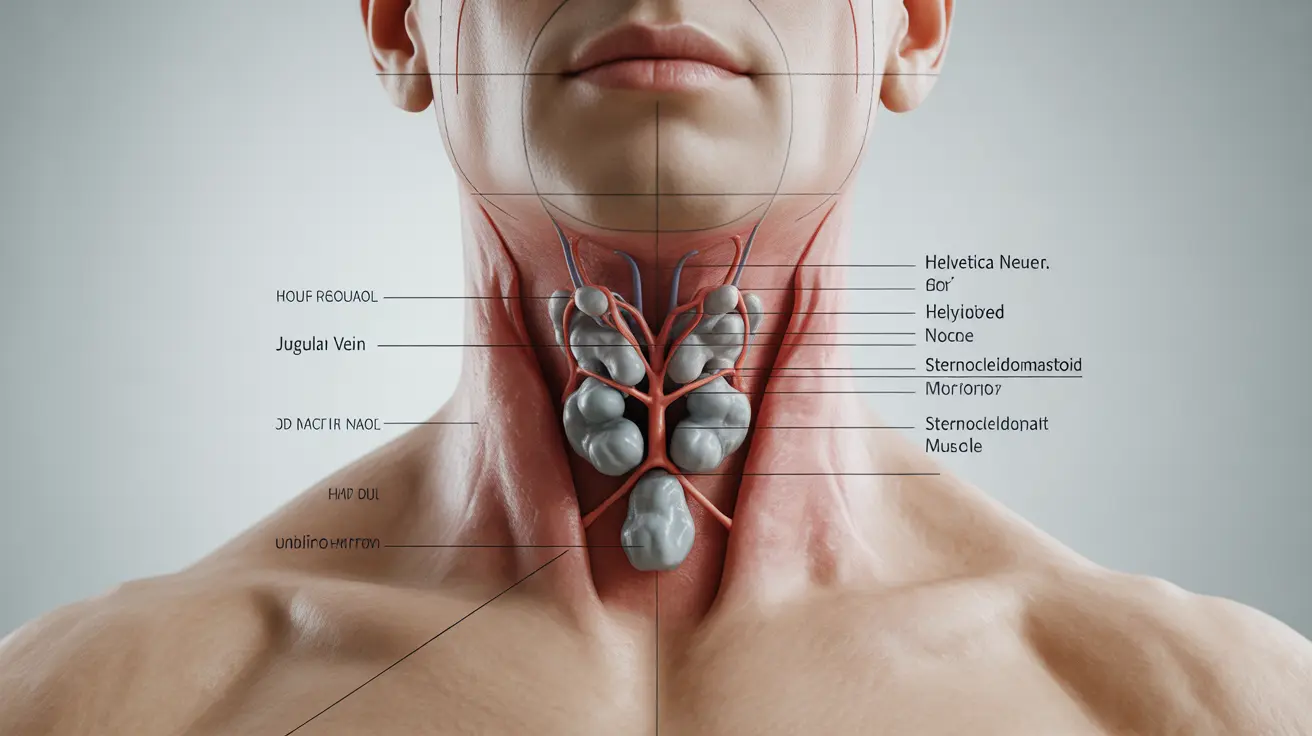
The anterior cervical lymph nodes play a crucial role in your body's immune system, acting as filtering stations that help fight infection and disease in the head and neck region. Located along the front and sides of your neck, these small, bean-shaped structures are part of your body's complex lymphatic system and serve as early warning signs when something isn't quite right with your health.
When these lymph nodes become swollen or tender, it's your body's way of signaling that it's fighting an infection or dealing with another underlying condition. Understanding what causes these changes and knowing when to seek medical attention can help ensure proper diagnosis and treatment.
The Role of Anterior Cervical Lymph Nodes in Immune Function
Anterior cervical lymph nodes are specialized structures that form an essential part of your immune defense system. They filter lymph fluid, which contains white blood cells, dead cells, bacteria, and other particles that need to be removed from your body. When functioning normally, these nodes help:
- Filter harmful substances from lymph fluid
- Store immune cells that fight infection
- Process and eliminate bacteria and viruses
- Signal the presence of infection or disease
Common Causes of Swollen Anterior Cervical Lymph Nodes
Lymph node swelling, also known as lymphadenopathy, can occur for various reasons. The most common causes include:
Infections
Many infections can trigger lymph node swelling, including:
- Upper respiratory infections
- Strep throat
- Tonsillitis
- Ear infections
- Dental infections
- Mononucleosis
Other Conditions
Less commonly, swollen anterior cervical lymph nodes might be due to:
- Autoimmune disorders
- Certain medications
- Cancer (such as lymphoma)
- Inflammatory conditions
When to Seek Medical Attention
While swollen anterior cervical lymph nodes often indicate a minor infection that will resolve on its own, certain symptoms warrant immediate medical attention:
- Lymph nodes larger than 1 inch in diameter
- Hard or fixed nodes that don't move when touched
- Nodes that have been swollen for more than two weeks
- Accompanying symptoms like unexplained weight loss or fever
- Night sweats
- Difficulty breathing or swallowing
Diagnostic Approaches
When evaluating swollen anterior cervical lymph nodes, healthcare providers may use several diagnostic tools:
- Physical examination
- Complete blood count
- Imaging tests (ultrasound, CT scan, or MRI)
- Fine-needle aspiration
- Lymph node biopsy (if necessary)
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the common causes of swelling in the anterior cervical lymph nodes? The most common causes include viral or bacterial infections like upper respiratory infections, strep throat, and dental infections. Less commonly, swelling may be due to autoimmune conditions or cancer.
How can I tell if swollen anterior cervical lymph nodes are due to an infection or something more serious like cancer? Infection-related swelling is usually tender, mobile, and resolves within a few weeks. Cancer-related nodes are typically harder, fixed in place, and persist or grow over time. Additional symptoms like weight loss or night sweats may indicate a more serious condition.
What symptoms should prompt me to see a doctor about enlarged anterior cervical lymph nodes? Seek medical attention if nodes are larger than 1 inch, hard or fixed in place, persist for more than two weeks, or are accompanied by fever, weight loss, or difficulty breathing or swallowing.
How do anterior cervical lymph nodes function in the body's immune response? These nodes filter lymph fluid, trap harmful substances, store immune cells, and help fight infections in the head and neck region. They are crucial components of the body's immune defense system.
What diagnostic tests are used to evaluate persistent swelling of anterior cervical lymph nodes? Diagnostic tests may include physical examination, blood tests, imaging studies (ultrasound, CT, or MRI), and in some cases, fine-needle aspiration or biopsy for definitive diagnosis.