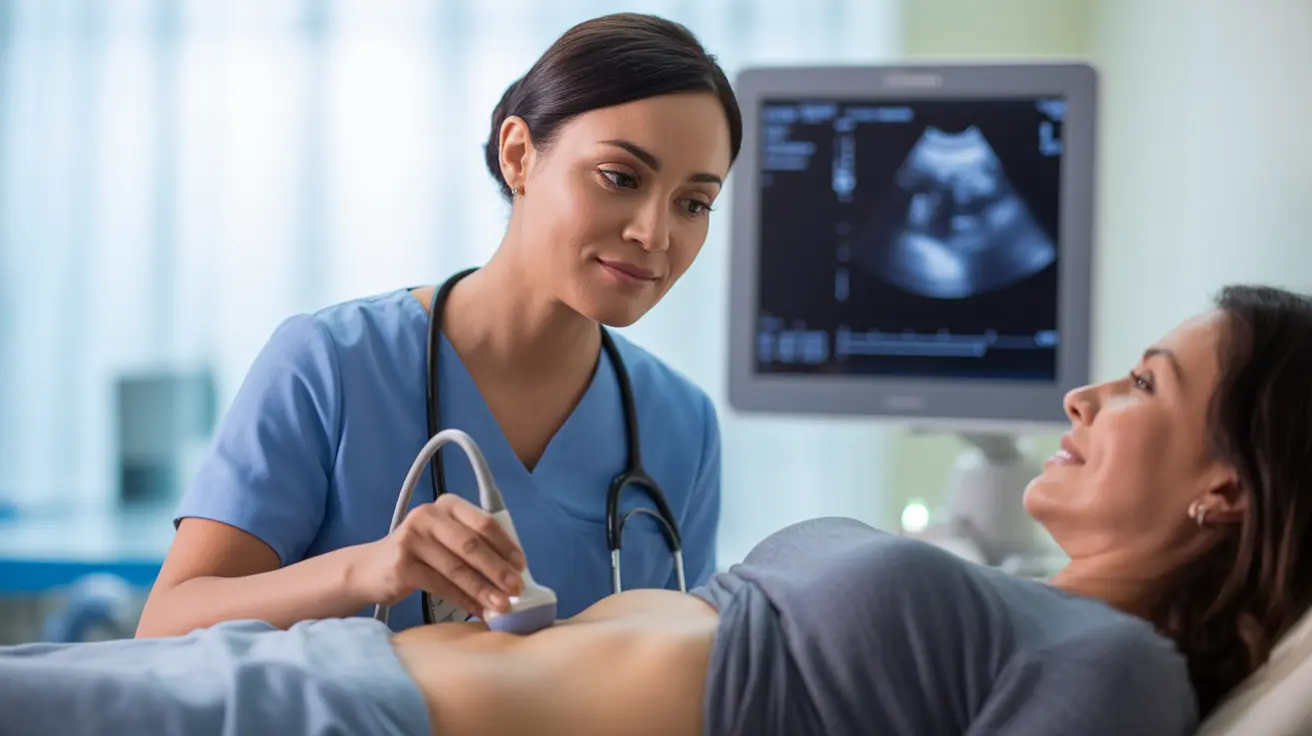
A bladder ultrasound is a non-invasive diagnostic procedure that uses sound waves to create detailed images of your bladder and measure its contents. This valuable medical tool helps healthcare providers evaluate various urinary conditions and assess bladder function without the need for more invasive testing.
Whether you're experiencing urinary problems or need to monitor your bladder health, understanding what a bladder ultrasound involves can help you feel more prepared and confident about the procedure. This comprehensive guide will walk you through everything you need to know about bladder ultrasounds.
How Bladder Ultrasound Works
During a bladder ultrasound, a trained technician uses a handheld device called a transducer to send high-frequency sound waves through your lower abdomen. These sound waves bounce off your bladder and surrounding tissues, creating detailed images that appear on a computer screen in real-time.
The procedure typically involves these steps:
- Application of clear gel to your lower abdomen
- Gentle pressing of the transducer against your skin
- Movement of the device to capture different angles and views
- Recording of images and measurements for medical evaluation
Preparation Guidelines
Preparing for a bladder ultrasound is relatively straightforward, but following these guidelines ensures the most accurate results:
- Drink plenty of water before the exam (usually 4-6 glasses)
- Avoid urinating for 1-2 hours before the procedure
- Wear comfortable, loose-fitting clothing
- Follow any specific instructions from your healthcare provider
- Arrive at least 15 minutes early for registration
Common Uses and Applications
Healthcare providers may recommend a bladder ultrasound for various reasons:
Diagnostic Purposes
- Investigating frequent urination
- Evaluating urinary incontinence
- Assessing urinary retention
- Checking for bladder stones
- Monitoring prostate-related issues
Monitoring and Assessment
- Measuring post-void residual volume
- Evaluating bladder wall thickness
- Detecting structural abnormalities
- Tracking treatment progress
- Screening for certain bladder conditions
Benefits and Safety Considerations
Bladder ultrasound offers numerous advantages as a diagnostic tool:
- Non-invasive and painless procedure
- No radiation exposure
- Real-time imaging capabilities
- Quick and convenient
- Highly accurate results
- No recovery time needed
What to Expect During the Procedure
A typical bladder ultrasound examination takes about 15-30 minutes to complete. You'll lie on an examination table while the technician performs the scan. The procedure is comfortable for most people, though you may feel slight pressure from the transducer.
Frequently Asked Questions
What should I do to prepare for a bladder ultrasound exam? Drink plenty of water to fill your bladder before the exam, avoid urinating for 1-2 hours prior, and wear comfortable clothing. Follow any specific instructions provided by your healthcare provider.
How does a bladder ultrasound help diagnose urinary problems like incontinence or urinary retention? The ultrasound creates detailed images of your bladder, measures its volume, and shows how well it empties. This information helps healthcare providers identify issues with bladder function, muscle control, and structural abnormalities that might cause incontinence or retention.
Is a bladder ultrasound safe, and does it cause any pain or side effects? Yes, bladder ultrasounds are completely safe and painless. The procedure uses sound waves instead of radiation and has no known side effects. You might feel mild pressure from the transducer, but this shouldn't cause discomfort.
How does the bladder ultrasound measure bladder volume and assess how well the bladder empties? The ultrasound equipment uses sound waves to create three-dimensional measurements of your bladder, calculating its volume before and after urination. This helps determine how effectively your bladder empties and identifies any retained urine.
What kinds of bladder abnormalities or conditions can a bladder ultrasound detect? A bladder ultrasound can detect various conditions including bladder stones, tumors, structural abnormalities, enlarged prostate, and incomplete bladder emptying. It can also identify bladder wall thickening and other changes that might indicate underlying problems.