Bronchial spasms occur when the muscles surrounding your airways suddenly tighten, making breathing difficult and potentially frightening. These episodes can significantly impact your quality of life, but understanding their causes, symptoms, and treatment options is the first step toward better management.
Whether you have a chronic respiratory condition like asthma or experience occasional bronchial spasms due to other triggers, this guide will help you recognize, manage, and prevent these challenging breathing events.
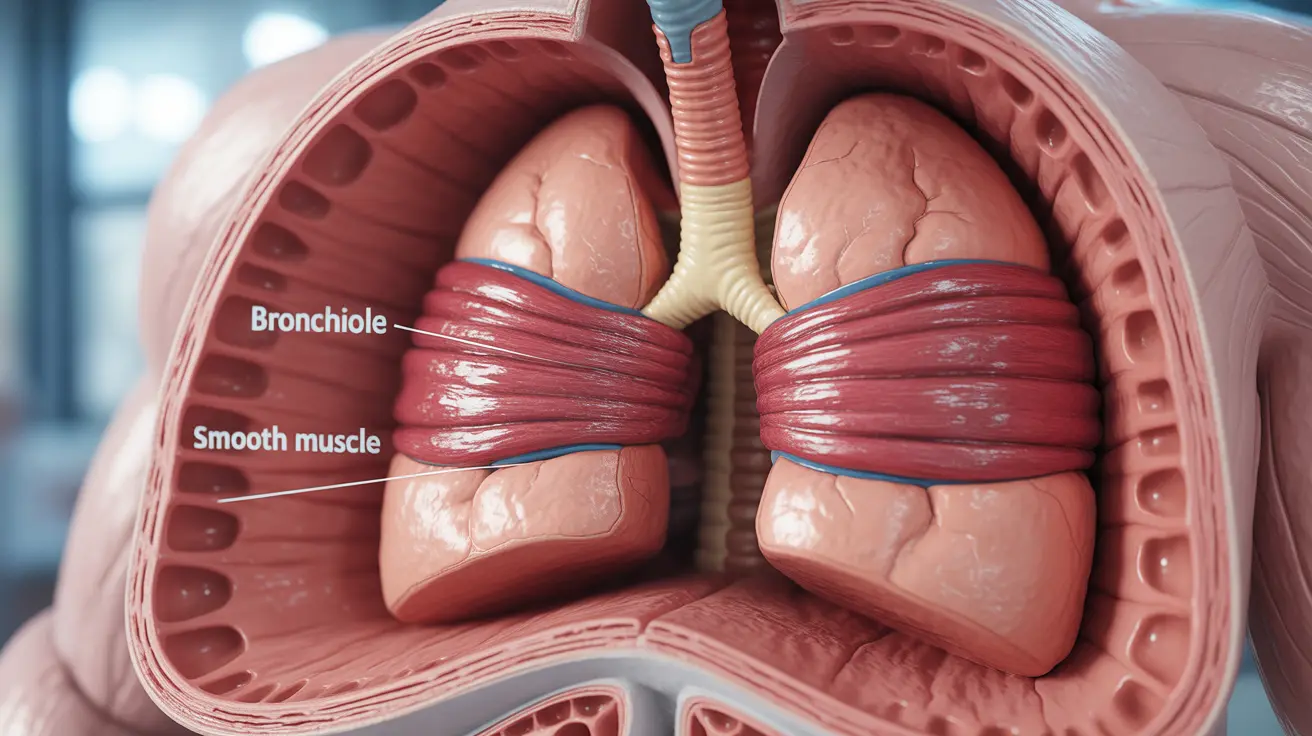
What Are Bronchial Spasms?
Bronchial spasms, also known as bronchospasms, are sudden contractions of the smooth muscles around your airways. These contractions narrow the air passages, making it harder for air to flow freely in and out of your lungs. This restriction can cause varying degrees of breathing difficulty, from mild discomfort to severe respiratory distress.
Common Triggers and Causes
Several factors can trigger bronchial spasms, including:
- Respiratory infections (viral or bacterial)
- Allergens (pollen, dust, pet dander)
- Exercise or physical exertion
- Cold air or sudden temperature changes
- Strong odors or irritants
- Stress or anxiety
- Air pollution
- Certain medications
Recognizing the Symptoms
Identifying bronchial spasms early is crucial for prompt treatment. Common symptoms include:
- Wheezing or whistling sound when breathing
- Chest tightness
- Shortness of breath
- Difficulty breathing
- Persistent coughing
- Chest pain
- Rapid breathing
Diagnosis Process
Healthcare providers use several methods to diagnose bronchial spasms and their underlying causes:
Physical Examination
Your doctor will listen to your breathing and examine your overall respiratory health. They'll also review your medical history and discuss your symptoms in detail.
Diagnostic Tests
Common tests may include:
- Spirometry to measure lung function
- Peak flow measurements
- Chest X-rays
- Bronchial challenge tests
- Blood tests to check for allergies or infections
Treatment Approaches
Treatment for bronchial spasms typically involves both immediate relief and long-term management strategies:
Immediate Relief
- Short-acting bronchodilators (rescue inhalers)
- Nebulizer treatments
- Supplemental oxygen (in severe cases)
Long-term Management
- Long-acting bronchodilators
- Inhaled corticosteroids
- Anti-inflammatory medications
- Leukotriene modifiers
- Regular monitoring and adjustment of medication
Prevention Strategies
Preventing bronchial spasms involves identifying and avoiding triggers while maintaining good respiratory health:
- Regular exercise appropriate for your condition
- Maintaining a clean living environment
- Using air purifiers
- Following your medication schedule
- Managing stress through relaxation techniques
- Getting annual flu shots
- Avoiding known triggers
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the most common causes and triggers of bronchial spasms?
The most common triggers include respiratory infections, allergens, exercise, cold air, and environmental irritants. People with asthma or COPD are particularly susceptible to these triggers.
What symptoms should make me suspect I am having a bronchial spasm?
Key symptoms include wheezing, chest tightness, difficulty breathing, shortness of breath, and a persistent cough. If you experience these symptoms, especially if they come on suddenly, you may be having a bronchial spasm.
How is a bronchial spasm diagnosed by doctors?
Doctors diagnose bronchial spasms through physical examination, listening to your breathing, reviewing your medical history, and conducting tests like spirometry and peak flow measurements. They may also order chest X-rays or allergy tests to determine underlying causes.
What treatments are available to relieve and prevent bronchial spasms?
Treatment options include short-acting bronchodilators for immediate relief, long-acting bronchodilators for prevention, inhaled corticosteroids, and other anti-inflammatory medications. The specific treatment plan depends on the frequency and severity of your symptoms.
How can I prevent bronchial spasms, especially if I have asthma or COPD?
Prevention strategies include taking prescribed medications as directed, avoiding known triggers, maintaining good indoor air quality, getting regular exercise, and working closely with your healthcare provider to develop an effective management plan. Regular monitoring and prompt treatment of respiratory infections are also important.