormal posturing a crucial indicator when assessing a patient's neurological status, as it often reflects the severity of brain damage and helps determine appropriate medical interventions.
Types of Abnormal Posturing
There are three main types of abnormal posturing, each indicating different levels of brain injury severity:
Decorticate Posturing
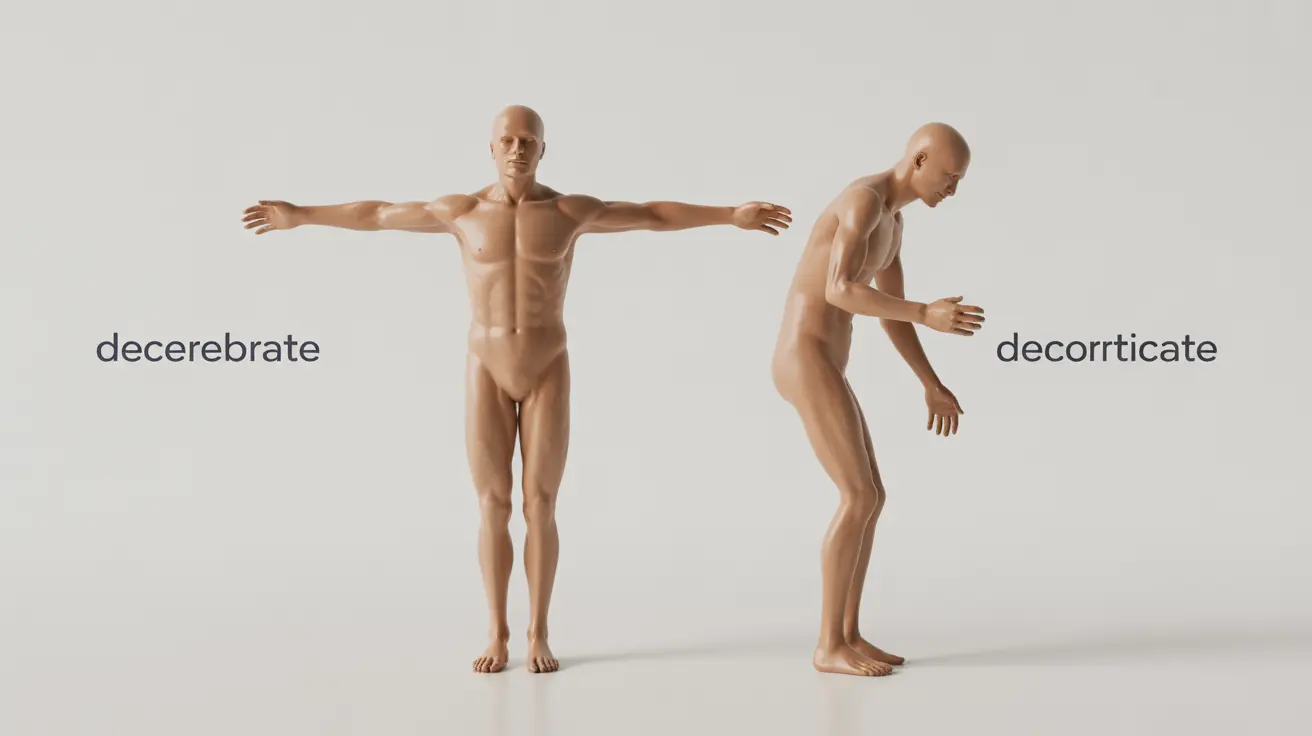
In this type, the arms bend inward toward the body, with clenched fists and legs extended straight. This pattern typically indicates damage to areas above the brainstem but below the cerebral cortex.
Decerebrate Posturing
This form involves rigid extension of the arms and legs, with the toes pointing downward and the head arched backward. It often signals a more severe brain injury, particularly affecting the brainstem area.
Opisthotonus
This rare form causes severe arching of the back, with the head, neck, and spine curved backward in a bow-like position. It can occur in severe cases of brain injury or certain types of infections.
Common Causes and Risk Factors
Abnormal posturing typically results from severe conditions affecting the brain, including:
- Traumatic brain injury
- Stroke
- Brain tumors
- Infections affecting the central nervous system
- Severe brain hemorrhage
- Drug overdose
- Lack of oxygen to the brain
- Status epilepticus
Diagnostic Approach
Medical professionals assess abnormal posturing as part of a comprehensive neurological examination, which typically includes:
- Glasgow Coma Scale evaluation
- Pupillary response testing
- Brain imaging (CT scans or MRI)
- Blood tests to identify underlying causes
- Evaluation of vital signs
Emergency Medical Response
When abnormal posturing is observed, immediate medical intervention is crucial. Emergency responders will typically:
- Secure the airway and ensure adequate breathing
- Stabilize the spine if trauma is suspected
- Monitor vital signs
- Provide immediate transport to an emergency facility
- Begin necessary interventions to reduce brain swelling
Treatment and Recovery Outlook
The treatment approach depends on the underlying cause but generally focuses on:
- Immediate life support measures
- Reducing intracranial pressure
- Treating the primary condition causing the posturing
- Preventing secondary brain injury
- Rehabilitation when appropriate
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the different types of abnormal posturing and how can I recognize them?
The three main types are decorticate posturing (arms bent inward, clenched fists), decerebrate posturing (rigid extension of arms and legs), and opisthotonus (severe back arching). Each type indicates different levels of brain injury severity and requires immediate medical attention.
What causes abnormal posturing and which brain injuries are most commonly associated with it?
Abnormal posturing is most commonly caused by severe traumatic brain injuries, strokes, brain tumors, and conditions that increase intracranial pressure. Any situation that severely disrupts normal brain function can potentially lead to abnormal posturing.
How is abnormal posturing diagnosed and what does it indicate about brain function?
Diagnosis involves neurological examination, including the Glasgow Coma Scale, imaging studies, and other diagnostic tests. The presence and type of posturing can indicate the severity and location of brain injury, helping guide treatment decisions.
What immediate medical steps should be taken if someone shows signs of abnormal posturing?
Immediate emergency medical services should be called. While waiting, ensure the person's airway is clear, prevent any injury from the rigid movements, and do not attempt to force the body into a normal position. Medical professionals will need to quickly assess and treat the underlying cause.
Can abnormal posturing improve with treatment, and what is the overall prognosis for patients showing these symptoms?
The prognosis varies significantly depending on the underlying cause, timing of treatment, and severity of brain injury. While some patients may recover with prompt medical intervention and rehabilitation, abnormal posturing often indicates a serious condition that can result in long-term complications or poor outcomes.