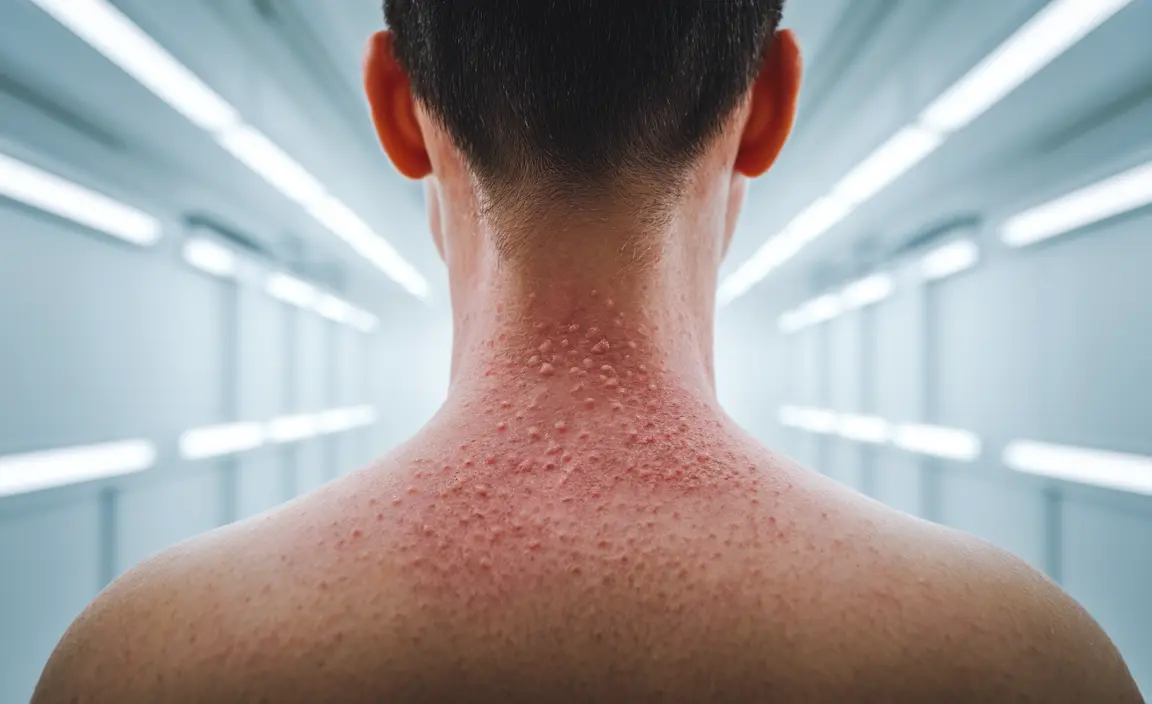
Acne keloidalis nuchae (AKN) is a chronic inflammatory condition that affects the back of the neck and scalp, particularly in individuals with curly or coarse hair. Understanding effective treatment approaches and proper hair care techniques is crucial for managing this challenging condition and preventing its progression.
This comprehensive guide explores proven treatment methods, proper hair care practices, and essential lifestyle modifications to help those affected by AKN maintain better control over their symptoms and improve their quality of life.
Understanding Early Signs and Symptoms
Early recognition of AKN symptoms is crucial for effective management. Initial signs typically include:
- Small, firm bumps at the hairline
- Mild irritation or tenderness
- Redness in the affected area
- Occasional itching or burning sensation
As the condition progresses without treatment, these bumps may develop into larger, harder growths that can become permanent. Early intervention is key to preventing such progression.
Medical Treatment Options
Several medical treatments have shown effectiveness in managing AKN. Your healthcare provider may recommend:
Topical Treatments
These are typically the first line of defense:
- Corticosteroid creams or lotions
- Antibiotic preparations
- Retinoids for inflammation control
Oral Medications
For more severe cases, systemic treatments may include:
- Oral antibiotics
- Anti-inflammatory medications
- Specialized medications to control inflammation
Advanced Procedures
When conservative treatments aren't sufficient, medical procedures might be considered:
- Laser therapy
- Surgical excision
- Steroid injections
- Cryotherapy
Proper Hair Care and Shampoo Usage
Appropriate hair care is fundamental in managing AKN. When using shampoo:
- Choose gentle, non-irritating formulations
- Avoid harsh chemicals and fragrances
- Use lukewarm water to minimize irritation
- Pat the neck area dry instead of rubbing
Regular cleansing is important, but over-washing can irritate the skin. Find a balance that works for your specific situation.
Lifestyle Modifications for Better Management
Several lifestyle changes can significantly impact AKN management:
- Avoid tight collars and clothing that rubs against the neck
- Use proper hair grooming techniques
- Maintain good hygiene practices
- Avoid close shaving of the affected area
- Manage stress levels, as stress can trigger flare-ups
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the most effective treatment options for acne keloidalis nuchae, including medical and procedural therapies?
The most effective treatments typically include a combination of topical medications (steroids and antibiotics), oral medications when needed, and procedural treatments like laser therapy or surgical excision for severe cases. Treatment effectiveness varies by individual and severity of the condition.
How can I use shampoo safely to help manage and prevent acne keloidalis nuchae flare-ups?
Use gentle, non-irritating shampoos with lukewarm water. Avoid harsh chemicals and fragrances. Wash the affected area carefully without scrubbing, and pat dry gently. Maintain regular but not excessive washing frequency to prevent irritation.
What lifestyle changes can reduce irritation and lower the risk of worsening acne keloidalis nuchae?
Key lifestyle modifications include avoiding tight collars, using proper hair grooming techniques, maintaining good hygiene, avoiding close shaving of the affected area, and managing stress levels. These changes can significantly reduce irritation and prevent worsening of symptoms.
What are the early symptoms of acne keloidalis nuchae and when should I see a doctor?
Early symptoms include small, firm bumps at the hairline, mild irritation, redness, and occasional itching. See a doctor when you notice persistent bumps, increasing discomfort, or if the condition starts affecting your daily life or self-esteem.
Can acne keloidalis nuchae be cured, or is it only manageable with ongoing treatment?
While AKN cannot be completely cured, it can be effectively managed with proper treatment and ongoing care. Early intervention and consistent management strategies can help control symptoms and prevent progression to more severe forms of the condition.