Amelanotic melanoma represents one of the most challenging forms of skin cancer to detect, primarily because it lacks the dark pigmentation typically associated with melanoma. This unique characteristic makes early identification crucial yet particularly difficult for both healthcare providers and patients.
Understanding the distinct features and warning signs of amelanotic melanoma can literally save lives. This comprehensive guide will help you recognize its characteristics, understand why early detection matters, and learn about available treatment options.
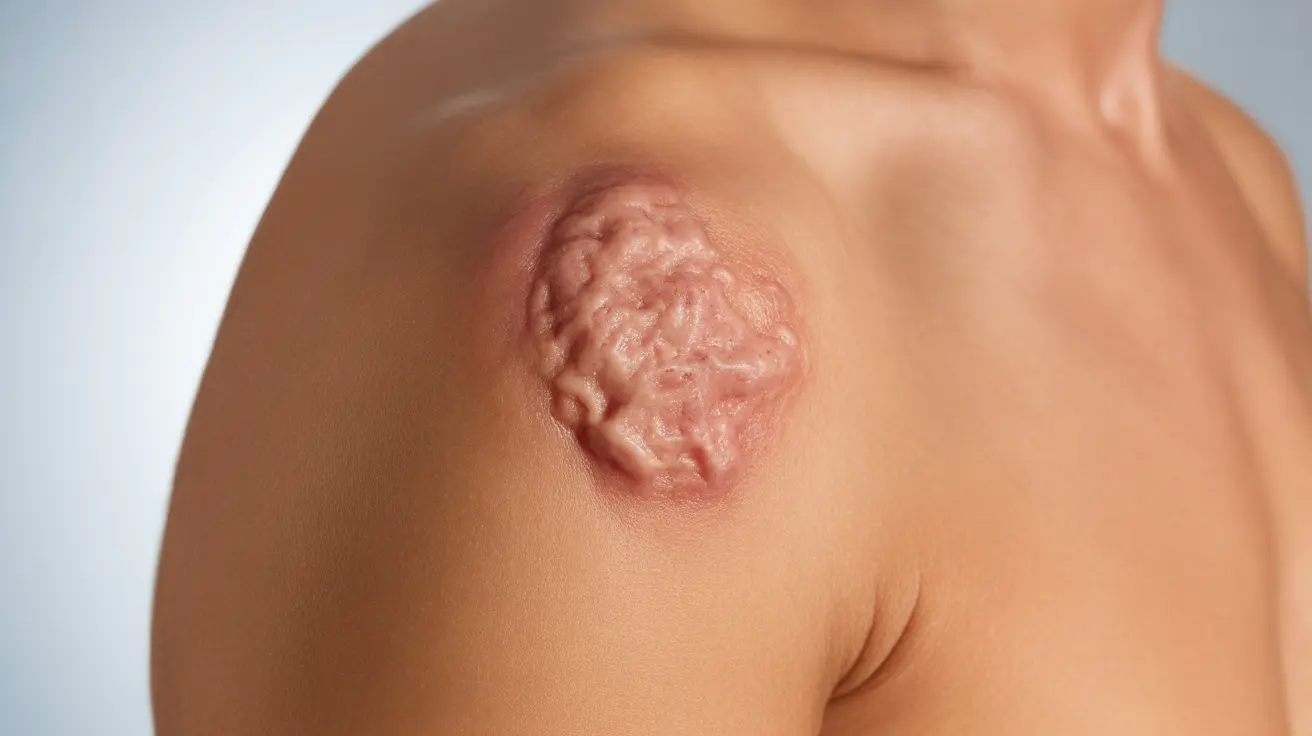
Characteristics and Appearance
Unlike typical melanomas that appear dark brown or black, amelanotic melanomas can be pink, red, or flesh-colored. They may resemble common skin conditions like dermatitis or harmless spots, which often leads to delayed diagnosis.
Key visual characteristics include:
- Asymmetrical shape
- Irregular or poorly defined borders
- Color variations within the same lesion (though lacking brown/black pigment)
- Diameter larger than 6 millimeters
- Evolution or changes in size, shape, or elevation
Understanding the Challenges of Detection
The absence of melanin makes amelanotic melanoma particularly deceptive. These lesions might be mistaken for:
- Benign skin growths
- Basal cell carcinoma
- Inflammatory skin conditions
- Healing wounds or scars
Risk Factors and Prevention
Several factors can increase your risk of developing amelanotic melanoma:
- Fair skin and light hair
- History of extensive sun exposure
- Previous melanoma diagnosis
- Family history of skin cancer
- Multiple atypical moles
- Weakened immune system
Preventive Measures
While you can't eliminate all risk factors, you can take important steps to reduce your risk:
- Regular comprehensive skin examinations
- Use of broad-spectrum sunscreen (SPF 30 or higher)
- Protective clothing and accessories
- Avoiding peak UV exposure hours
- Regular dermatologist visits, especially for high-risk individuals
Diagnosis and Treatment Options
Diagnosis typically involves a thorough physical examination and biopsy of suspicious lesions. Healthcare providers may use dermoscopy or other specialized imaging techniques to examine concerning areas more closely.
Treatment approaches depend on various factors, including:
- Stage of the cancer
- Location and size of the lesion
- Overall health of the patient
- Presence of genetic mutations
Common Treatment Methods
Treatment options may include:
- Surgical excision
- Lymph node biopsy
- Immunotherapy
- Targeted therapy
- Radiation therapy in specific cases
Frequently Asked Questions
What do amelanotic melanoma spots look like, and how are they different from regular moles?
Amelanotic melanoma spots typically appear pink, red, or flesh-colored, unlike regular moles which are usually brown or black. They often have irregular borders, asymmetrical shapes, and may show varying colors within the same lesion. Unlike typical moles, they might appear more like a scar or patch of dry skin.
Why is amelanotic melanoma harder to diagnose early compared to other skin cancers?
Amelanotic melanoma is challenging to diagnose early because it lacks the dark pigmentation that makes other melanomas obvious. Its appearance can mimic benign skin conditions, leading to delayed recognition and diagnosis. The absence of melanin often means these lesions don't follow the typical ABCDE rules of melanoma as clearly.
What are the main symptoms or warning signs I should watch for with amelanotic melanoma?
Key warning signs include new pink or red spots that change in size, shape, or elevation; lesions that are asymmetrical or have irregular borders; spots that look different from surrounding moles; and any lesions that itch, bleed, or don't heal normally.
How is amelanotic melanoma treated, and what are the survival rates for this type of skin cancer?
Treatment typically involves surgical removal of the tumor and surrounding tissue. Depending on the stage, additional treatments like immunotherapy or targeted therapy may be necessary. Survival rates vary significantly based on how early the cancer is detected, emphasizing the importance of early diagnosis.
What can I do to reduce my risk of missing amelanotic melanoma during a skin check?
Pay attention to any new or changing skin spots, regardless of color. Regular self-examinations should include checking for pink or red lesions, not just dark ones. Document changes with photos, and have regular professional skin checks, especially if you're at higher risk. Don't dismiss non-pigmented lesions that show any suspicious characteristics.