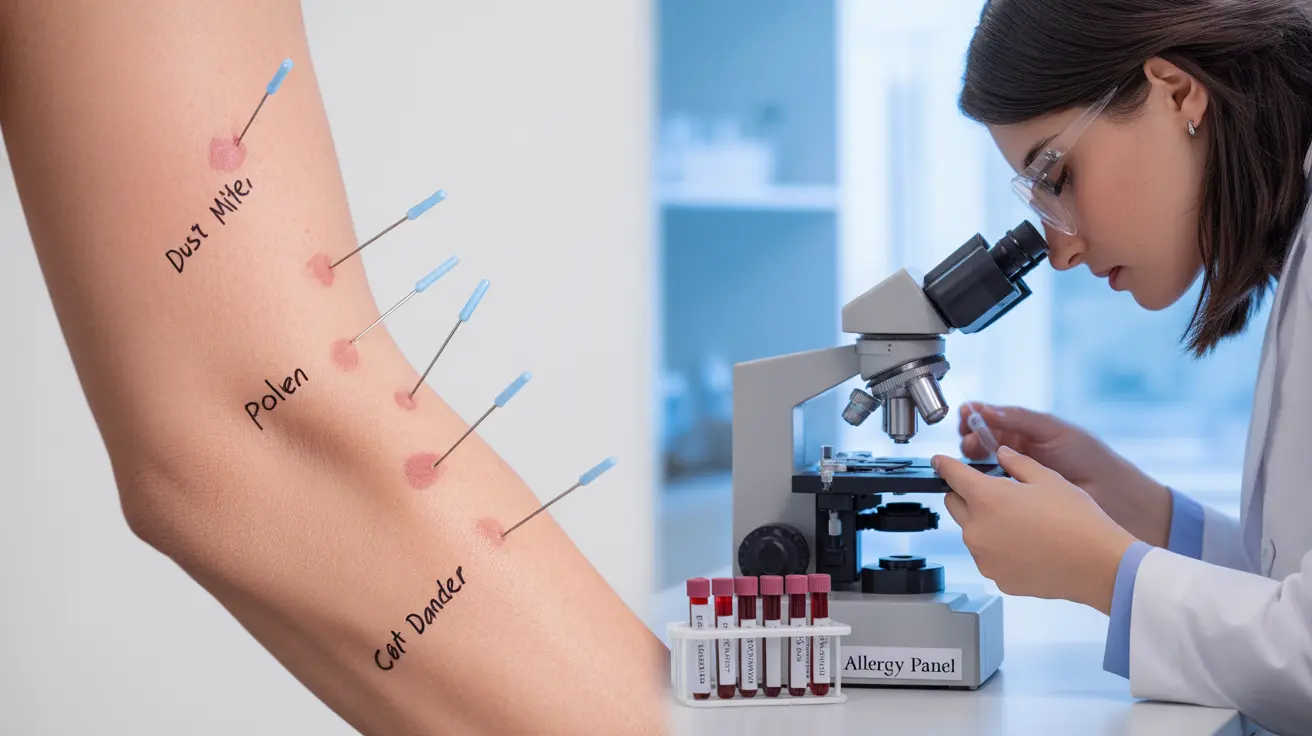
When it comes to diagnosing allergies, healthcare providers primarily rely on two testing methods: blood tests and skin tests. Understanding the differences between these diagnostic tools can help you feel more prepared for your allergy evaluation and make informed decisions about your healthcare.
In this comprehensive guide, we'll explore how these two testing methods work, their accuracy, and when one might be more appropriate than the other for your specific situation.
How Allergy Tests Work
Skin Prick Testing
Skin prick tests involve placing small amounts of potential allergens on or under the skin's surface. The healthcare provider typically:
- Places drops of different allergens on marked areas of your skin
- Creates tiny punctures through the drops using sterile needles
- Observes the skin's reaction over 15-20 minutes
- Measures any resulting wheals (raised bumps) to determine sensitivity
Blood Allergy Testing
Blood tests, also known as specific IgE (sIgE) tests, measure the levels of antibodies your immune system produces in response to specific allergens. These tests require:
- A simple blood draw
- Laboratory analysis
- Measurement of IgE antibody levels for specific allergens
- Interpretation by an allergist or healthcare provider
Accuracy and Reliability
Both testing methods have proven track records for accuracy, though their reliability can vary depending on the specific allergen being tested. Skin tests typically show results immediately, while blood tests may take several days to process but can often detect a broader range of potential allergies.
Choosing the Right Test
When to Consider Skin Testing
Skin tests may be preferred when:
- Immediate results are needed
- Testing for common environmental or food allergies
- The patient can temporarily stop antihistamine medications
- There are no contraindications like severe skin conditions
When to Consider Blood Testing
Blood tests might be more appropriate when:
- The patient has severe skin conditions like eczema
- Cannot stop taking antihistamine medications
- Has a history of severe allergic reactions
- Young children need testing but may not tolerate skin tests well
Preparing for Allergy Testing
Proper preparation is crucial for accurate results. Your healthcare provider will give you specific instructions, which may include stopping certain medications before testing. Blood tests generally require no special preparation, making them more convenient for some patients.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the main differences between allergy blood tests and skin prick tests in diagnosing allergies?
The main differences lie in the testing method and timing of results. Skin prick tests provide immediate results through direct skin reaction, while blood tests measure antibody levels in a laboratory setting and take several days to process. Skin tests require direct exposure to allergens, whereas blood tests can be performed with a simple blood draw.
How accurate are skin prick tests compared to blood allergy tests for different allergens?
Both tests generally show comparable accuracy levels. Skin prick tests typically have a sensitivity of 80-95% for inhalant allergens, while blood tests show similar accuracy rates. However, accuracy can vary depending on the specific allergen being tested and the quality of the testing materials used.
When should a doctor recommend a blood allergy test instead of a skin prick test?
Doctors typically recommend blood tests when patients have extensive skin conditions, cannot stop taking antihistamines, have a history of severe allergic reactions, or when testing young children who may not tolerate skin testing well. Blood tests are also preferred when testing for certain food allergies or when skin test results are unclear.
Do I need to stop taking allergy medications before a skin prick test or a blood test?
For skin prick tests, you typically need to stop taking antihistamines and certain other medications for 5-7 days before testing. Blood tests do not require you to stop taking any medications, making them more convenient for patients who cannot discontinue their allergy medications.
What are the risks and benefits of skin tests versus blood tests for allergy diagnosis?
Skin tests offer immediate results and are generally less expensive, but carry a small risk of allergic reaction and require medication discontinuation. Blood tests are safer with no risk of allergic reaction, don't require medication changes, but are typically more expensive and take longer to get results. Both methods are considered safe and reliable diagnostic tools.