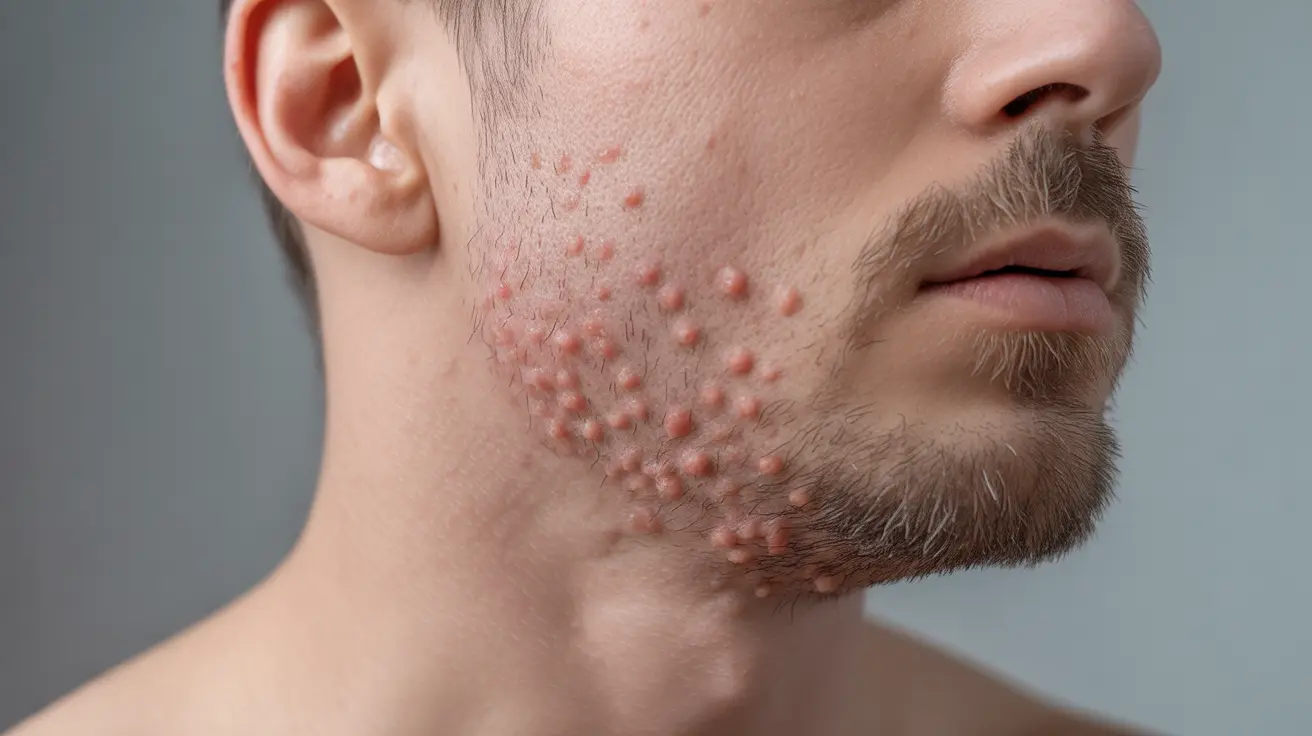
Barber's itch, medically known as folliculitis barbae, is a common skin condition that affects the beard area in men. This uncomfortable inflammation of hair follicles can cause both physical discomfort and cosmetic concerns. Understanding its causes, symptoms, and treatment options is crucial for effective management and prevention.
While the condition's historical name comes from its association with unsanitary barbershop practices, today it can occur for various reasons, ranging from improper shaving techniques to bacterial infections. Let's explore everything you need to know about managing and preventing this common skin concern.
Understanding Barber's Itch and Its Symptoms
Barber's itch typically appears as small, red bumps or pustules around hair follicles in the beard area. These bumps can be tender to the touch and may cause itching or burning sensations. The condition commonly affects the neck area and can spread across the entire beard region.
Common symptoms include:
- Red, inflamed bumps around hair follicles
- Itching or burning sensation
- Small pustules containing pus
- Tenderness when touching the affected area
- Possible crusting or scabbing
Common Causes and Risk Factors
Several factors can contribute to the development of barber's itch:
Bacterial Infections
The most common cause is bacterial infection, particularly from Staphylococcus aureus. These bacteria can enter hair follicles through small cuts or abrasions during shaving.
Improper Shaving Techniques
Using dull razors, shaving too closely, or shaving without proper lubrication can irritate hair follicles and create entry points for bacteria.
Environmental Factors
Hot, humid conditions and tight clothing that causes friction can create an environment where bacteria thrive, increasing the risk of developing barber's itch.
Treatment Options and Solutions
Treatment for barber's itch varies depending on severity and cause. Many cases can be managed with over-the-counter remedies, while others may require prescription medications.
Over-the-Counter Solutions
- Antibacterial soaps and washes
- Warm compresses to relieve inflammation
- Over-the-counter antibiotic ointments
- Gentle exfoliating products
Prescription Treatments
For more severe cases, a healthcare provider may prescribe:
- Oral antibiotics
- Prescription-strength topical antibiotics
- Antifungal medications if needed
- Medicated shaving creams
Prevention and Best Practices
Preventing barber's itch involves maintaining good hygiene and proper shaving techniques:
- Use sharp, clean razors
- Change razor blades regularly
- Shave in the direction of hair growth
- Use warm water and proper shaving cream
- Clean and disinfect electric razors after each use
- Consider taking breaks from shaving to allow skin to heal
Frequently Asked Questions
- What does barber's itch look like, and what are the main symptoms I should watch for?
Barber's itch appears as small, red, inflamed bumps around hair follicles in the beard area. Main symptoms include itching, burning, tenderness, and small pustules that may contain pus. The affected area may also develop crusting or scabbing.
- What are the best treatments for barber's itch, and do I need a prescription?
Mild cases can be treated with over-the-counter antibacterial soaps, warm compresses, and antibiotic ointments. Severe cases may require prescription oral antibiotics or topical medications from a healthcare provider.
- How do you get barber's itch, and what are the most common causes?
Barber's itch typically develops from bacterial infections, particularly Staphylococcus aureus, entering hair follicles through small cuts or irritation from shaving. Poor shaving techniques, dull razors, and inadequate hygiene can increase the risk.
- Can barber's itch cause permanent hair loss or scarring?
While rare, severe or untreated cases of barber's itch can potentially lead to scarring and temporary hair loss. However, with proper treatment, most cases heal completely without permanent damage.
- How can I prevent barber's itch, and what hygiene tips help avoid getting it again?
Prevention includes using sharp, clean razors, proper shaving technique, regular cleaning of shaving equipment, and maintaining good hygiene. Shaving with the grain of hair growth and using appropriate shaving products can significantly reduce the risk of recurrence.