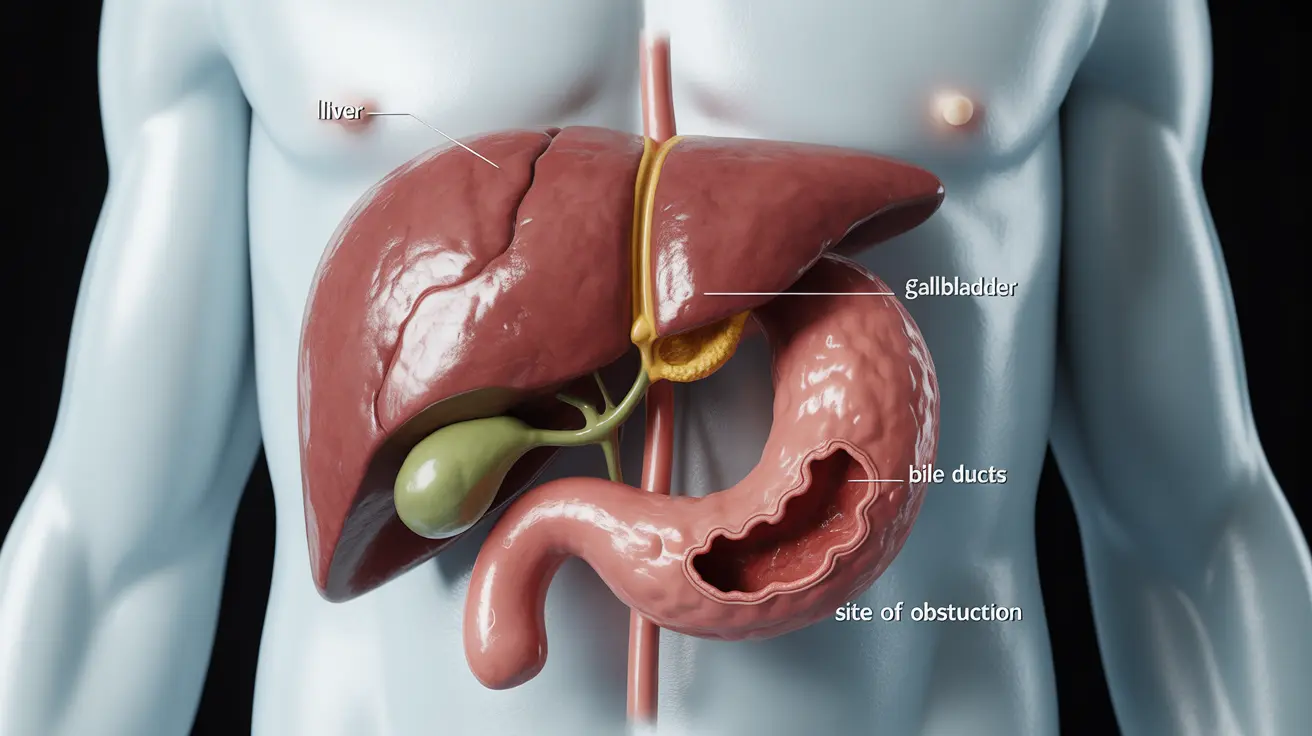
When your bile ducts become blocked, it can lead to serious health complications if left untreated. These vital pathways normally carry bile from your liver to your small intestine, playing a crucial role in digestion and waste removal. Understanding the symptoms of a blocked bile duct is essential for early detection and treatment.
In this comprehensive guide, we'll explore the key signs and symptoms of bile duct obstruction, how it's diagnosed, and what treatment options are available. We'll also discuss potential complications and what changes in your body might indicate this condition.
Common Signs and Symptoms of Blocked Bile Ducts
Recognizing the symptoms of a blocked bile duct early can lead to more effective treatment. Here are the primary indicators to watch for:
Pain and Discomfort
- Upper right abdominal pain
- Sudden and intense discomfort below the ribs
- Pain that may radiate to the back or shoulder
Visible Physical Changes
- Yellowing of the skin (jaundice)
- Yellowing of the whites of the eyes
- Dark urine color
- Pale or clay-colored stools
Additional Symptoms
- Fever and chills
- Loss of appetite
- Unexplained weight loss
- Nausea and vomiting
- Itchy skin
Diagnostic Process for Bile Duct Blockages
Healthcare providers use various methods to diagnose bile duct obstructions accurately:
Initial Assessment
- Physical examination
- Medical history review
- Discussion of symptoms
- Blood tests to check liver function
Imaging Tests
- Ultrasound
- CT scan
- MRI
- ERCP (Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography)
- MRCP (Magnetic Resonance Cholangiopancreatography)
Treatment Approaches
Treatment options vary depending on the cause and severity of the blockage:
Non-surgical Treatments
- Antibiotics for infections
- Medications to dissolve small gallstones
- Endoscopic procedures to remove blockages
- Stent placement to keep ducts open
Surgical Options
When necessary, surgical interventions may include:
- Gallbladder removal (cholecystectomy)
- Bile duct surgery
- Tumor removal if cancer is present
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the most common symptoms that indicate a blocked bile duct?
The most common symptoms include jaundice (yellowing of skin and eyes), upper right abdominal pain, dark urine, pale stools, fever, and itchy skin. These symptoms often develop gradually but can sometimes appear suddenly.
How is a blocked bile duct diagnosed and what tests are involved?
Diagnosis typically involves blood tests to check liver function, along with imaging studies such as ultrasound, CT scans, MRI, ERCP, or MRCP. These tests help doctors identify the location and cause of the blockage.
What treatments are available to relieve a blocked bile duct caused by gallstones or tumors?
Treatment options include endoscopic procedures to remove blockages, stent placement, medications to dissolve gallstones, and surgery when necessary. The specific treatment depends on the cause and severity of the obstruction.
Can a blocked bile duct cause changes in urine or stool color, and why?
Yes, a blocked bile duct typically causes dark or brown urine and pale or clay-colored stools. This occurs because bile pigments that normally color stool brown are blocked from reaching the intestine and instead build up in the blood, being excreted through urine.
What complications can arise if a blocked bile duct is left untreated?
Untreated bile duct blockages can lead to serious complications including cholangitis (bile duct infection), liver damage, chronic liver disease, and in severe cases, liver failure. Prompt treatment is essential to prevent these complications.