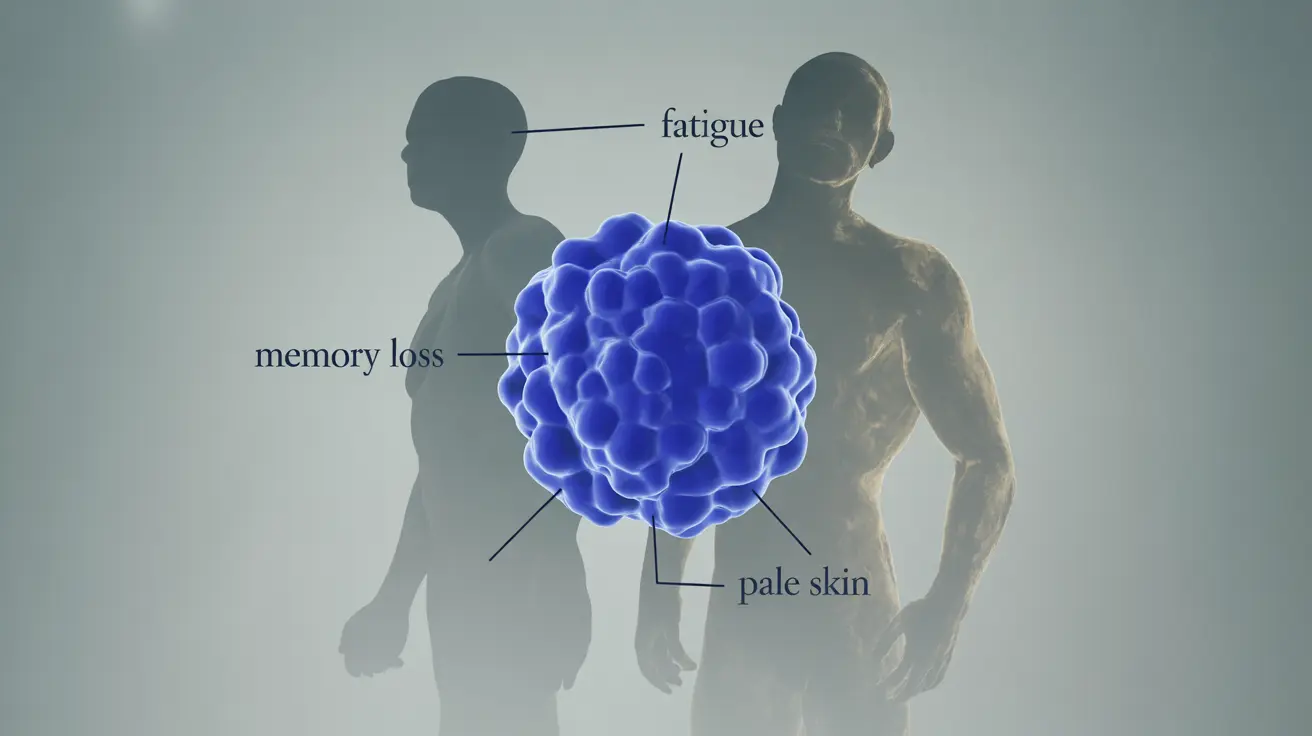
Vitamin B12 deficiency is a serious health concern that can significantly impact your overall well-being if left unaddressed. Recognizing the early warning signs of B12 deficiency is crucial for prompt intervention and treatment. This comprehensive guide will help you understand the key indicators, risk factors, and treatment options available.
Key Signs and Symptoms of B12 Deficiency
B12 deficiency often develops gradually, manifesting through various physical and neurological symptoms. Understanding these warning signals can help you seek medical attention before the condition becomes severe.
Physical Manifestations
The most common physical signs of B12 deficiency include:
- Unusual fatigue and weakness
- Pale or slightly yellow skin tone
- Shortness of breath
- Heart palpitations
- Unexplained weight loss
- Smooth, red tongue
- Digestive issues
Neurological and Mental Health Impact
B12 deficiency can significantly affect your nervous system and mental well-being, leading to:
- Vision changes
- Memory problems
- Difficulty maintaining balance
- Pins and needles sensations
- Depression and mood changes
- Brain fog and difficulty concentrating
High-Risk Groups for B12 Deficiency
Certain individuals are more susceptible to developing B12 deficiency due to various factors:
Dietary Factors
People following strict vegetarian or vegan diets face higher risks due to limited natural B12 sources in plant-based foods. Regular B12 supplementation is often necessary for these individuals.
Medical Conditions
Several health conditions can increase the risk of B12 deficiency:
- Pernicious anemia
- Celiac disease
- Crohn's disease
- Previous gastrointestinal surgery
- Atrophic gastritis
Diagnosis and Testing
Healthcare providers typically use several methods to diagnose B12 deficiency:
- Complete blood count (CBC)
- Serum B12 level test
- Methylmalonic acid test
- Homocysteine level test
Treatment Approaches
Treatment options vary depending on the severity of the deficiency and its underlying cause:
Supplementation Methods
Common supplementation approaches include:
- Oral B12 supplements
- B12 injections
- Nasal spray forms
- Dietary modifications
Recovery Timeline
Most people begin to notice improvement within a few weeks of starting treatment, though complete recovery may take several months. Neurological symptoms typically take the longest to resolve.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the common signs and early symptoms of vitamin B12 deficiency?
The most common early signs include unusual fatigue, pale skin, shortness of breath, and neurological symptoms like tingling in hands and feet, memory problems, and difficulty with balance. Some people may also experience mood changes and depression.
How does vitamin B12 deficiency affect the nervous system and mental health?
B12 deficiency can cause various neurological symptoms including numbness and tingling in extremities, balance problems, memory issues, and mood disorders. It can also lead to cognitive decline and depression if left untreated.
Who is most at risk for developing vitamin B12 deficiency and why?
Those at highest risk include strict vegetarians/vegans, older adults, people with gastrointestinal disorders, individuals who've had stomach surgery, and those taking certain medications like metformin or proton pump inhibitors.
What tests are used to diagnose vitamin B12 deficiency?
Doctors typically use a combination of blood tests including serum B12 levels, complete blood count, methylmalonic acid test, and homocysteine levels to diagnose B12 deficiency accurately.
What are the available treatment options for vitamin B12 deficiency and how quickly do symptoms improve?
Treatment options include oral supplements, B12 injections, or nasal sprays, depending on the severity and cause of the deficiency. Most people start feeling better within a few weeks of treatment, though complete recovery can take several months.