Experiencing blood clots after surgery is a serious concern that requires careful attention and preventive measures. While surgical procedures are often necessary for health improvement, they can increase the risk of developing potentially dangerous blood clots. Understanding how to prevent and identify these clots is crucial for a safe recovery period.
This comprehensive guide explores essential information about post-surgical blood clots, including prevention strategies, warning signs, and treatment options. By following proper preventive measures and knowing when to seek medical attention, patients can significantly reduce their risk of developing these potentially life-threatening complications.
Understanding Post-Surgical Blood Clots
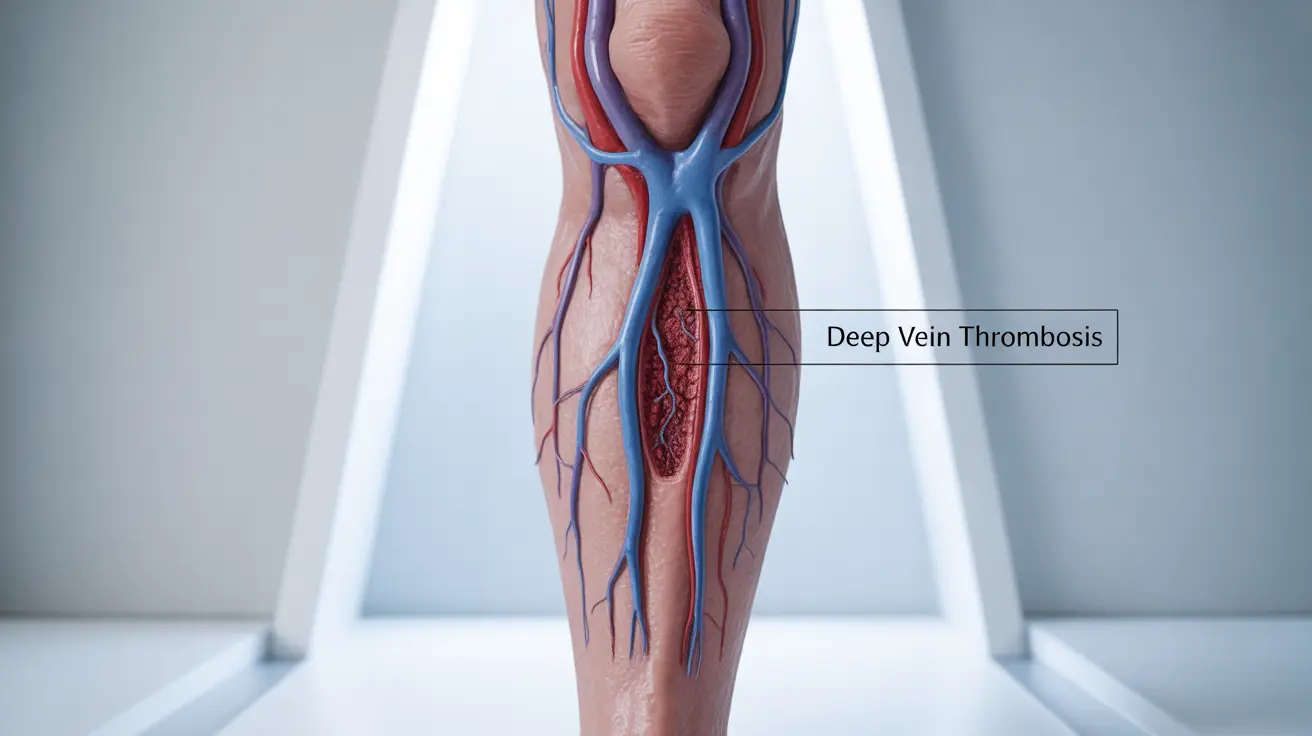
Blood clots that form after surgery, also known as post-operative thrombosis, typically develop in the deep veins of the legs (deep vein thrombosis or DVT). These clots can be dangerous because they may break loose and travel to the lungs, causing a pulmonary embolism. Certain factors, such as prolonged immobility during and after surgery, can increase the risk of clot formation.
Recognizing the Warning Signs
Early detection of blood clots is crucial for preventing serious complications. Common warning signs include:
- Swelling in one leg or arm
- Pain or tenderness in the affected area
- Warm or reddish skin around the affected area
- Unexplained shortness of breath
- Chest pain or discomfort
- Rapid heartbeat
- Coughing up blood
Preventive Measures Before Surgery
Taking proactive steps before surgery can help reduce the risk of blood clots. These measures include:
- Discussing personal and family history of blood clots with your healthcare provider
- Maintaining a healthy weight
- Stopping smoking
- Reviewing current medications that might affect blood clotting
- Following pre-operative instructions carefully
Post-Surgery Prevention Strategies
After surgery, several approaches can help prevent blood clot formation:
- Early mobilization when approved by your healthcare team
- Proper use of compression devices
- Following prescribed medication schedules
- Staying hydrated
- Performing recommended exercises while in bed or seated
Medical Interventions and Devices
Healthcare providers often use various tools and medications to prevent post-surgical blood clots:
- Anticoagulant medications (blood thinners)
- Compression stockings
- Sequential compression devices
- Special foot pumps
- Early mobilization protocols
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the common symptoms of blood clots after surgery that I should watch for?
Common symptoms include swelling in one leg or arm, pain or tenderness, warm or reddish skin in the affected area, and unexplained shortness of breath. If you experience chest pain, rapid heartbeat, or cough up blood, seek immediate medical attention.
How can blood clots be prevented before and after surgery?
Blood clots can be prevented through early mobilization, proper use of prescribed medications, wearing compression stockings, staying hydrated, and following your healthcare provider's specific instructions for activity and medication.
What types of medications and devices are used to reduce the risk of blood clots following surgery?
Healthcare providers typically use anticoagulant medications (blood thinners), compression stockings, sequential compression devices, and mechanical foot pumps. The specific combination depends on your individual risk factors and type of surgery.
How soon after surgery should I start moving to lower my risk of deep vein thrombosis (DVT)?
Most patients should start moving as soon as their healthcare team approves it, typically within 24-48 hours after surgery. However, the exact timing depends on the type of surgery and individual recovery progress.
What are the risks and benefits of taking blood thinners after surgery to prevent clots?
Blood thinners effectively reduce clot formation risk but may increase bleeding risk. Benefits include decreased likelihood of developing dangerous blood clots, while risks include potential bleeding complications. Your healthcare provider will carefully weigh these factors based on your individual situation.
Always follow your healthcare provider's specific instructions regarding post-surgical care and blood clot prevention, as recommendations may vary based on your individual circumstances and type of surgery.