Many people experience digestive changes after eating asparagus, particularly increased gas production. This common reaction has led many to question the relationship between asparagus consumption and digestive comfort. Understanding why asparagus can cause gas and how to minimize this effect can help you continue enjoying this nutritious vegetable without discomfort.
Why Asparagus Can Cause Gas
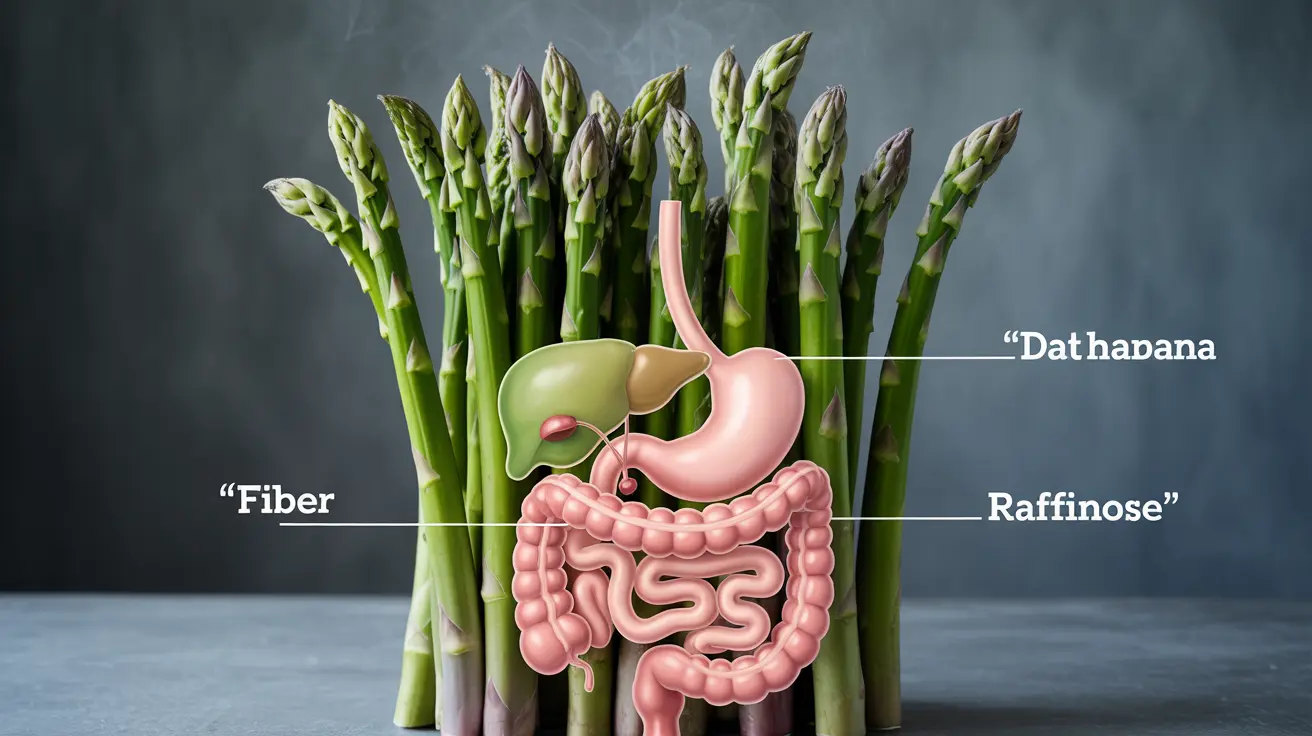
Asparagus contains several compounds that can contribute to gas production in the digestive system. The primary culprits are fiber and raffinose, a type of complex carbohydrate. When these substances reach your large intestine, gut bacteria break them down through fermentation, producing gas as a byproduct.
The Role of Fiber and Prebiotics
Asparagus is rich in both soluble and insoluble fiber, as well as prebiotic compounds. While these elements are beneficial for gut health and regular digestion, they can initially cause increased gas production, especially if you're not used to consuming high-fiber foods regularly.
Managing Gas When Eating Asparagus
There are several effective strategies to reduce gas production when consuming asparagus:
- Start with small portions and gradually increase intake
- Chew thoroughly to aid digestion
- Cook asparagus until tender rather than eating it raw
- Consider taking digestive enzymes before meals
- Stay well-hydrated to help fiber move through your system
Cooking Methods That May Help
The way you prepare asparagus can significantly impact its digestibility. Steaming or roasting asparagus until tender can help break down some of the fiber that causes gas. Avoid undercooking or eating raw asparagus, as this can make the vegetable harder to digest.
Health Benefits Worth Considering
Despite its potential to cause gas, asparagus offers numerous health benefits that make it worth including in your diet:
- Rich in vitamins A, C, E, and K
- High in folate and other B vitamins
- Contains powerful antioxidants
- Supports healthy blood pressure
- Promotes digestive health through fiber content
Other Effects of Asparagus Consumption
Beyond gas production, asparagus can cause other notable effects, including changes in urine odor due to asparagusic acid. This effect is harmless and typically occurs within 15-30 minutes of consumption.
Frequently Asked Questions
Does asparagus cause gas and bloating, and why does this happen?
Yes, asparagus can cause gas and bloating due to its high fiber content and presence of raffinose, a complex carbohydrate. When gut bacteria ferment these substances, gas is produced as a natural byproduct.
How can I reduce or prevent gas and bloating when eating asparagus?
You can minimize gas by starting with small portions, chewing thoroughly, cooking asparagus well, staying hydrated, and gradually increasing your intake to allow your digestive system to adapt.
Is it better to eat cooked or raw asparagus to avoid digestive discomfort?
Cooked asparagus is generally easier to digest than raw asparagus. Steaming or roasting until tender helps break down the fibers that can cause gas while preserving nutrients.
What are the health benefits of asparagus despite its potential to cause gas?
Asparagus is packed with vitamins, minerals, antioxidants, and fiber. It supports immune function, heart health, and digestive health, and provides anti-inflammatory benefits that outweigh its temporary gas-producing effects.
Can eating too much asparagus cause other side effects besides gas, such as changes in urine odor or increased urination?
Yes, asparagus can cause a distinctive urine odor due to asparagusic acid. It may also have a mild diuretic effect, leading to increased urination. These effects are harmless and temporary.