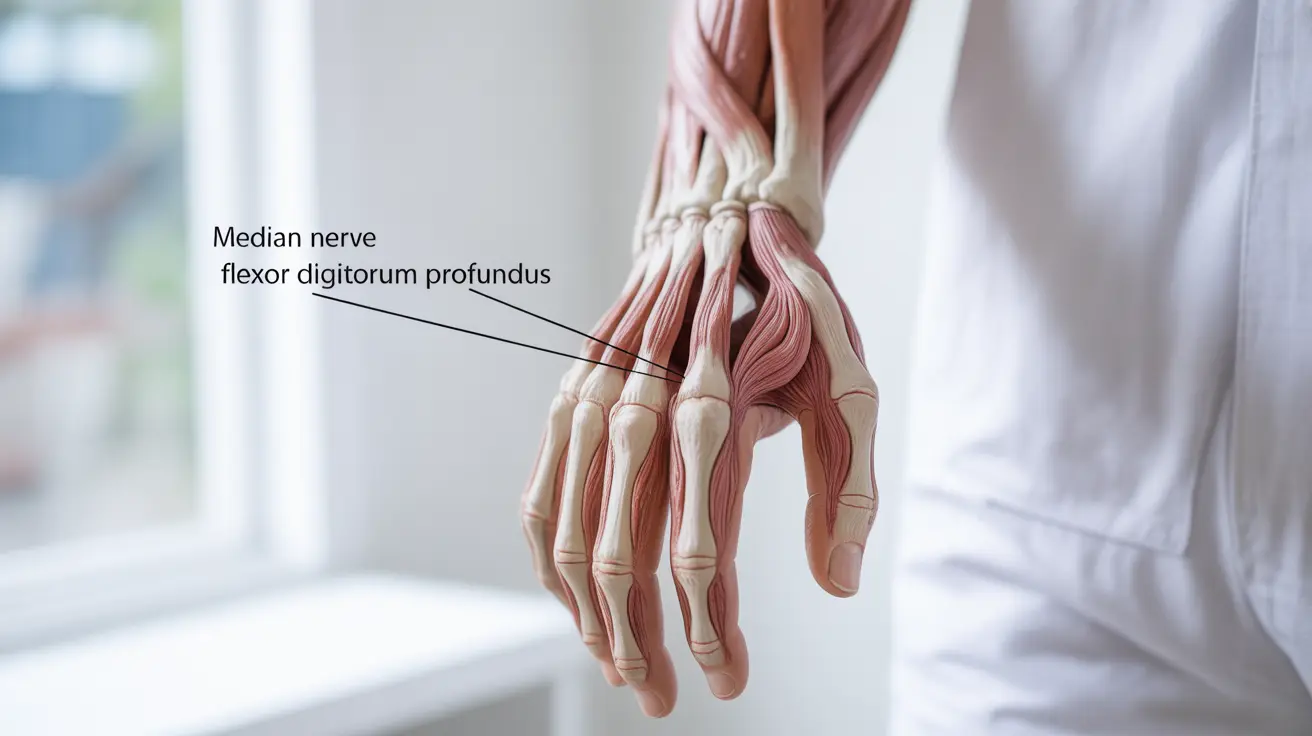
Ape hand deformity is a distinctive medical condition that affects hand function and appearance, primarily resulting from damage to the median nerve. This condition gets its name from the characteristic hand position that resembles the natural posture of an ape's hand. Understanding this condition is crucial for early detection and proper treatment to prevent long-term complications.
For healthcare providers and patients alike, recognizing the signs and symptoms of ape hand deformity is essential for proper diagnosis and treatment. This comprehensive guide will explore the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options available for managing this condition effectively.
Understanding the Causes of Ape Hand Deformity
Ape hand deformity primarily occurs due to injury or damage to the median nerve, which is responsible for controlling several crucial hand muscles. The median nerve runs from the forearm through the carpal tunnel in the wrist and into the hand, controlling various thumb movements and hand functions.
Common causes of median nerve injury leading to ape hand deformity include:
- Trauma to the forearm or wrist
- Compression injuries
- Deep cuts or lacerations
- Prolonged pressure on the median nerve
- Complications from certain medical procedures
Recognizing the Signs and Symptoms
The characteristic features of ape hand deformity include several distinct signs that healthcare professionals and patients should be aware of:
Primary Physical Signs
The most notable physical manifestations include:
- Inability to perform thumb opposition
- Flattening of the thenar eminence (thumb muscle)
- Difficulty with pincer grip
- Weakness in thumb movements
- Altered hand positioning at rest
Associated Symptoms
Patients may also experience:
- Numbness in the thumb and first two fingers
- Decreased grip strength
- Difficulty with fine motor tasks
- Pain or discomfort in the affected area
- Reduced hand coordination
Diagnostic Approaches
Healthcare professionals use various methods to diagnose ape hand deformity accurately:
Physical Examination
The initial assessment typically includes:
- Testing thumb opposition strength
- Evaluating muscle wasting
- Checking sensory function
- Assessing overall hand function
- Examining for visible deformities
Medical Testing
Diagnostic procedures may include:
- Nerve conduction studies
- Electromyography (EMG)
- MRI scanning
- X-rays to rule out other conditions
- Detailed neurological examination
Treatment Options and Management
Treatment for ape hand deformity varies depending on the severity and cause of the condition. A comprehensive treatment plan may include:
Conservative Management
Initial treatment often focuses on non-surgical approaches:
- Physical therapy exercises
- Occupational therapy
- Splinting and bracing
- Pain management techniques
- Activity modification
Surgical Interventions
When conservative treatment isn't sufficient, surgical options may include:
- Nerve repair or grafting
- Tendon transfers
- Decompression procedures
- Neurolysis
- Reconstructive surgery
Frequently Asked Questions
What causes ape hand deformity and how does median nerve injury lead to this condition? Ape hand deformity is primarily caused by injury or damage to the median nerve. When this nerve is compromised, it affects the muscles controlling thumb movement and hand function, leading to the characteristic appearance and functional limitations of ape hand deformity.
What are the common symptoms and signs to recognize ape hand deformity? The main signs include inability to oppose the thumb, flattening of the thumb muscles, weakened grip strength, and difficulty with fine motor tasks. Patients may also experience numbness in the thumb and first two fingers.
How is ape hand deformity diagnosed by healthcare professionals? Healthcare professionals diagnose ape hand deformity through physical examination, nerve conduction studies, EMG testing, and imaging studies such as MRI. They assess muscle strength, sensory function, and overall hand functionality.
What treatment options are available for ape hand deformity, including physiotherapy and surgery? Treatment options range from conservative approaches like physical therapy, splinting, and activity modification to surgical interventions such as nerve repair, tendon transfers, and reconstructive procedures, depending on the severity and cause.
How can ape hand deformity be distinguished from similar conditions like claw hand or carpal tunnel syndrome? Ape hand deformity specifically affects thumb opposition and thenar muscles, while claw hand affects different muscle groups and finger positioning. Carpal tunnel syndrome may have similar symptoms but typically presents with more widespread hand numbness and pain without the characteristic thumb position changes.