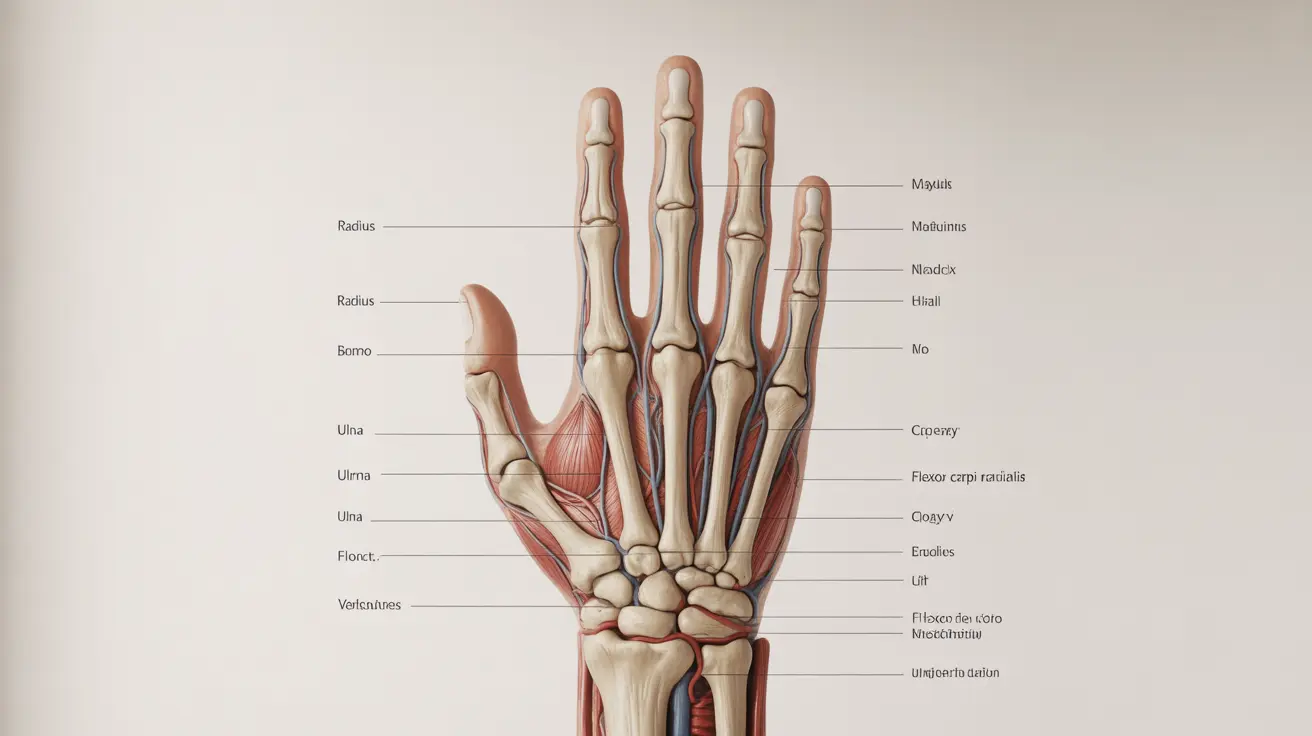
The human hand is a marvel of biological engineering, combining intricate bones, muscles, nerves, and blood vessels to perform countless daily tasks. Understanding hand anatomy is crucial for recognizing potential problems and maintaining optimal hand health. This comprehensive guide explores the complex structures that make our hands such versatile tools.
The Skeletal Framework of the Hand
The human hand contains 27 bones, forming a remarkable foundation for both powerful gripping and delicate manipulation. These bones are arranged in three distinct groups:
- Carpals (8 bones in the wrist)
- Metacarpals (5 bones forming the palm)
- Phalanges (14 bones making up the fingers)
Each finger contains three phalanges (proximal, middle, and distal), while the thumb has only two (proximal and distal). This arrangement allows for the precise movements we need for activities ranging from writing to playing musical instruments.
Nervous System Control
Three major nerves control hand function, each serving specific areas and purposes:
- Median nerve: Controls thumb movement and sensation in the palm's thumb side
- Ulnar nerve: Provides feeling to the pinkie side and controls fine motor skills
- Radial nerve: Supports wrist extension and thumb movement
These nerves work together to provide both sensory feedback and motor control, enabling the complex movements we often take for granted.
Muscular and Connective Tissue System
The hand's impressive range of motion comes from an intricate network of muscles, tendons, and ligaments. Two main muscle groups control hand movement:
Intrinsic Muscles
Located within the hand itself, these muscles control fine motor movements and precise finger positioning.
Extrinsic Muscles
Originating in the forearm, these muscles control larger movements through long tendons that extend into the hand.
Vascular Supply and Circulation
Two main arterial arches supply blood to the hand:
- Superficial palmar arch
- Deep palmar arch
These vessels ensure proper blood flow to hand tissues, supporting healing, temperature regulation, and optimal function. Good circulation is essential for maintaining hand health and promoting recovery from injury.
Common Hand Problems and When to Seek Help
Understanding hand anatomy helps identify when problems require medical attention. Common issues include:
- Carpal tunnel syndrome
- Tendonitis
- Arthritis
- Nerve compression
- Vascular insufficiency
Frequently Asked Questions
How many bones are in the human hand, and what are they called?
The human hand contains 27 bones: 8 carpals in the wrist, 5 metacarpals in the palm, and 14 phalanges in the fingers. The thumb has 2 phalanges, while each finger has 3 phalanges.
What nerves control movement and feeling in the hand, and what happens if they are damaged?
The median, ulnar, and radial nerves control hand movement and sensation. Nerve damage can result in weakness, numbness, tingling, or loss of function in specific areas of the hand, depending on which nerve is affected.
Why do my hands feel stiff or painful, and when should I see a doctor for hand problems?
Hand stiffness and pain can result from various conditions, including arthritis, tendonitis, or nerve compression. Seek medical attention if you experience persistent pain, numbness, weakness, or limited range of motion that affects daily activities.
How do all the muscles, tendons, and ligaments in the hand work together to make gripping and fine movements possible?
Intrinsic hand muscles work with extrinsic forearm muscles via tendons to control finger movement. Ligaments stabilize joints while allowing movement. This complex system enables both powerful gripping and precise manipulation of objects.
What are the main blood vessels in the hand, and why are they important for healing and sensation?
The superficial and deep palmar arches are the main arterial blood supplies to the hand. These vessels provide oxygen and nutrients necessary for tissue health, wound healing, and maintaining proper sensation and function.