Brain herniation is a life-threatening condition that occurs when brain tissue shifts or is forced into an adjacent compartment within the skull. This displacement can cause severe damage to vital brain structures and requires immediate medical attention. Understanding the signs, causes, and treatment options is crucial for recognizing and responding to this serious medical emergency.
This comprehensive guide will explore the essential aspects of brain herniation, including its warning signs, risk factors, diagnostic approaches, and available treatments. Early recognition and prompt medical intervention are vital for improving outcomes in patients affected by this condition.
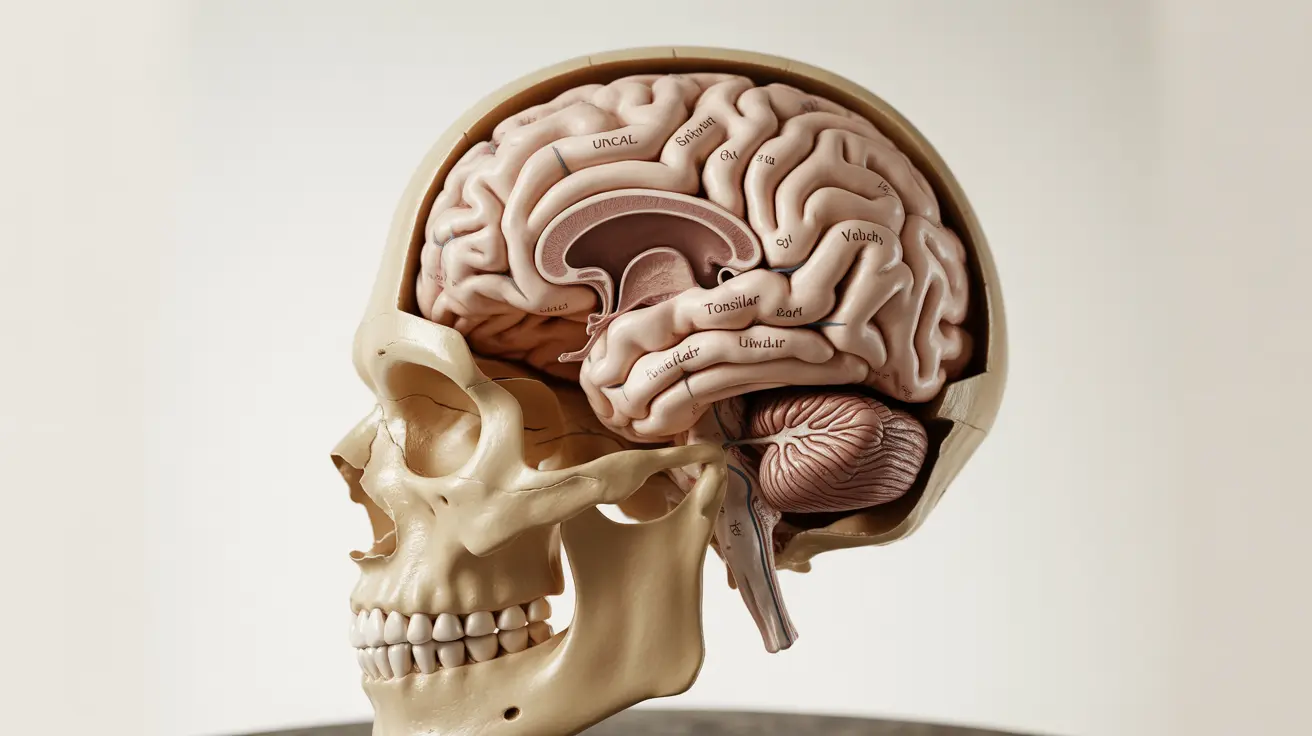
Types of Brain Herniation and Their Characteristics
Brain herniation can occur in several different patterns, each with distinct features and implications:
- Uncal herniation: Occurs when the temporal lobe shifts downward
- Subfalcine herniation: Involves brain tissue moving under the falx cerebri
- Tonsillar herniation: When the cerebellar tonsils descend through the foramen magnum
- Central herniation: Downward displacement of the central brain structures
- Upward herniation: Less common, involving upward movement of brain tissue
Warning Signs and Symptoms
The symptoms of brain herniation often develop rapidly and may include:
- Severe headache that worsens over time
- Altered consciousness or confusion
- Abnormal breathing patterns
- Dilated or unequal pupils
- Weakness or paralysis on one side of the body
- Seizures
- Difficulty with balance and coordination
These symptoms typically progress quickly and require emergency medical evaluation.
Common Causes and Risk Factors
Several conditions can lead to brain herniation:
- Traumatic brain injury
- Brain tumors
- Stroke or bleeding in the brain
- Infections causing brain swelling
- Hydrocephalus
- Severe brain inflammation
Understanding these risk factors is crucial for prevention and early intervention in high-risk patients.
Diagnostic Approach
Healthcare providers use various methods to diagnose brain herniation:
- CT scans of the head
- MRI imaging
- Neurological examinations
- Intracranial pressure monitoring
- Assessment of vital signs and consciousness levels
Quick and accurate diagnosis is essential for implementing life-saving treatments.
Treatment Options and Management
Treatment for brain herniation focuses on reducing intracranial pressure and addressing the underlying cause:
- Emergency medications to reduce brain swelling
- Surgical decompression when necessary
- Mechanical ventilation to support breathing
- Temperature management
- Positioning of the patient to optimize blood flow
- Treatment of underlying conditions
Prevention and Risk Reduction
While not all cases can be prevented, certain measures can help reduce risk:
- Prompt treatment of underlying conditions
- Regular medical follow-up for high-risk patients
- Wearing protective equipment during high-risk activities
- Managing conditions that increase intracranial pressure
- Following medical advice regarding medication and lifestyle modifications
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the common symptoms and warning signs of brain herniation?
The most common signs include severe headache, altered consciousness, abnormal pupil responses, breathing changes, and weakness or paralysis on one side of the body. These symptoms typically develop rapidly and require immediate medical attention.
What causes brain herniation and which conditions increase the risk?
Brain herniation is typically caused by conditions that increase pressure within the skull, such as traumatic brain injuries, tumors, strokes, infections, or severe inflammation. Any condition that causes significant brain swelling can potentially lead to herniation.
How is brain herniation diagnosed and what tests are used?
Diagnosis typically involves emergency imaging studies such as CT scans and MRIs, along with neurological examinations and monitoring of intracranial pressure. Doctors will also assess vital signs and consciousness levels to determine the severity of the condition.
What treatments are available to manage brain herniation and reduce brain pressure?
Treatment options include emergency medications to reduce swelling, surgical decompression, mechanical ventilation, and careful management of the patient's position and temperature. The specific approach depends on the underlying cause and severity of the herniation.
What is the prognosis and potential complications if brain herniation is not treated promptly?
Without prompt treatment, brain herniation can be fatal or lead to severe permanent brain damage. The outcome largely depends on how quickly treatment is initiated and the underlying cause. Immediate medical intervention provides the best chance for survival and recovery.