Living with arthritis can significantly impact your quality of life, and when conservative treatments aren't providing adequate relief, surgery might become a necessary consideration. Understanding the various surgical options available for arthritis treatment is crucial for making informed decisions about your healthcare journey.
This comprehensive guide explores the different types of arthritis surgery, their indications, and what you can expect during recovery. We'll help you understand when surgery might be the right choice and what factors healthcare providers consider when recommending surgical intervention.
Types of Arthritis Surgery
Several surgical procedures are available for treating arthritis, each designed to address specific symptoms and conditions:
Joint Replacement Surgery
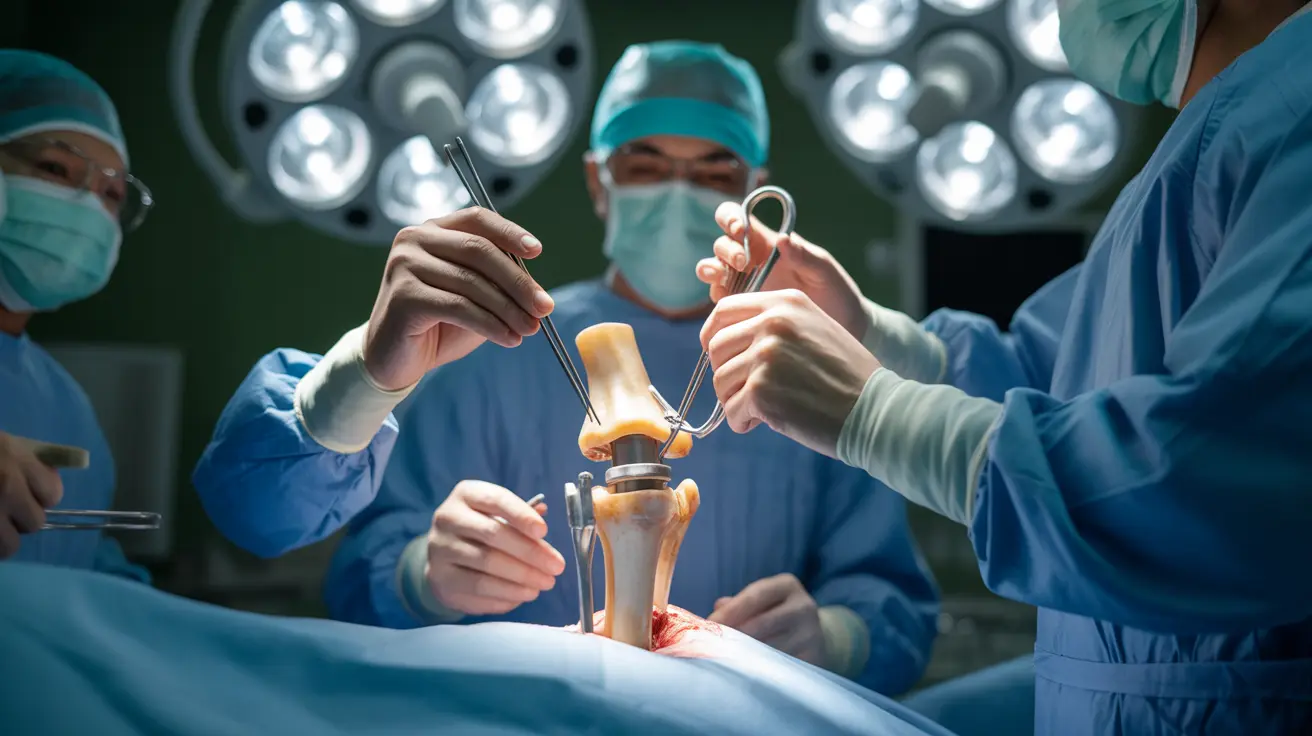
Total or partial joint replacement (arthroplasty) involves removing damaged joint surfaces and replacing them with artificial components. This procedure is commonly performed on knees, hips, and shoulders, offering significant pain relief and improved mobility for many patients.
Arthroscopic Surgery
This minimally invasive procedure uses small incisions and specialized instruments to remove damaged tissue, repair tears, or clean out joint spaces. While not a cure for arthritis, it can provide temporary relief and improved function in select cases.
Joint Fusion Surgery
Also known as arthrodesis, this procedure permanently joins two bones together, eliminating painful motion in severely damaged joints. It's commonly used in smaller joints like those in the fingers, ankles, or spine.
When Surgery Becomes Necessary
Healthcare providers typically recommend arthritis surgery when:
- Severe pain persists despite conservative treatments
- Joint damage significantly limits daily activities
- Non-surgical treatments no longer provide adequate relief
- Quality of life is substantially impacted
- Joint deformity becomes severe
Preparing for Arthritis Surgery
Proper preparation can significantly impact surgical outcomes. Key steps include:
- Complete medical evaluation
- Medication adjustments
- Physical therapy to strengthen surrounding muscles
- Home modifications for post-surgery recovery
- Arranging support for recovery period
Recovery and Rehabilitation
Recovery timelines vary depending on the type of surgery performed:
Early Recovery Phase
The initial recovery period focuses on pain management, wound healing, and preventing complications. This typically lasts 2-6 weeks, depending on the procedure.
Rehabilitation Period
Physical therapy and rehabilitation exercises are crucial for restoring strength and mobility. This phase may last several months, with continued improvement possible for up to a year.
Frequently Asked Questions
What types of arthritis surgery are available and how do they differ?
Arthritis surgery options include joint replacement (arthroplasty), arthroscopic procedures, and joint fusion (arthrodesis). Joint replacement replaces damaged surfaces with artificial components, arthroscopy uses minimally invasive techniques for repairs, and fusion permanently joins bones together.
When is arthritis surgery recommended instead of medication or physical therapy?
Surgery is typically recommended when conservative treatments fail to provide adequate relief, joint damage is severe, daily activities are significantly limited, or quality of life is substantially impacted by arthritis symptoms.
What are the risks and possible complications of arthritis surgery?
Common risks include infection, blood clots, implant loosening (in joint replacement), nerve damage, and ongoing pain. The specific risks vary by procedure type and individual patient factors.
How long does recovery take after common arthritis surgeries like joint replacement or arthroscopy?
Recovery varies by procedure: arthroscopy typically requires 4-6 weeks, while joint replacement may need 3-6 months for full recovery. Rehabilitation continues beyond these periods, with improvements possible for up to a year.
What are the benefits and limitations of joint fusion (arthrodesis) compared to joint replacement?
Joint fusion provides permanent pain relief by eliminating motion but results in permanent stiffness. While more durable than replacement, it significantly restricts movement. Joint replacement preserves motion but may require future revision surgery.
Remember to discuss all surgical options thoroughly with your healthcare provider to determine the most appropriate treatment for your specific situation.