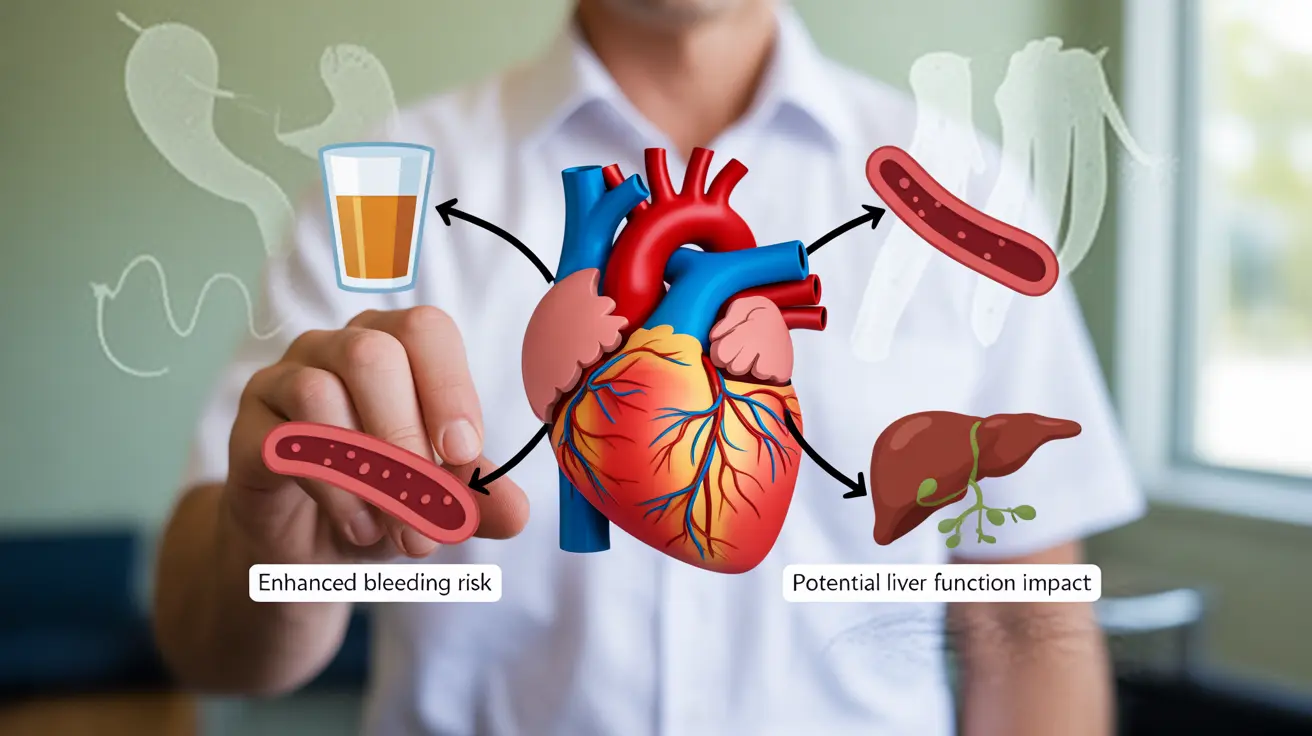
If you're taking blood thinners (anticoagulants), understanding how alcohol affects your medication is crucial for your safety. While moderate alcohol consumption may be acceptable for some patients on blood thinners, the combination requires careful consideration and awareness of potential risks.
This comprehensive guide explores the relationship between blood thinners and alcohol consumption, helping you make informed decisions about your health while taking anticoagulant medications.
Understanding Blood Thinners and Their Interaction with Alcohol
Blood thinners, such as warfarin, apixaban, and rivaroxaban, work by preventing dangerous blood clots from forming. When combined with alcohol, these medications can pose additional risks due to their overlapping effects on blood clotting and liver function.
How Alcohol Affects Blood Thinning Medications
- Enhances the blood-thinning effect
- Affects medication metabolism in the liver
- Increases risk of internal bleeding
- May lead to unpredictable blood thickness levels
Safe Drinking Guidelines While Taking Blood Thinners
For those who choose to drink while taking blood thinners, following strict guidelines is essential:
- Limit alcohol to no more than 1-2 drinks per day (depending on gender and medical advice)
- Never binge drink
- Maintain consistent drinking patterns
- Monitor for signs of abnormal bleeding
- Keep regular appointments for blood tests
Warning Signs and Risk Factors
Signs of Dangerous Bleeding
- Unusual bruising or bruises that grow larger
- Persistent bleeding from minor cuts
- Blood in urine or stool
- Severe headaches or dizziness
- Unexplained pain or swelling
High-Risk Groups
- Those with liver disease
- Patients with a history of bleeding problems
- People taking multiple medications
- Individuals with unstable blood pressure
- Those with stomach ulcers
Managing Your Medication Safely
- Maintain regular communication with your healthcare provider
- Keep consistent vitamin K intake through diet
- Track your alcohol consumption
- Monitor your INR levels as recommended
- Carry medical identification
Frequently Asked Questions
Is it safe to drink alcohol while taking blood thinners, and what amount is considered moderate?
Moderate alcohol consumption may be safe for some people on blood thinners, typically defined as up to one drink daily for women and up to two for men. However, individual recommendations vary based on specific health conditions and medications. Always consult your healthcare provider for personalized guidance.
How does alcohol increase the risk of bleeding when combined with blood thinner medications?
Alcohol enhances the blood-thinning effects of anticoagulant medications by interfering with the liver's ability to metabolize both substances and independently affecting blood clotting factors. This dual impact increases the risk of excessive bleeding.
What are the warning signs of abnormal bleeding to watch for if I drink alcohol while on blood thinners?
Key warning signs include unusual bruising, prolonged bleeding from cuts, blood in urine or stool, severe headaches, unexplained pain or swelling, and dizziness. If you experience any of these symptoms, seek immediate medical attention.
Can alcohol affect how my blood thinner medication works or how it is processed in my body?
Yes, alcohol can significantly impact how blood thinners work. It affects the liver's ability to process the medication, potentially leading to fluctuating blood thickness levels and making it harder to maintain stable therapeutic effects.
Who should avoid alcohol completely when taking blood thinners due to higher health risks?
Individuals with liver disease, bleeding disorders, stomach ulcers, uncontrolled high blood pressure, or those taking multiple medications should avoid alcohol while on blood thinners. Additionally, patients with a history of falls or unstable medical conditions should abstain from alcohol use.