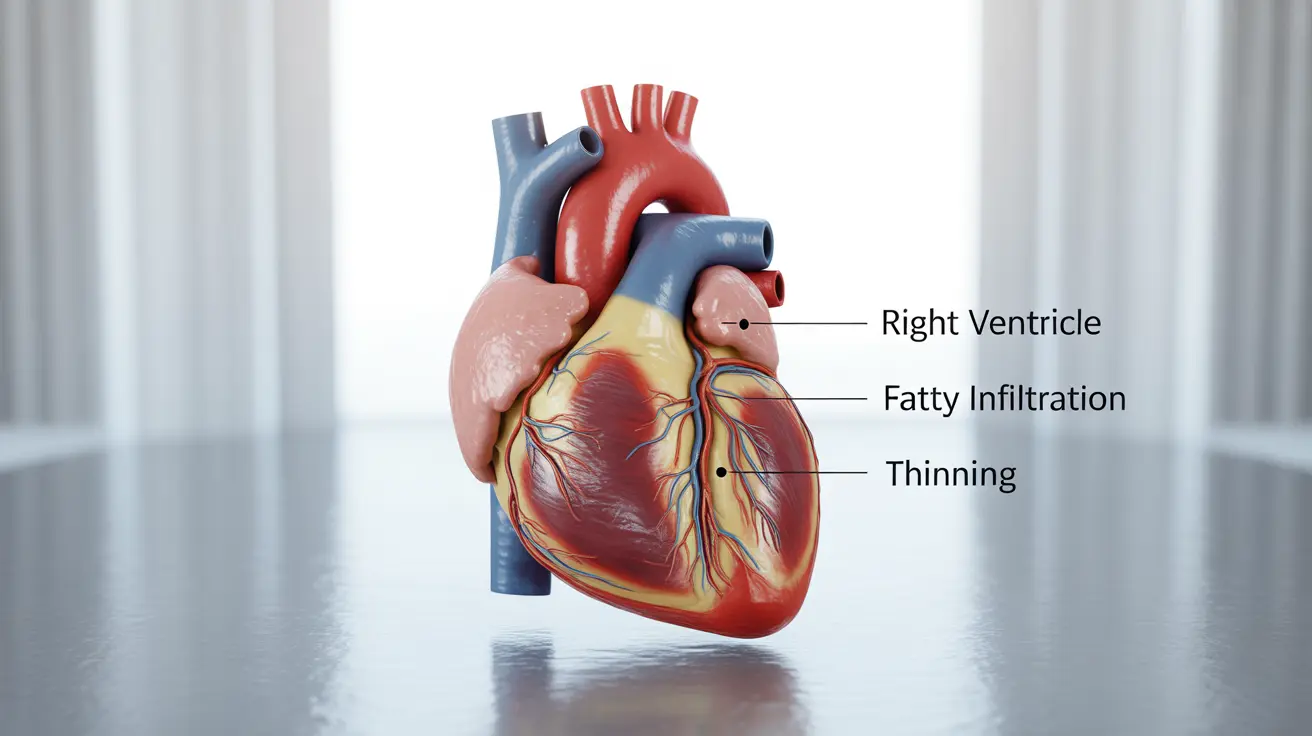
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy (ARVC) is a progressive heart condition that affects the heart muscle, particularly the right ventricle. Understanding life expectancy with ARVC is crucial for patients and their families, as proper management and treatment can significantly impact long-term outcomes.
While ARVC is a serious condition, advances in medical treatment and careful management have helped improve prognosis for many patients. This comprehensive guide explores life expectancy, treatment options, and essential lifestyle modifications for people living with ARVC.
Understanding ARVC and Life Expectancy
The life expectancy for individuals with ARVC varies significantly based on several factors, including early detection, proper treatment implementation, and adherence to medical recommendations. With appropriate management, many patients can lead full lives, though regular medical monitoring is essential.
- Age at diagnosis
- Disease progression rate
- Presence of dangerous arrhythmias
- Family history
- Compliance with treatment plans
Early Detection and Diagnosis
Early diagnosis of ARVC is crucial for optimal outcomes. Diagnostic procedures typically include:
- Electrocardiogram (ECG)
- Cardiac MRI
- Genetic testing
- Holter monitoring
- Echocardiogram
- Cardiac biopsy in select cases
Critical Symptoms and Warning Signs
Recognizing ARVC symptoms early can lead to prompt treatment and better outcomes. Common symptoms include:
- Heart palpitations
- Shortness of breath, especially during exercise
- Fainting (syncope)
- Chest pain
- Unexplained fatigue
- Racing heartbeat
Treatment Approaches and Management
Medication Management
Various medications may be prescribed to manage ARVC symptoms and reduce complications:
- Antiarrhythmic drugs
- Beta-blockers
- ACE inhibitors
- Anti-coagulants when necessary
Device Therapy
Implantable cardioverter-defibrillators (ICDs) play a crucial role in preventing sudden cardiac death in ARVC patients. These devices continuously monitor heart rhythm and can deliver life-saving shocks when dangerous arrhythmias occur.
Lifestyle Modifications for Better Outcomes
Proper lifestyle management is essential for ARVC patients:
- Limiting competitive sports and intense physical activity
- Maintaining moderate, physician-approved exercise
- Avoiding triggers that may cause arrhythmias
- Regular medical check-ups
- Stress management techniques
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the typical life expectancy for someone diagnosed with arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy (ARVC)?
The life expectancy with ARVC varies significantly among individuals. With proper management, early detection, and appropriate treatment, many patients can have a normal or near-normal life expectancy. Regular medical monitoring and adherence to treatment plans are crucial factors in long-term survival.How do implantable cardiac defibrillators (ICDs) affect the survival and sudden death risk in ARVC patients?
ICDs significantly improve survival rates by preventing sudden cardiac death in ARVC patients. These devices can detect and treat dangerous heart rhythms immediately, reducing the risk of fatal arrhythmias by up to 70% in high-risk patients.What are the main symptoms and signs that indicate the presence of ARVC?
The main symptoms include heart palpitations, fainting episodes (especially during exercise), chest pain, shortness of breath, and unexplained fatigue. Some patients may experience irregular heartbeats or racing heart sensations.How is ARVC diagnosed and what tests are most effective for early detection?
ARVC is diagnosed through a combination of tests including ECG, cardiac MRI, genetic testing, Holter monitoring, and echocardiogram. Cardiac MRI is particularly effective for early detection as it can reveal structural changes in the heart muscle before symptoms become severe.What lifestyle changes and treatments can help reduce the risk of sudden cardiac death in people with ARVC?
Key lifestyle changes include avoiding competitive sports and intense physical activity, maintaining moderate exercise as approved by physicians, regular medical check-ups, and stress management. Treatment options include medications, ICD implantation, and in some cases, catheter ablation procedures.
By understanding ARVC and following appropriate medical guidance, patients can significantly improve their prognosis and quality of life. Regular consultation with healthcare providers and adherence to treatment plans remain essential for optimal outcomes.