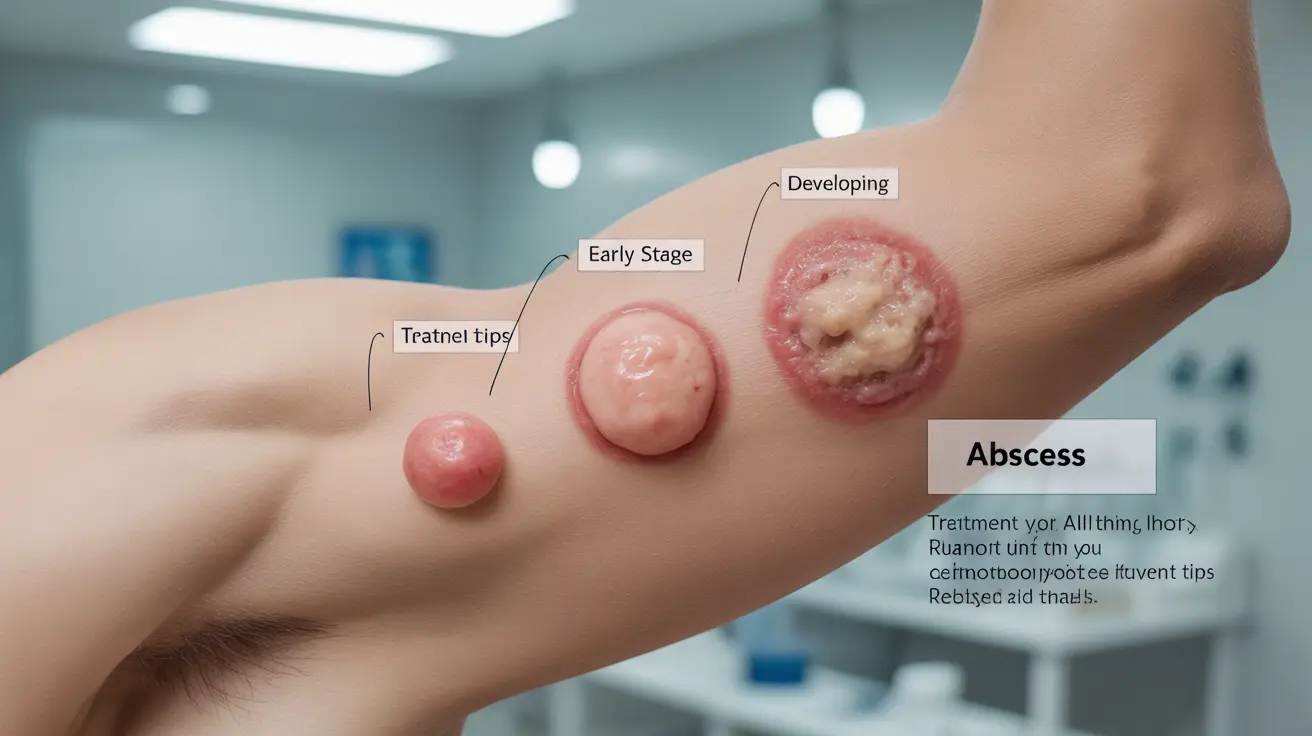
An armpit boil can be an uncomfortable and concerning skin condition that develops in the sensitive underarm area. These painful, pus-filled bumps occur when hair follicles or sweat glands become infected with bacteria, leading to inflammation and swelling beneath the skin. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and proper treatment approaches is essential for managing this common condition effectively.
While armpit boils can be distressing, most cases can be treated successfully with proper care and attention. This comprehensive guide will explore everything you need to know about managing and preventing armpit boils, including when to seek professional medical attention.
Understanding Armpit Boils
Armpit boils typically begin as small, red bumps that gradually enlarge and become more painful. They form when Staphylococcus bacteria enter hair follicles or sweat glands, causing an infection that develops into an abscess. The warm, moist environment of the armpit makes it particularly susceptible to these infections.
Common Causes and Risk Factors
Several factors can increase your risk of developing armpit boils:
- Poor hygiene practices
- Tight clothing that causes friction
- Compromised immune system
- Certain medical conditions like diabetes
- Excessive sweating
- Shaving or hair removal trauma
Signs and Symptoms
Recognizing the early signs of an armpit boil can help you seek appropriate treatment promptly. Common symptoms include:
- A tender, red bump that grows larger over time
- Warmth and swelling in the affected area
- Pain that increases with movement
- Development of a white or yellow center (pustule)
- Possible fever in severe cases
Treatment Options
Home Care Methods
Many armpit boils can be treated effectively at home with proper care:
- Apply warm compresses 3-4 times daily
- Keep the area clean and dry
- Wear loose-fitting clothing
- Use over-the-counter pain relievers if needed
- Practice good hygiene
Medical Treatment
More severe cases may require professional medical intervention, including:
- Incision and drainage procedures
- Prescription antibiotics
- Professional wound care
- Laboratory testing to identify the specific bacteria
Prevention Strategies
Taking preventive measures can significantly reduce your risk of developing armpit boils:
- Maintain good personal hygiene
- Use antibacterial soap when showering
- Wear breathable, loose-fitting clothing
- Change clothes after heavy sweating
- Use clean razors and proper shaving techniques
When to See a Doctor
Seek medical attention if you experience:
- Severe pain or swelling
- Fever or chills
- Multiple or recurring boils
- No improvement after a week of home treatment
- Spreading redness or warmth around the area
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the typical symptoms of an armpit boil, and how do they appear?
Armpit boils typically appear as red, tender bumps that gradually enlarge and become more painful. They often develop a white or yellow center as pus accumulates, and the surrounding skin becomes warm and swollen. Initial symptoms may include itching or discomfort, progressing to more significant pain and swelling.
How do you treat an armpit boil, and when should you seek medical attention?
Initial treatment involves warm compresses, keeping the area clean, and avoiding tight clothing. Seek medical attention if you develop fever, severe pain, multiple boils, or if the boil shows no improvement after a week of home treatment. A healthcare provider may need to perform incision and drainage or prescribe antibiotics.
Can armpit boils be caused by poor hygiene, and what are the best practices for preventing them?
Yes, poor hygiene can contribute to armpit boils. Prevention includes regular showering, using antibacterial soap, wearing clean, breathable clothing, and maintaining proper hair removal practices. Good hygiene habits significantly reduce the risk of developing boils.
Is it safe to use tea tree oil or other home remedies for treating armpit boils?
While tea tree oil has natural antibacterial properties, it should be used with caution and properly diluted. Some home remedies may help with minor boils, but they should not replace proper medical treatment for severe or recurring cases. Always consult a healthcare provider before trying alternative treatments.
What are the risks of trying to pop or squeeze an armpit boil, and why is this not recommended?
Attempting to pop or squeeze a boil can force the infection deeper into the skin or spread it to surrounding areas, potentially causing more severe infection or scarring. This can also introduce additional bacteria into the wound. Let boils drain naturally or have them properly treated by a healthcare professional.