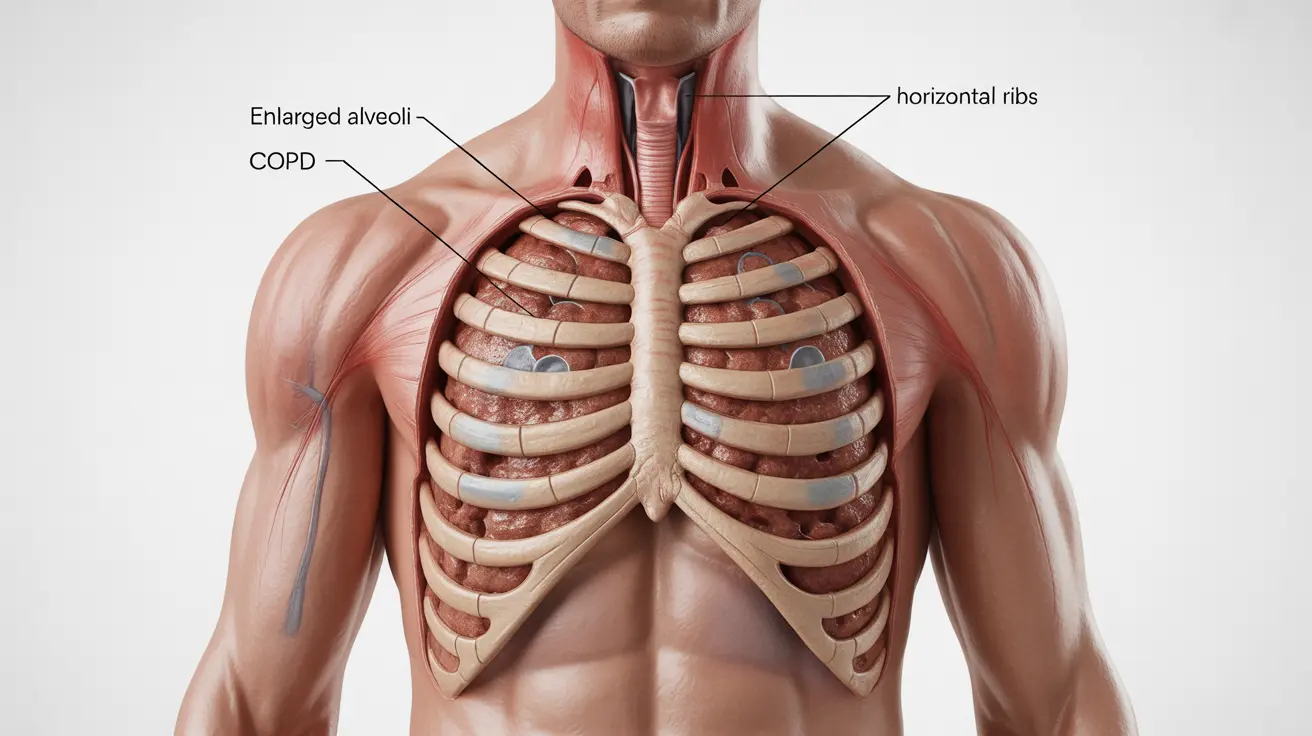
Barrel chest is a significant physical change that can occur in people with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD). This condition causes the chest to appear permanently expanded or barrel-shaped, reflecting important changes in lung function and chest wall structure. Understanding barrel chest in COPD is crucial for both diagnosis and management of the underlying respiratory condition.
For individuals living with COPD, the development of barrel chest can significantly impact their breathing mechanics and quality of life. This article explores the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options available for managing barrel chest associated with COPD.
Understanding Barrel Chest and Its Relationship to COPD
Barrel chest develops in COPD patients due to lung hyperinflation, where air becomes trapped in the lungs, causing them to remain partially inflated even during exhalation. This ongoing expansion of the lungs leads to changes in chest wall structure, resulting in the characteristic barrel-shaped appearance.
The condition occurs when the natural elasticity of lung tissue diminishes, making it harder for patients to fully exhale. Over time, this creates a permanent expansion of the rib cage and changes in posture that contribute to the barrel chest appearance.
Common Signs and Symptoms
Several distinctive signs and symptoms indicate the presence of barrel chest in COPD patients:
- Rounded, expanded chest appearance
- Increased anterior-posterior chest diameter
- Horizontal positioning of the ribs
- Shortened neck appearance
- Forward-leaning posture
- Difficulty with complete exhalation
- Increased work of breathing
Diagnostic Process and Assessment
Healthcare providers use various methods to diagnose barrel chest in COPD patients:
Physical Examination
Doctors conduct thorough physical examinations to assess chest shape, breathing patterns, and posture changes. They may measure the ratio between the anterior-posterior and transverse chest diameters.
Imaging Studies
Medical professionals often utilize:
- Chest X-rays
- CT scans
- Pulmonary function tests
- Arterial blood gas analysis
Treatment and Management Approaches
While barrel chest itself cannot be completely reversed, several management strategies can help improve breathing and quality of life:
Pulmonary Rehabilitation
This comprehensive program includes:
- Breathing exercises
- Physical conditioning
- Education about COPD management
- Posture improvement techniques
Medical Management
Treatment options may include:
- Bronchodilators
- Anti-inflammatory medications
- Oxygen therapy when needed
- Smoking cessation support
Prevention and Long-term Care
Preventing the progression of barrel chest in COPD involves several key strategies:
- Early intervention when COPD is diagnosed
- Regular exercise and physical activity
- Maintaining good posture
- Following prescribed medication regimens
- Regular medical check-ups
Frequently Asked Questions
What causes barrel chest in people with COPD and how does it affect breathing? Barrel chest in COPD is caused by lung hyperinflation and trapped air, leading to permanent chest expansion. This affects breathing by altering chest wall mechanics and making it harder to fully exhale air from the lungs.
What are the common symptoms and signs of barrel chest related to COPD? Common signs include a rounded, expanded chest appearance, horizontal ribs, shortened neck, forward-leaning posture, and difficulty with complete exhalation.
How is barrel chest diagnosed in patients with COPD? Diagnosis involves physical examination, chest measurements, imaging studies like X-rays and CT scans, and pulmonary function tests to assess the extent of chest wall changes and lung function.
Can barrel chest from COPD be treated or reversed, and what management options are available? While barrel chest cannot be completely reversed, it can be managed through pulmonary rehabilitation, medication, breathing exercises, and lifestyle modifications to improve breathing and quality of life.
How does lung hyperinflation lead to barrel chest in COPD and what can be done to prevent it? Lung hyperinflation occurs when air becomes trapped in the lungs, causing permanent chest expansion. Prevention focuses on early COPD treatment, regular exercise, good posture maintenance, and following prescribed treatment plans.