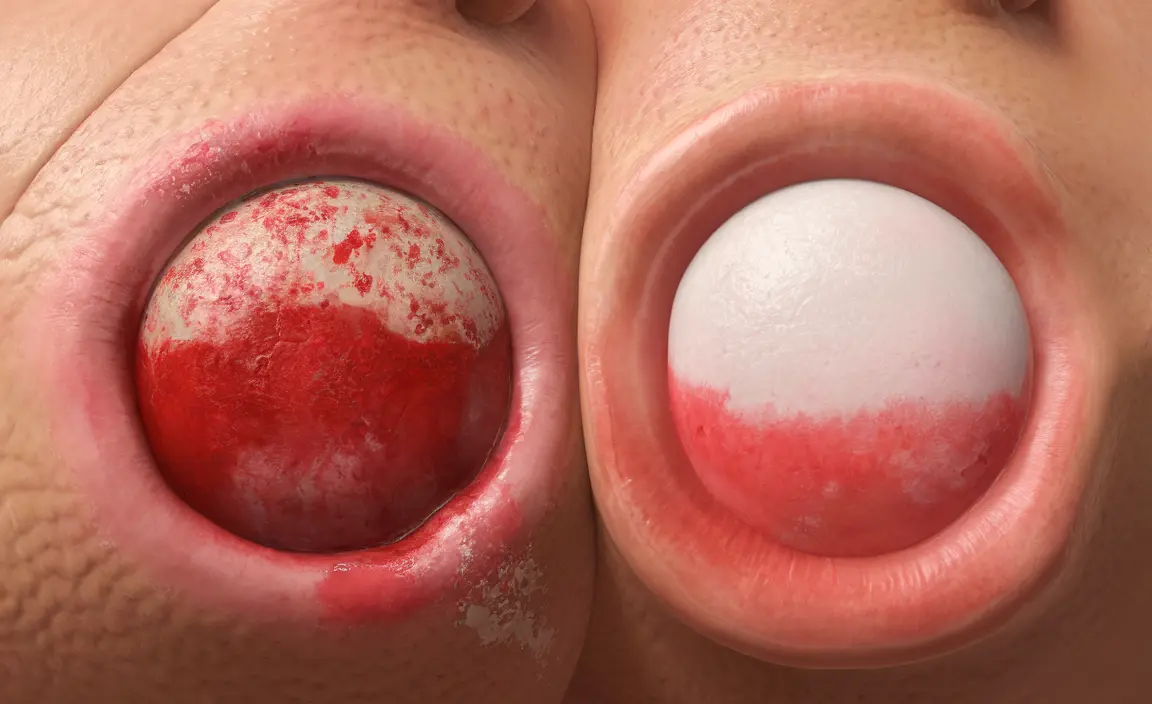
Blood-filled pimples can be a concerning and sometimes painful skin condition that occurs when a regular pimple becomes damaged or traumatized. While most people are familiar with white or yellow pus-filled acne, blood-filled variants require special attention and care to prevent complications like scarring or infection.
Understanding how these distinctive blemishes form and knowing the proper treatment approaches can help you manage them effectively while minimizing the risk of lasting skin damage. Let's explore the essential information about blood-filled pimples and learn the best practices for their care.
What Causes Blood-Filled Pimples?
Blood-filled pimples typically develop when a regular acne lesion experiences trauma or damage. This commonly occurs due to:
- Aggressive picking or squeezing of existing pimples
- Accidental injury to an inflamed area
- Excessive friction from clothing or accessories
- Deep inflammation that ruptures blood vessels
The presence of blood indicates that small blood vessels beneath the skin's surface have been damaged, leading to bleeding within the pimple cavity. This differs from typical acne, where white blood cells and bacteria create pus.
Identifying Blood-Filled Pimples
These distinctive blemishes have several characteristic features that set them apart from regular acne:
- Dark red or purple coloration
- Firm, raised appearance
- Tender or painful to touch
- May appear after attempting to pop a regular pimple
- Often surrounded by inflammation
Safe Treatment Approaches
Proper treatment of blood-filled pimples requires a gentle, patient approach to prevent further complications:
Immediate Care
When you notice a blood-filled pimple, follow these initial steps:
- Clean the area with mild soap and warm water
- Apply a cold compress to reduce swelling
- Avoid touching or attempting to pop the pimple
- Keep the area clean and dry
Topical Treatments
Several over-the-counter options can help manage blood-filled pimples:
- Benzoyl peroxide to fight bacteria
- Salicylic acid to reduce inflammation
- Hydrocolloid patches to protect the area
- Tea tree oil for its antimicrobial properties
Prevention Strategies
To minimize the occurrence of blood-filled pimples:
- Maintain a consistent skincare routine
- Use non-comedogenic products
- Avoid touching your face unnecessarily
- Never pick or squeeze existing pimples
- Change pillowcases regularly
When to Seek Medical Help
Consult a healthcare provider if you experience:
- Severe pain or spreading redness
- Multiple blood-filled pimples
- Signs of infection
- Recurring issues despite proper care
- Development of scarring
Frequently Asked Questions
What causes a pimple to fill with blood instead of pus? Blood-filled pimples occur when blood vessels beneath a pimple become damaged, usually due to trauma from picking, squeezing, or injury to the area. This causes blood to fill the cavity instead of the typical white or yellow pus.
How can I treat a blood-filled pimple at home safely? Apply a warm compress, keep the area clean, use over-the-counter treatments like benzoyl peroxide or salicylic acid, and most importantly, avoid picking or squeezing. Hydrocolloid patches can also help protect the area while it heals.
Are blood-filled pimples more likely to cause infections or scars? Yes, blood-filled pimples have a higher risk of scarring and infection because they indicate damaged blood vessels and deeper trauma to the skin. Proper care and avoiding further irritation is crucial to prevent these complications.
When should I see a doctor for blood-filled pimples or severe acne? Seek medical attention if you experience severe pain, spreading redness, signs of infection, multiple blood-filled pimples, or if the condition persists despite proper home care.
How can I prevent blood-filled pimples from forming after popping or picking? The best prevention is to avoid popping or picking pimples entirely. Maintain good skin hygiene, use appropriate skincare products, and if you must address a pimple, use proper extraction techniques or seek professional help.