While bananas are generally considered a healthy fruit packed with essential nutrients, there are certain situations where consuming them might not be ideal for everyone. Understanding the potential drawbacks and risks of banana consumption is crucial for making informed dietary choices, especially if you have specific health conditions or concerns.
In this comprehensive guide, we'll explore the potential negative effects of bananas, who should be cautious about eating them, and when they might pose health risks. This information will help you make better decisions about including bananas in your diet.
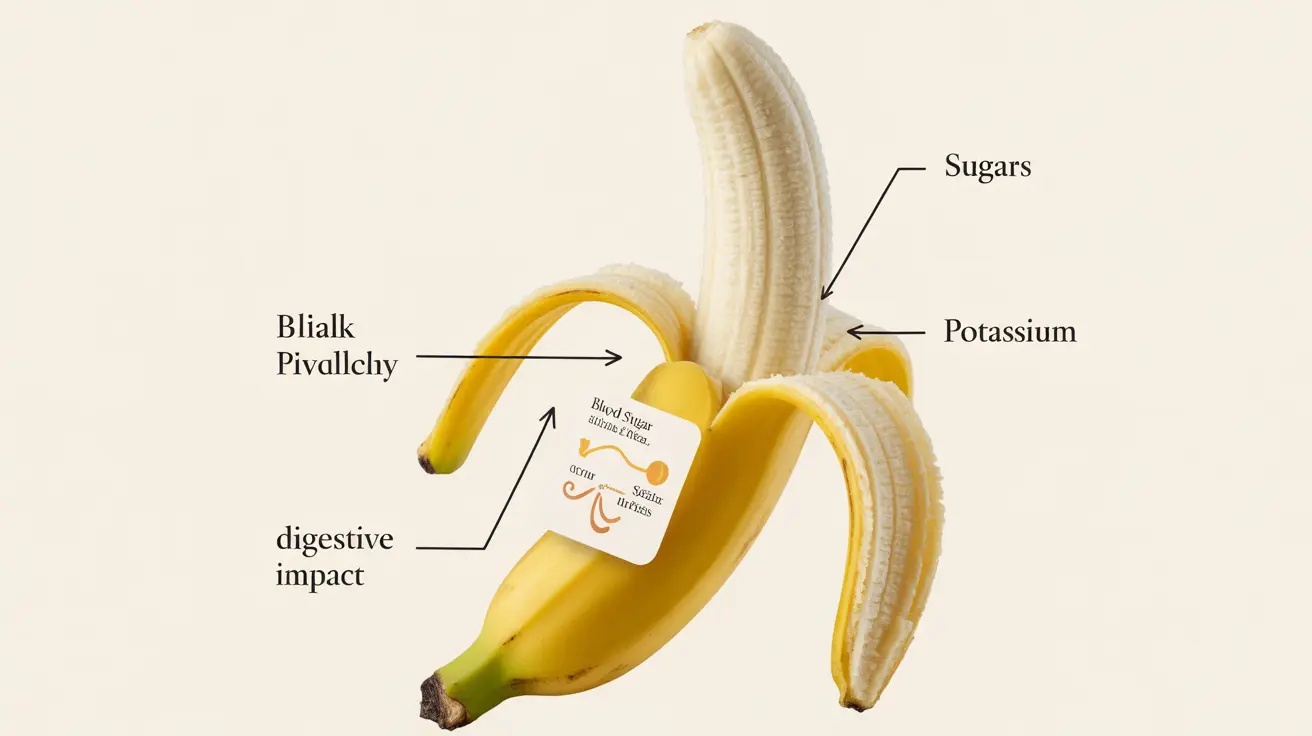
Blood Sugar Impact and Diabetes Concerns
Bananas contain natural sugars and carbohydrates that can affect blood glucose levels. While they have a moderate glycemic index, their glycemic load can vary depending on ripeness. Very ripe bananas have more sugar content and can cause faster blood sugar spikes compared to their less-ripe counterparts.
For people with diabetes, portion control becomes especially important. Consider these factors:
- Choose slightly underripe bananas
- Pair with protein or healthy fats to slow sugar absorption
- Monitor portion sizes carefully
- Track blood sugar responses individually
Potassium Content and Medical Considerations
While potassium is an essential mineral, excessive intake can be problematic for certain individuals. People with kidney problems or those taking specific medications need to be particularly careful about their banana consumption.
High-Risk Groups for Potassium Concerns
The following groups should monitor their banana intake:
- Individuals with kidney disease
- People taking ACE inhibitors
- Those using beta-blockers
- Patients on potassium-sparing diuretics
Digestive Issues and Intolerance
Some people may experience digestive discomfort after eating bananas. Common issues include:
- Bloating and gas
- Stomach cramping
- Constipation (especially when unripe)
- Digestive slowdown
These effects are often related to the banana's fiber content and natural compounds that some individuals may be sensitive to.
Medical Conditions Requiring Banana Limitation
Several medical conditions may warrant limiting or avoiding banana consumption:
- Chronic kidney disease
- Hyperkalemia (high blood potassium)
- Certain types of medication interactions
- Latex allergies (due to cross-reactivity)
- Migraine sensitivity (in some individuals)
Frequently Asked Questions
Can eating too many bananas be bad for you, and what health problems can it cause?
Yes, excessive banana consumption can lead to problems such as high potassium levels, blood sugar spikes, and digestive issues. While rare, eating too many bananas could potentially cause hyperkalemia in susceptible individuals, especially those with kidney problems or on certain medications.
Do bananas raise blood sugar, and should people with diabetes avoid eating them?
Bananas can raise blood sugar levels, but people with diabetes don't need to avoid them completely. Instead, they should monitor portion sizes, choose less ripe bananas, and pair them with protein or healthy fats to slow sugar absorption.
Is the potassium in bananas dangerous for people with kidney disease or those taking certain medications?
Yes, the high potassium content in bananas can be dangerous for people with kidney disease or those taking medications that affect potassium levels, such as ACE inhibitors or potassium-sparing diuretics. These individuals should consult their healthcare provider about appropriate banana consumption.
Can bananas cause stomach problems like gas, bloating, or digestive discomfort for some people?
Yes, some people may experience digestive issues from bananas, including gas, bloating, and constipation. This is often due to their fiber content and certain compounds that can affect digestion in sensitive individuals.
Are there certain medical conditions or situations when bananas should be limited or avoided?
Yes, bananas should be limited or avoided in several situations, including chronic kidney disease, hyperkalemia, certain medication interactions, latex allergies, and some cases of migraine sensitivity. Always consult with a healthcare provider about specific dietary restrictions for your condition.