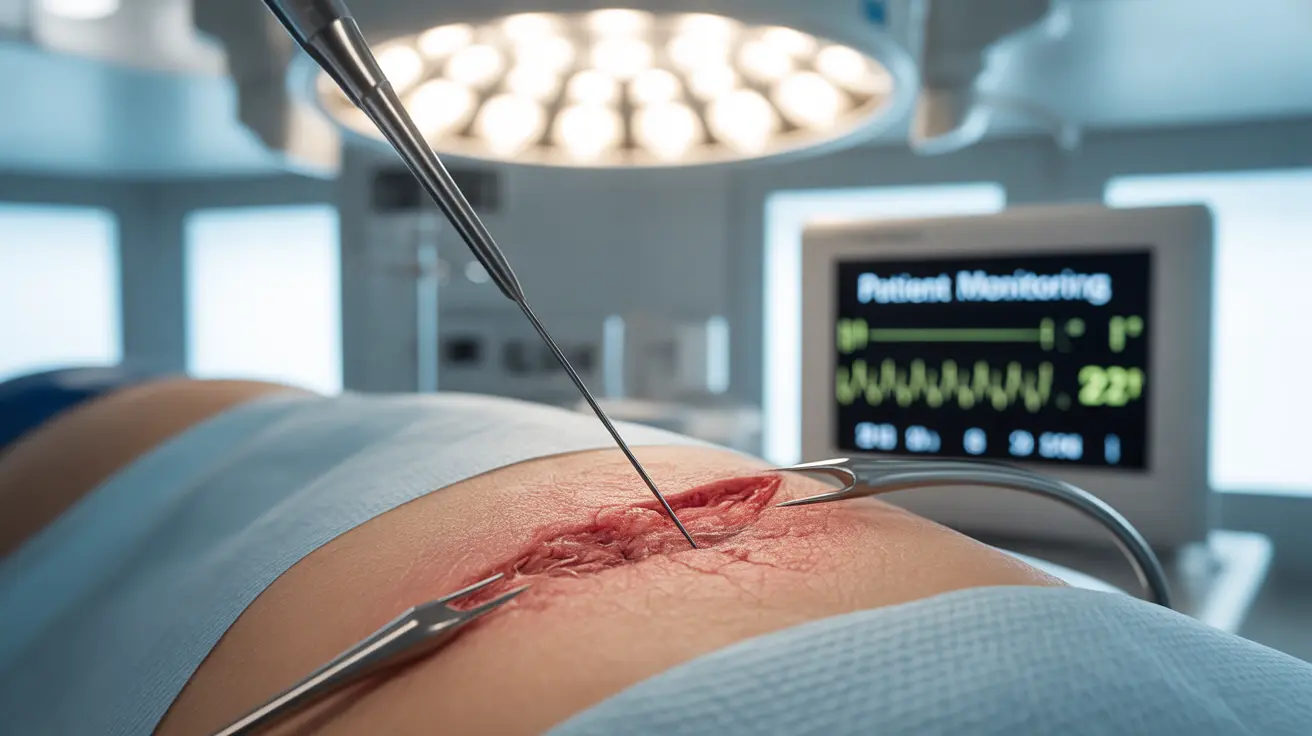
A biopsy is a crucial medical diagnostic procedure where doctors remove a small sample of tissue from your body for detailed laboratory examination. This vital test helps healthcare providers accurately diagnose various conditions, particularly when screening for cancer or investigating suspicious growths. Understanding what a biopsy involves can help ease concerns and prepare you for this important diagnostic tool.
Whether you're facing a potential skin condition, breast abnormality, or internal organ issue, biopsies provide definitive answers that guide treatment decisions. This comprehensive guide will walk you through everything you need to know about biopsy procedures, from preparation to results.
Types of Biopsy Procedures
Medical professionals use several different biopsy techniques, choosing the most appropriate method based on the location and nature of the tissue being examined:
Needle Biopsy
This common technique uses a needle to extract tissue or fluid samples. It includes fine-needle aspiration (FNA), which uses a very thin needle, and core needle biopsies, which use a slightly larger needle to obtain a fuller tissue sample. These procedures are frequently used for breast, thyroid, and lung biopsies.
Surgical Biopsy
Surgical biopsies involve removing tissue through an incision. These can be excisional (removing the entire suspicious area) or incisional (removing only a portion). This method is often used when larger tissue samples are needed or when the area is difficult to access with needles.
Endoscopic Biopsy
During an endoscopic procedure, doctors use a flexible tube with a camera to view internal organs and collect tissue samples. This technique is commonly used for digestive tract, bladder, or lung biopsies.
Preparing for Your Biopsy
Proper preparation can help ensure a successful biopsy procedure. Your healthcare provider will provide specific instructions based on your type of biopsy, but general preparations often include:
- Informing your doctor about any medications or supplements you take
- Fasting for several hours before certain procedures
- Arranging transportation home if sedation will be used
- Wearing comfortable clothing appropriate for the procedure
The Biopsy Procedure Process
While specific procedures vary, most biopsies follow a general pattern:
- Local or general anesthesia administration
- Careful identification of the target area
- Tissue sample collection using the chosen method
- Sample preservation for laboratory analysis
- Wound closure or dressing application if needed
Recovery and Aftercare
Most biopsy procedures are outpatient, meaning you can go home the same day. Recovery typically involves:
- Monitoring the biopsy site for signs of infection
- Following specific wound care instructions
- Taking prescribed pain medications if needed
- Limiting certain activities temporarily
- Attending follow-up appointments as scheduled
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a biopsy and why is it performed?
A biopsy is a medical procedure where tissue samples are removed from the body for detailed laboratory examination. It's performed to diagnose various conditions, particularly when cancer is suspected, or to determine the cause of unexplained inflammation or other tissue abnormalities.
What are the different types of biopsy procedures and how do they differ?
The main types include needle biopsies (using fine or core needles), surgical biopsies (removing tissue through incisions), and endoscopic biopsies (using a flexible tube with a camera). Each type is chosen based on the location of the tissue, the size of the sample needed, and the suspected condition.
How should I prepare for a biopsy, and what happens during the procedure?
Preparation varies by biopsy type but may include fasting, stopping certain medications, and arranging transportation. During the procedure, you'll receive appropriate anesthesia, the tissue sample will be collected using the chosen method, and the site will be closed or dressed as needed.
What are the risks and potential side effects associated with biopsies?
Common side effects include minor pain, bruising, and slight bleeding at the biopsy site. Serious complications are rare but may include infection, excessive bleeding, or accidental damage to surrounding tissues. Your doctor will discuss specific risks based on your procedure type.
How long does it take to get biopsy results and what will they tell me?
Results typically take anywhere from a few days to two weeks, depending on the type of tissue and tests required. The results will indicate whether cells are normal, show signs of infection, inflammation, or cancer, helping your healthcare team determine appropriate treatment options.