Knee replacement surgery has become an increasingly sophisticated and effective solution for individuals suffering from severe knee pain and mobility issues. With modern medical advancements, patients now have access to various surgical approaches, each offering unique benefits for specific conditions and circumstances. Understanding these options is crucial for making an informed decision about your knee replacement journey.
This comprehensive guide explores the different types of knee replacement procedures, helping you understand which might be your best knee replacement surgery option based on your specific condition, lifestyle, and medical needs.
Types of Knee Replacement Procedures
Knee replacement surgery isn't a one-size-fits-all solution. Modern orthopedic surgery offers several specialized approaches to address different patterns of knee damage and patient needs.
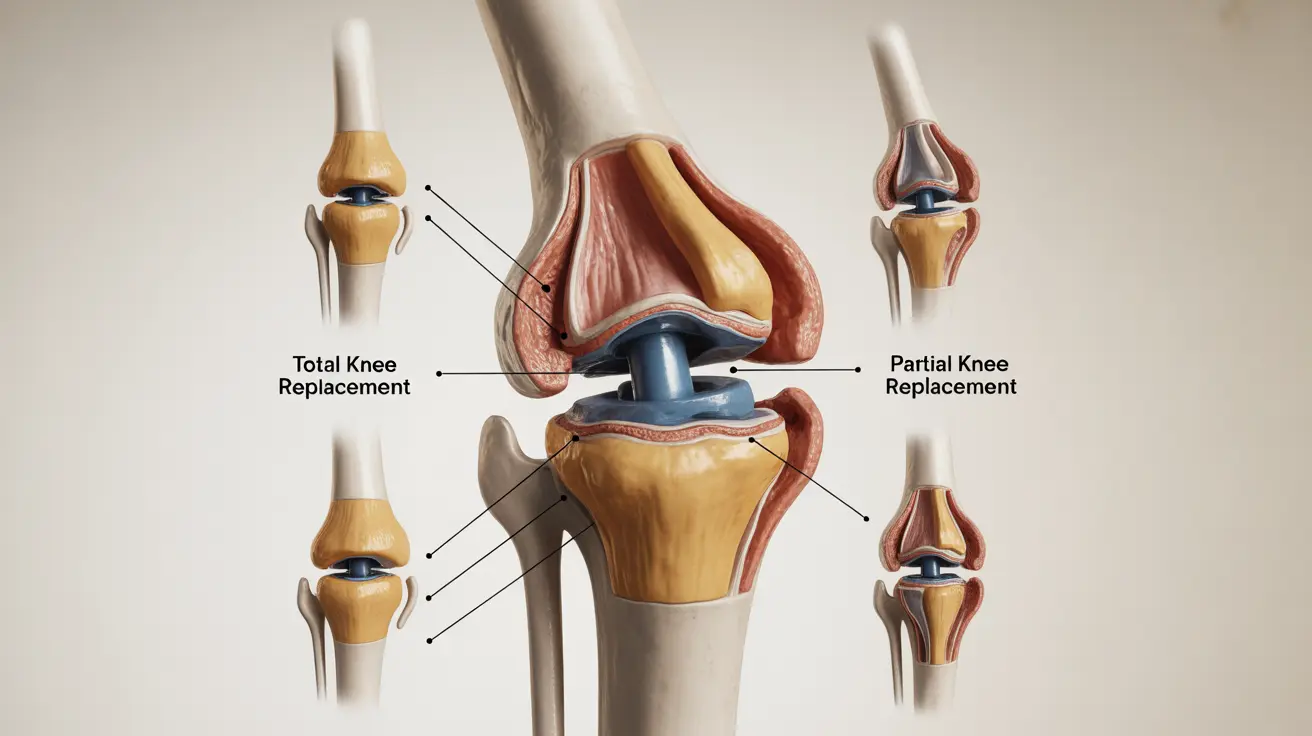
Total Knee Replacement
Total knee replacement (TKR) involves replacing all major components of the knee joint, including the medial and lateral compartments and often the patellofemoral joint. This comprehensive approach is typically recommended for patients with widespread knee damage or severe arthritis affecting multiple areas of the joint.
Partial Knee Replacement
Partial knee replacement, also known as unicompartmental knee replacement, focuses on replacing only the damaged portion of the knee while preserving healthy tissue and bone. This less invasive approach often results in quicker recovery times and more natural knee movement for suitable candidates.
Advanced Surgical Technologies
Robotic-Assisted Surgery
Modern knee replacement procedures increasingly utilize robotic-assisted technology, offering unprecedented precision in surgical planning and execution. This advanced approach enables surgeons to create highly detailed, patient-specific surgical plans and execute them with remarkable accuracy.
Computer-Navigated Surgery
Computer navigation systems provide real-time imaging and guidance during surgery, helping surgeons achieve optimal implant positioning and alignment. This technology can contribute to better surgical outcomes and longer-lasting results.
Recovery and Rehabilitation
The success of knee replacement surgery largely depends on proper rehabilitation and recovery protocols. Most patients can expect a structured recovery period lasting several months, with specific milestones and exercises at each stage.
Initial Recovery Phase
The first few weeks after surgery focus on pain management, wound healing, and basic mobility exercises. Most patients begin walking with assistance within 24 hours of surgery, gradually increasing their activity level under professional guidance.
Long-term Rehabilitation
Comprehensive rehabilitation typically continues for 3-6 months post-surgery, involving targeted exercises to restore strength, flexibility, and range of motion. The goal is to help patients return to their normal daily activities and achieve optimal knee function.
Revision Surgery Considerations
While most knee replacements last 15-20 years or longer, some patients may eventually need revision surgery. Understanding the circumstances that might necessitate revision can help in long-term planning and maintenance of your knee replacement.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What is the difference between total and partial knee replacement surgery? A: Total knee replacement involves replacing all major components of the knee joint, while partial knee replacement only replaces the damaged portion while preserving healthy tissue. The choice between them depends on the extent and pattern of knee damage.
Q: Who is the best candidate for partial knee replacement versus total knee replacement? A: Ideal candidates for partial knee replacement have damage limited to one compartment of the knee, with healthy ligaments and good range of motion. Total knee replacement is better suited for patients with widespread joint damage or severe arthritis affecting multiple areas.
Q: How does robotic-assisted knee replacement improve surgical outcomes? A: Robotic-assisted surgery enhances precision in both planning and execution, allowing for more accurate implant positioning and better preservation of healthy tissue. This can lead to improved alignment, faster recovery, and potentially better long-term outcomes.
Q: What is the typical recovery time after knee replacement surgery and what does rehabilitation involve? A: Recovery typically spans 3-6 months, beginning with basic mobility exercises and progressing to more advanced strengthening and flexibility work. Rehabilitation includes physical therapy, home exercises, and gradual return to daily activities under professional guidance.
Q: When is revision knee replacement surgery necessary and how does it differ from initial knee replacement? A: Revision surgery may be needed if the original implant wears out, becomes loose, gets infected, or causes persistent pain. It's typically more complex than initial surgery, often requiring specialized implants and bone grafting to address any deterioration that has occurred.