For many men, understanding what constitutes normal testicle size can be a source of concern or curiosity. This comprehensive guide will explore typical testicle measurements, variations, and when size changes might indicate a need for medical attention.
While testicular size can vary significantly among healthy adult males, having accurate information about normal ranges and potential warning signs is essential for maintaining reproductive health and overall well-being.
Normal Testicle Size in Adult Males
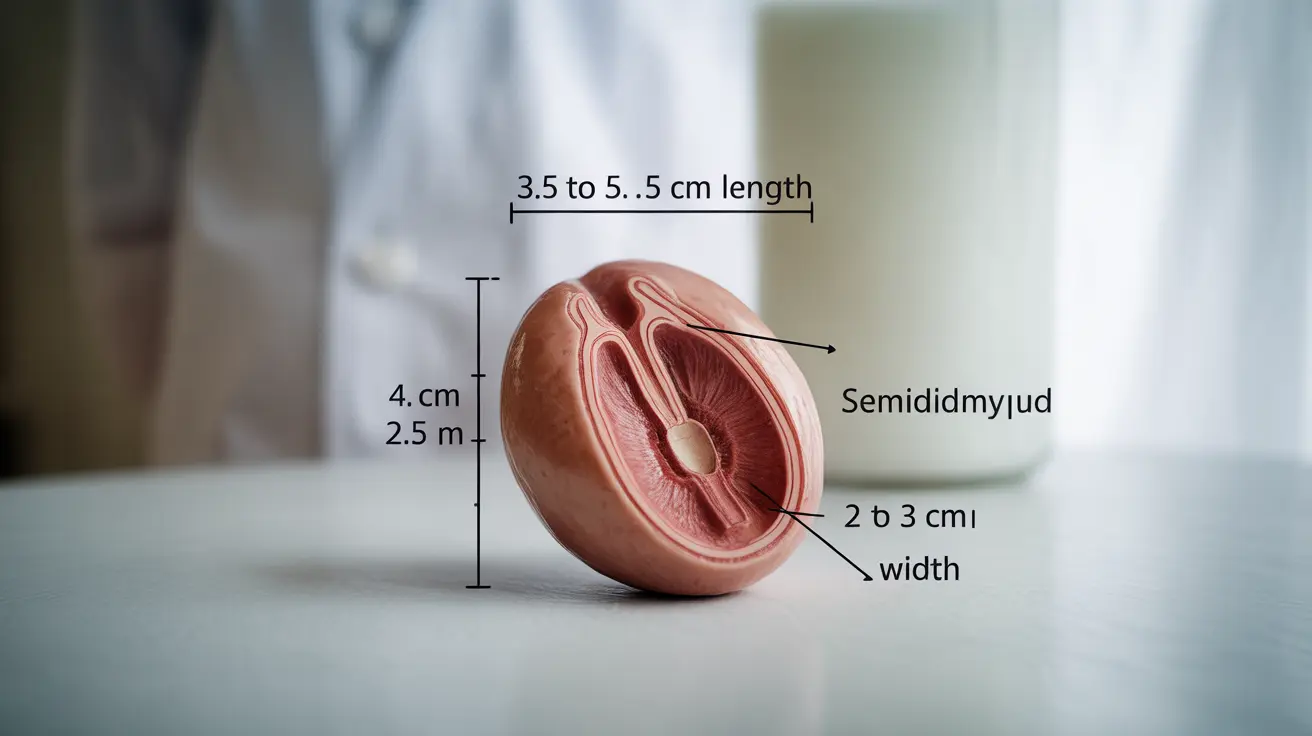
The average adult testicle typically measures between 3.5 to 5.5 centimeters (cm) in length and about 2 to 3 centimeters in width. By volume, normal testicles usually range from 15 to 25 milliliters. These measurements can be obtained using specialized medical tools called orchidometers.
It's important to note that the left testicle is often slightly smaller and hangs lower than the right one, which is completely normal and doesn't affect function.
Factors Affecting Testicle Size
Age-Related Changes
Testicle size naturally changes throughout a man's life. During puberty, the testicles grow significantly, reaching their adult size by around age 18. Some slight shrinkage may occur naturally with aging, but dramatic changes should be evaluated by a healthcare provider.
Temperature and Environmental Factors
Temporary size fluctuations can occur due to temperature changes, physical activity, or sexual arousal. These variations are normal and usually don't indicate any health concerns.
Impact on Fertility and Sexual Function
While testicle size can influence fertility, having slightly smaller or larger testicles doesn't necessarily indicate fertility problems. However, significantly small testicles might produce less testosterone and fewer sperm, potentially affecting fertility.
Signs of Potential Issues
Medical attention may be needed if you notice:
- Sudden changes in size or shape
- Pain or discomfort
- Lumps or unusual firmness
- Significant asymmetry between testicles
- Swelling or inflammation
Common Causes of Size Changes
Several factors can affect testicle size:
- Hormonal imbalances
- Certain medications
- Infections or inflammation
- Varicocele (enlarged veins in the scrotum)
- Medical conditions affecting hormone production
- Previous injuries or trauma
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is considered a normal testicle size for an adult male? A normal adult testicle typically measures 3.5-5.5 cm in length and 2-3 cm in width, with a volume of 15-25 milliliters. Some natural variation outside these ranges can be normal.
2. How do variations in testicle size affect fertility or sexual function? While extreme variations might impact fertility, moderate size differences usually don't affect sexual function or fertility. However, significantly small testicles may produce less testosterone and sperm.
3. What are the common causes of testicular shrinkage, and is it a concern? Testicular shrinkage can be caused by hormonal changes, medications, aging, or medical conditions. While some shrinkage is normal with age, sudden or significant changes should be evaluated by a healthcare provider.
4. Can having one testicle significantly larger than the other be a health issue? Some size difference between testicles is normal. However, sudden or significant asymmetry should be examined by a doctor to rule out underlying conditions like varicocele or tumors.
5. When should I seek medical attention if I notice changes in my testicles? Seek immediate medical attention if you notice sudden size changes, pain, lumps, swelling, or significant asymmetry. Regular self-examinations can help you identify concerning changes early.
Remember: maintaining awareness of your testicular health through regular self-examinations and promptly addressing any concerns with a healthcare provider is crucial for overall reproductive health.