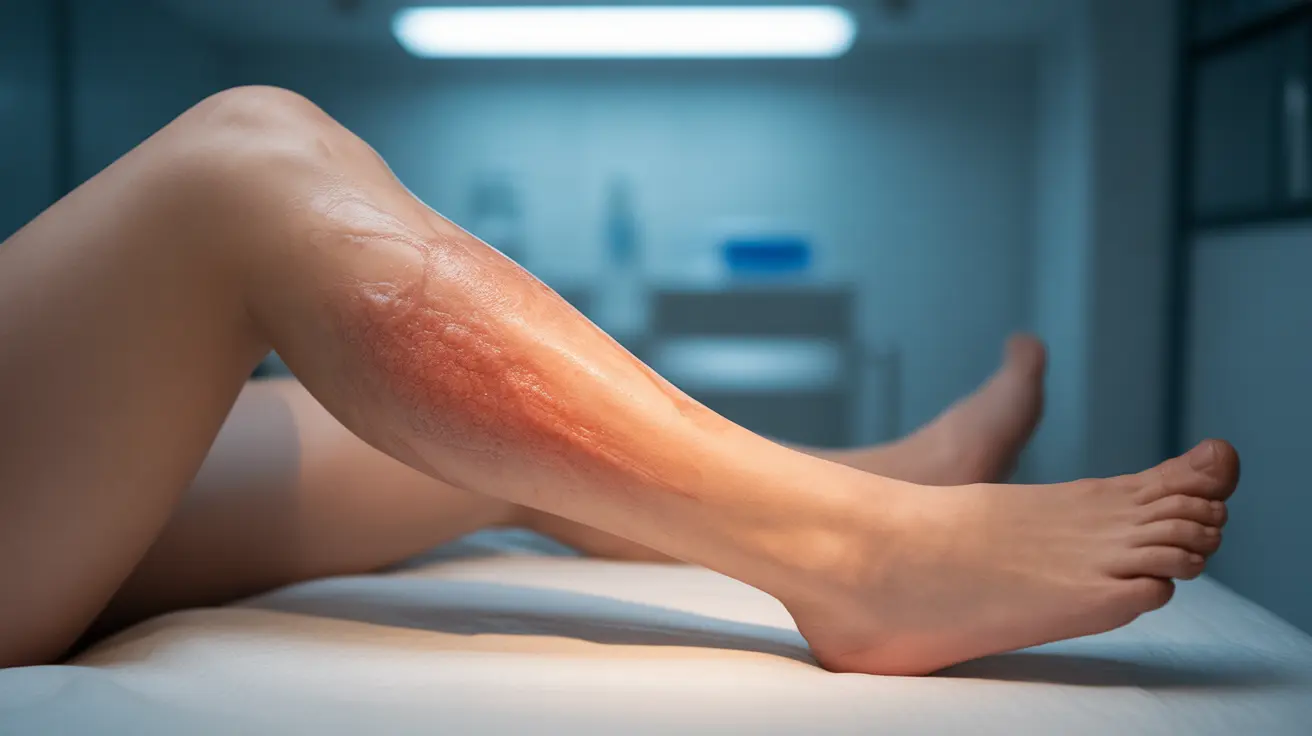
Angioedema in legs can be a concerning condition characterized by sudden, deep swelling beneath the skin's surface. This swelling occurs when small blood vessels leak fluid into surrounding tissues, causing significant discomfort and potential mobility issues. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options is crucial for managing this condition effectively.
While angioedema can affect various parts of the body, leg involvement presents unique challenges and may require specific attention. This comprehensive guide will help you understand when to seek medical care and how to manage leg-specific angioedema symptoms.
Identifying Angioedema in Legs
Angioedema in legs typically presents with distinctive characteristics that set it apart from other types of swelling:
- Rapid onset of swelling
- Deep tissue involvement
- Asymmetrical presentation
- Warm or slightly reddish skin
- Possible pain or discomfort
- May last 24-72 hours without treatment
Common Causes of Leg Angioedema
Several factors can trigger angioedema in the legs:
Allergic Reactions
Common allergens that may cause leg angioedema include:
- Food allergies
- Insect bites or stings
- Environmental allergens
- Medication reactions
Hereditary Factors
Some individuals inherit a genetic condition that makes them prone to angioedema episodes, particularly affecting the extremities like legs.
Medication-Induced
Certain medications can trigger angioedema, with ACE inhibitors being a notable cause. Other medications that may contribute include:
- NSAIDs
- Blood pressure medications
- Hormonal treatments
Treatment Approaches
Managing angioedema in legs typically involves several strategies:
Immediate Relief Measures
- Elevation of affected legs
- Cold compresses
- Loose-fitting clothing
- Avoiding pressure on swollen areas
Medical Treatments
Healthcare providers may prescribe:
- Antihistamines
- Corticosteroids
- Specific medications for hereditary angioedema
- Alternative blood pressure medications if ACE inhibitors are the cause
When to Seek Emergency Care
Certain symptoms warrant immediate medical attention:
- Difficulty breathing
- Severe pain
- Rapid progression of swelling
- Signs of infection
- Associated chest pain or dizziness
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the common causes of angioedema swelling in the legs?
Common causes include allergic reactions, hereditary factors, medications (especially ACE inhibitors), and autoimmune conditions. Environmental triggers, stress, and certain foods can also contribute to leg angioedema.
How can I tell if leg swelling is caused by angioedema or another condition?
Angioedema typically presents as deep, rapid-onset swelling that may be asymmetrical and accompanied by warmth or slight redness. Unlike general edema, it's usually more localized and can be painful. A healthcare provider can perform specific tests to confirm the diagnosis.
What treatments are available to reduce angioedema swelling in the legs?
Treatment options include antihistamines, corticosteroids, and specific medications for hereditary angioedema. Lifestyle measures like leg elevation and cold compresses can provide relief. For chronic cases, long-term preventive medications may be prescribed.
Can certain medications like ACE inhibitors cause angioedema in the legs?
Yes, ACE inhibitors are a well-known cause of angioedema, including in the legs. This side effect can occur even after taking the medication for years. If ACE inhibitors are the cause, your doctor will typically switch you to an alternative blood pressure medication.
When should I seek emergency care for angioedema swelling in my legs or elsewhere?
Seek immediate medical attention if you experience difficulty breathing, severe pain, rapidly progressing swelling, signs of infection, or if the swelling is accompanied by chest pain or dizziness. These symptoms could indicate a severe reaction requiring emergency treatment.