The term "biological clock" has become deeply ingrained in discussions about women's fertility and reproductive timeline. This natural phenomenon reflects the relationship between age and reproductive potential, encompassing both biological realities and personal choices about motherhood.
Understanding how age impacts fertility can help women make informed decisions about their reproductive future while navigating the complex interplay of biological, social, and personal factors that influence family planning.
The Science Behind Female Fertility and Age
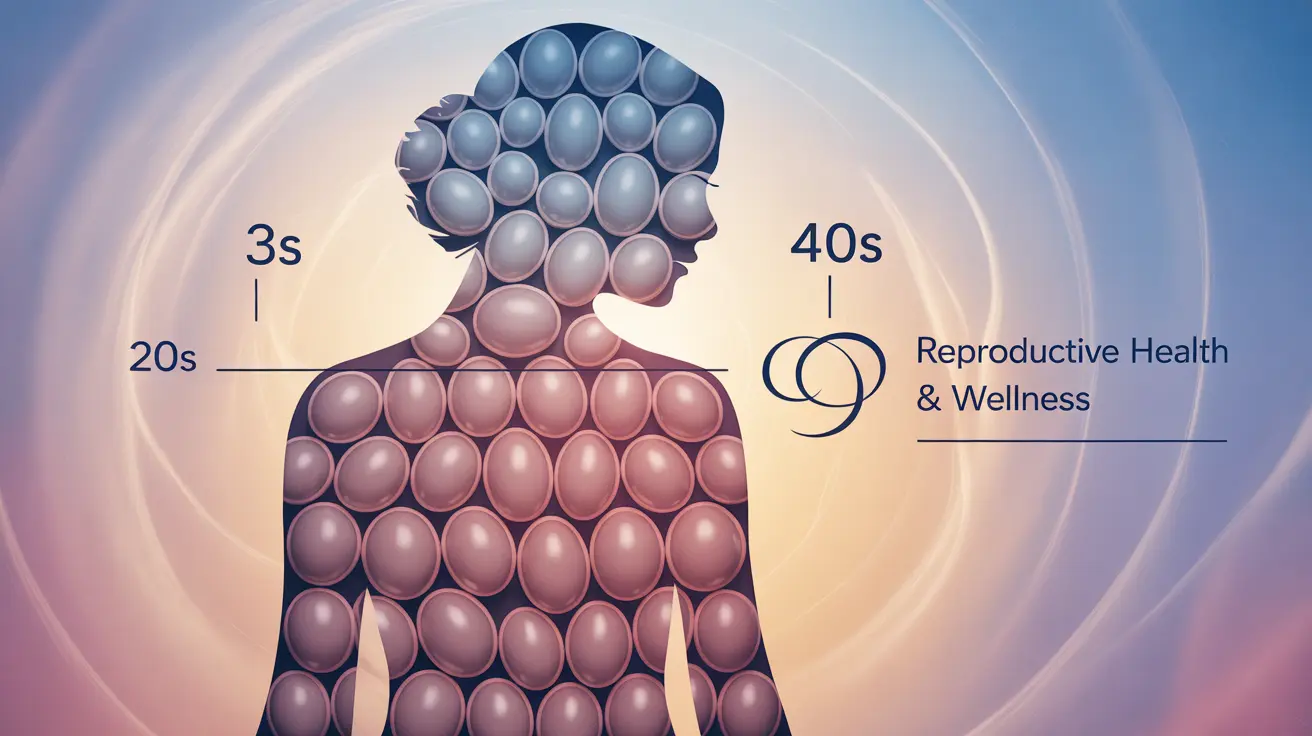
Female fertility is intricately connected to both the quantity and quality of eggs (oocytes) available in the ovaries. Women are born with approximately 1-2 million eggs, but this number steadily declines throughout their lifetime, with the most significant changes occurring after age 35.
Peak Fertility Years
Women experience their highest fertility potential during their 20s and early 30s. During this time, both egg quantity and quality are optimal, resulting in higher chances of natural conception and healthy pregnancies.
Age-Related Fertility Decline
The decline in fertility typically becomes more pronounced after age 35, with a sharp decrease occurring after 37. This reduction affects both:
- The number of viable eggs remaining in the ovaries
- The quality of the eggs, which impacts their ability to result in successful pregnancies
- The increased risk of chromosomal abnormalities
Modern Approaches to Fertility Management
Fertility Preservation Options
Modern medicine offers several options for women who wish to preserve their fertility:
- Egg freezing (oocyte cryopreservation)
- Embryo freezing
- Ovarian tissue preservation
- Fertility-aware lifestyle choices
Medical Interventions and Assistance
When natural conception becomes challenging, various medical interventions can help:
- Fertility medications
- Intrauterine insemination (IUI)
- In vitro fertilization (IVF)
- Donor eggs or embryos
Social and Emotional Considerations
The concept of the biological clock often carries significant psychological and social weight. Women may experience pressure from various sources, including family, society, and their own expectations about motherhood timing.
Balancing Career and Family Planning
Many women face the challenge of coordinating career advancement with family planning. This often involves careful consideration of:
- Professional goals and timeline
- Financial stability
- Personal readiness for parenthood
- Available support systems
Frequently Asked Questions
What does it mean when people say a woman's biological clock is ticking?
This phrase refers to the limited window of time during which a woman can naturally conceive and carry a pregnancy to term. It reflects the biological reality that fertility decreases with age, particularly after 35.
At what age does female fertility start to decline significantly?
Female fertility begins a gradual decline in the early 30s, with a more marked decrease after age 35. By age 37, the decline becomes more pronounced, and fertility continues to decrease rapidly through the 40s.
How does aging affect the number and quality of a woman's eggs?
Aging affects both egg quantity and quality. Women are born with all their eggs, and this number decreases over time. Additionally, the remaining eggs become more susceptible to chromosomal abnormalities, potentially affecting fertility and pregnancy outcomes.
What social and psychological pressures do women face related to their biological clock?
Women often face pressures from family expectations, societal norms, and personal goals. These may include balancing career advancement, finding the right partner, achieving financial stability, and meeting social expectations about the "right time" for motherhood.
What options are available for women who want to preserve fertility or delay childbirth?
Modern medicine offers several fertility preservation options, including egg freezing, embryo freezing, and ovarian tissue preservation. Additionally, women can work with fertility specialists to develop personalized family planning strategies that align with their life goals.