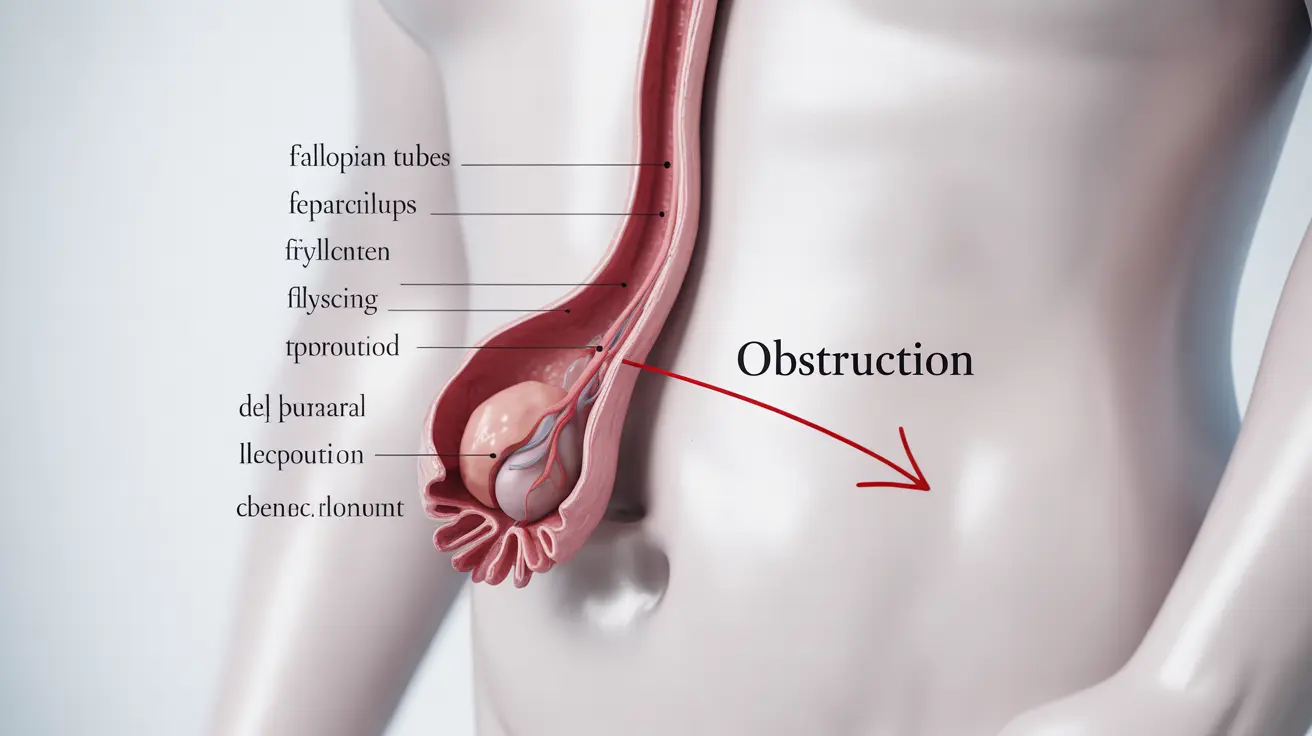
Blocked fallopian tubes, also known as tubal occlusion, can significantly impact a woman's fertility and reproductive health. These vital reproductive structures serve as pathways for eggs to travel from the ovaries to the uterus, and when blocked, can prevent successful conception. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and available treatments is crucial for women experiencing fertility challenges.
This comprehensive guide explores everything you need to know about blocked fallopian tubes, from risk factors to diagnostic procedures and treatment possibilities. Whether you're trying to conceive or concerned about your reproductive health, this information will help you make informed decisions about your care.
Understanding Fallopian Tube Function and Blockage
The fallopian tubes play a critical role in reproduction by providing a meeting place for sperm and egg, and facilitating the transport of a fertilized egg to the uterus. When these tubes become blocked, it can prevent this natural process from occurring, potentially leading to fertility problems or other complications.
Common Causes and Risk Factors
Several factors can contribute to fallopian tube blockage:
- Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID)
- Previous pelvic or abdominal surgery
- Endometriosis
- Sexually transmitted infections
- Ruptured appendix
- Severe pelvic adhesions
- Previous ectopic pregnancy
Understanding these risk factors can help in early detection and prevention of tubal blockages. Women with any of these conditions should discuss potential impacts on their fertility with their healthcare provider.
Recognizing the Signs
Blocked fallopian tubes often don't cause noticeable symptoms, which can make detection challenging. However, some women may experience:
- Chronic pelvic pain
- Irregular menstrual cycles
- Pain during intercourse
- Difficulty becoming pregnant
- Increased risk of ectopic pregnancy
Diagnostic Procedures
Healthcare providers use several methods to diagnose blocked fallopian tubes:
Hysterosalpingogram (HSG)
This X-ray procedure involves injecting contrast dye through the cervix to visualize the fallopian tubes and identify any blockages.
Laparoscopy
A minimally invasive surgical procedure that allows direct visualization of the reproductive organs and can identify blockages, adhesions, or other problems.
Sonohysterography
This ultrasound procedure uses saline solution to help create clearer images of the reproductive tract.
Treatment Approaches
Treatment options vary depending on the location and severity of the blockage:
Surgical Options
- Laparoscopic surgery to remove adhesions
- Tubal cannulation
- Fimbrioplasty
- Salpingostomy
Alternative Treatments
- Fertility medications
- In vitro fertilization (IVF)
- Natural therapeutic approaches
Natural Conception Possibilities
Women with one blocked fallopian tube may still conceive naturally, as long as the other tube is healthy and functional. However, success rates depend on various factors, including overall reproductive health and age.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the common causes and risk factors for blocked fallopian tubes?
The most common causes include pelvic inflammatory disease, endometriosis, previous surgeries, and sexually transmitted infections. Risk factors include a history of pelvic infections, ruptured appendix, or previous ectopic pregnancy.
What symptoms might indicate that my fallopian tubes are blocked?
Most women with blocked fallopian tubes don't experience obvious symptoms. However, some may notice difficulty conceiving, chronic pelvic pain, or irregular menstrual cycles. The primary indication is often the inability to become pregnant after regular unprotected intercourse.
How do doctors diagnose fallopian tube blockages?
Doctors primarily use hysterosalpingogram (HSG), which is an X-ray test using contrast dye, or laparoscopy for diagnosis. Additional tests may include sonohysterography or blood tests to check for underlying infections.
What treatment options are available to unblock fallopian tubes and improve fertility?
Treatment options include surgical procedures like laparoscopic surgery to remove adhesions, tubal cannulation, or fimbrioplasty. If these aren't successful, fertility treatments like IVF may be recommended. The choice of treatment depends on the location and severity of the blockage.
Can natural pregnancy occur if only one fallopian tube is blocked?
Yes, natural pregnancy is possible with one blocked fallopian tube, provided the other tube is healthy and functional. The unaffected tube can still allow for egg pickup from either ovary, though fertility rates may be somewhat reduced compared to having two open tubes.