For people living with diabetes, choosing the right sweeteners is crucial for managing blood sugar levels while still enjoying sweet flavors. Aspartame, a widely used artificial sweetener, has been a topic of discussion and research regarding its safety and effects on diabetes management. This comprehensive guide explores the relationship between aspartame and diabetes, examining both its benefits and potential concerns.
What is Aspartame and How Does It Work?
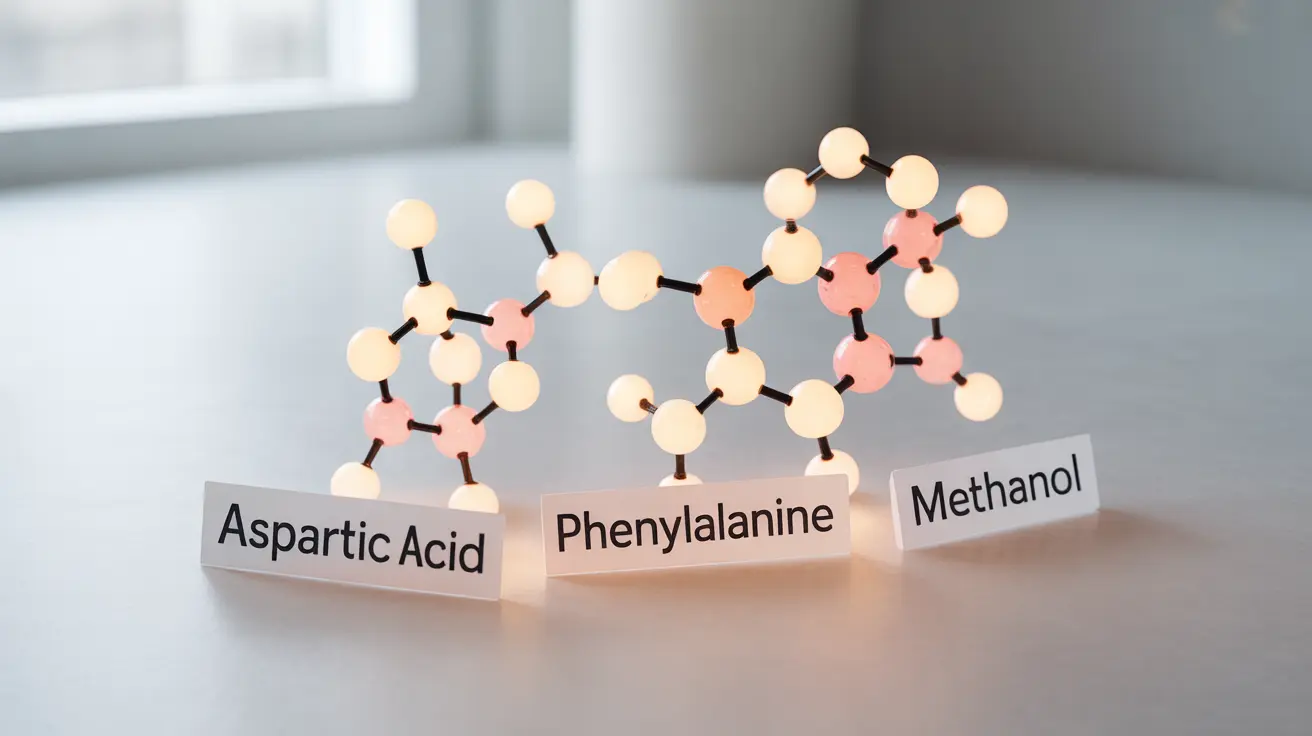
Aspartame is a low-calorie artificial sweetener that's approximately 200 times sweeter than regular sugar. Unlike natural sugar, it doesn't significantly impact blood glucose levels because the body processes it differently. The sweetener breaks down into three components: aspartic acid, phenylalanine, and methanol, which are naturally present in many foods.
Blood Sugar Impact and Diabetes Management
One of the primary advantages of aspartame for people with diabetes is its minimal effect on blood sugar levels. Unlike regular sugar, which causes rapid spikes in blood glucose, aspartame doesn't require insulin for metabolism, making it a potentially suitable option for blood sugar management.
Blood Sugar Response
Research has consistently shown that aspartame doesn't cause significant changes in:
- Blood glucose levels
- Insulin secretion
- HbA1c levels
- Overall glycemic control
Safety Profile and FDA Guidelines
The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has established clear guidelines for aspartame consumption. The acceptable daily intake (ADI) is set at 50 milligrams per kilogram of body weight per day. For perspective, this means a 150-pound person could safely consume about 3,400 milligrams of aspartame daily.
Monitoring and Considerations
While aspartame is generally recognized as safe, individuals should consider:
- Personal tolerance levels
- Existing health conditions
- Individual blood sugar responses
- Overall artificial sweetener consumption
Long-term Health Considerations
When considering aspartame as a long-term sugar substitute, it's important to understand both its benefits and potential risks. While research continues, current evidence suggests that moderate aspartame consumption as part of a balanced diet is generally safe for people with diabetes.
Metabolic Effects
Some studies have examined potential metabolic effects, including:
- Impact on gut bacteria
- Influence on appetite regulation
- Effects on metabolic syndrome
- Potential influence on insulin sensitivity
Frequently Asked Questions
Is aspartame safe for people with diabetes to use as a sugar substitute?
Yes, aspartame is generally considered safe for people with diabetes when consumed within FDA guidelines. It doesn't affect blood sugar levels and can be part of a diabetes-friendly diet plan.
How does aspartame affect blood sugar and insulin levels in people with diabetes?
Aspartame has virtually no effect on blood sugar or insulin levels because the body doesn't process it like regular sugar. This makes it a suitable option for people who need to manage their blood glucose levels.
Can consuming aspartame increase the risk of developing type 2 diabetes?
Current research doesn't show a direct causal link between aspartame consumption and type 2 diabetes development. However, maintaining an overall healthy lifestyle remains crucial for diabetes prevention.
What are the potential metabolic or long-term health risks of aspartame for individuals with diabetes?
While extensive research has shown aspartame to be safe when consumed within recommended limits, some studies suggest monitoring long-term use. Individual responses may vary, and it's important to discuss any concerns with healthcare providers.
How much aspartame can a person with diabetes safely consume daily according to FDA guidelines?
The FDA has set the acceptable daily intake (ADI) at 50 mg/kg of body weight per day. For example, a 150-pound (68 kg) person could safely consume approximately 3,400 mg of aspartame daily.