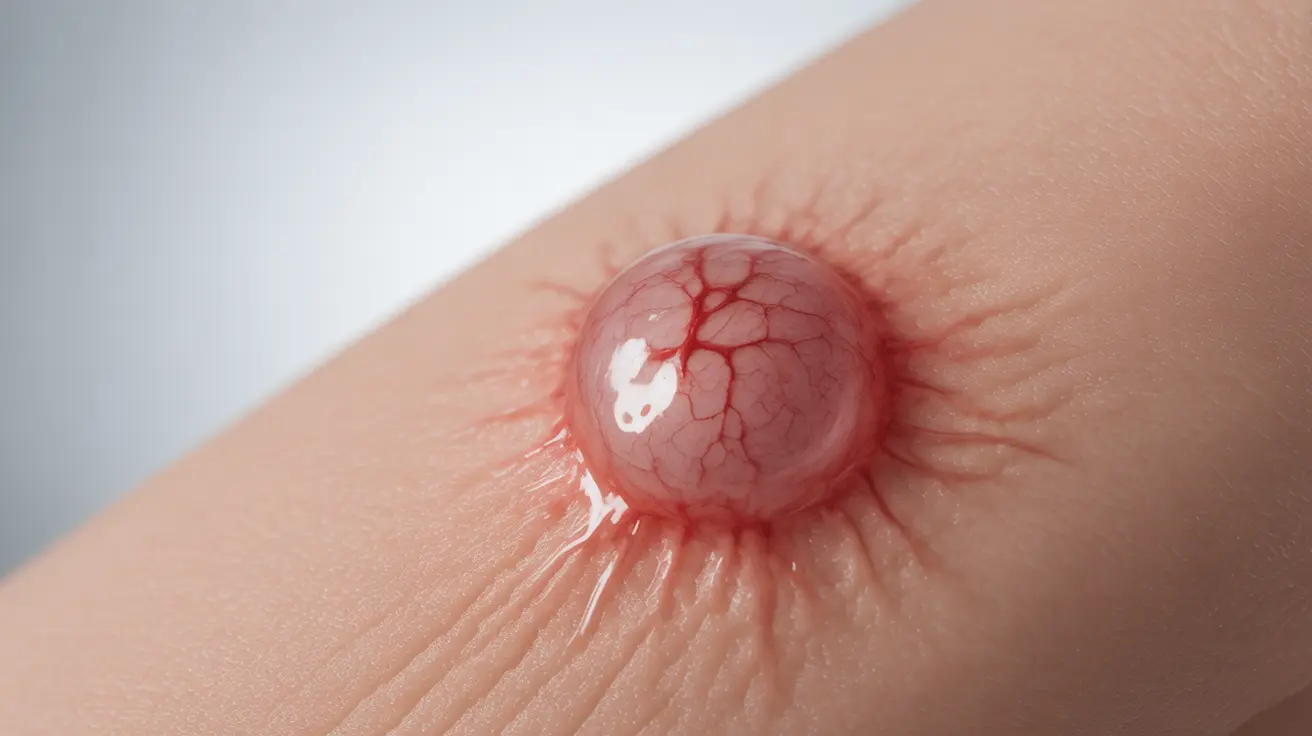
Blood blisters are common skin injuries that occur when blood vessels near the skin's surface are damaged, causing blood to pool beneath a protective layer of skin. While usually harmless, these fluid-filled sacs require proper care to prevent complications and ensure optimal healing.
In this comprehensive guide, we'll explore what causes blood blisters, how to treat them effectively, and when you should seek medical attention. Understanding these aspects will help you manage blood blisters safely and prevent their recurrence.
What Are Blood Blisters?
A blood blister forms when the skin experiences intense pressure or friction, causing small blood vessels to break while the top layer of skin remains intact. Unlike regular blisters that contain clear fluid, blood blisters are filled with blood and appear dark red or purple.
These blisters serve as your body's natural protective mechanism, creating a cushion over the injured area to prevent further damage and allow healing to occur underneath.
Common Causes and Risk Factors
Blood blisters typically develop due to specific types of skin trauma:
- Pinching injuries
- Repeated friction from tight shoes or tools
- Severe pressure on the skin
- Burns or frostbite
- Sports activities
- Manual labor with hand tools
Certain factors can increase your risk of developing blood blisters:
- Ill-fitting footwear
- Using tools without proper protection
- Participating in activities without appropriate protective gear
- Certain medications that thin the blood
Treatment and Care Guidelines
Proper treatment of blood blisters is crucial for preventing infection and promoting healing:
Immediate Care Steps
- Keep the blister clean and dry
- Cover with a loose, sterile bandage
- Avoid puncturing or draining the blister
- Protect from further pressure or friction
Long-term Management
To ensure proper healing and prevent complications:
- Change bandages daily or when they become wet
- Monitor for signs of infection
- Allow the blister to heal naturally
- Use padding or protective covering during activities
Prevention Strategies
Taking preventive measures can significantly reduce your risk of developing blood blisters:
- Wear properly fitting shoes and gloves
- Use protective equipment during sports and manual activities
- Break in new shoes gradually
- Apply moisture-wicking socks during physical activities
- Use protective padding in high-pressure areas
When to Seek Medical Attention
While most blood blisters heal on their own, certain situations require professional medical care:
- Blisters that appear without obvious cause
- Signs of infection (redness, warmth, swelling)
- Recurring blisters in the same location
- Blisters in sensitive areas like the mouth
- Large or particularly painful blisters
Frequently Asked Questions
- What causes blood blisters and how can I prevent them from forming?
Blood blisters are caused by intense pressure or friction that damages blood vessels while leaving the skin intact. Prevention includes wearing properly fitting shoes and protective gear, using appropriate padding, and avoiding prolonged pressure on sensitive areas.
- How should I treat a blood blister to avoid infection and promote healing?
Keep the blister clean, covered with a sterile bandage, and avoid popping it. Change bandages regularly, monitor for signs of infection, and protect the area from further trauma while it heals.
- What is the difference between a blood blister and a regular blister?
Blood blisters contain blood from damaged vessels and appear dark red or purple, while regular blisters contain clear fluid (serum) and are typically transparent. Blood blisters often result from more intense trauma to the skin.
- When should I see a doctor for a blood blister, especially if it is in the mouth or keeps coming back?
Seek medical attention if the blister shows signs of infection, appears without cause, keeps recurring, is located in sensitive areas like the mouth, or is unusually large or painful. Mouth blisters require particular attention due to the risk of complications.
- Can blood blisters be a sign of an underlying health problem or blood disorder?
While most blood blisters are caused by trauma, recurring or unexplained blisters could indicate underlying health issues such as blood disorders, autoimmune conditions, or circulation problems. Consult a healthcare provider if you experience unusual or frequent blood blisters.