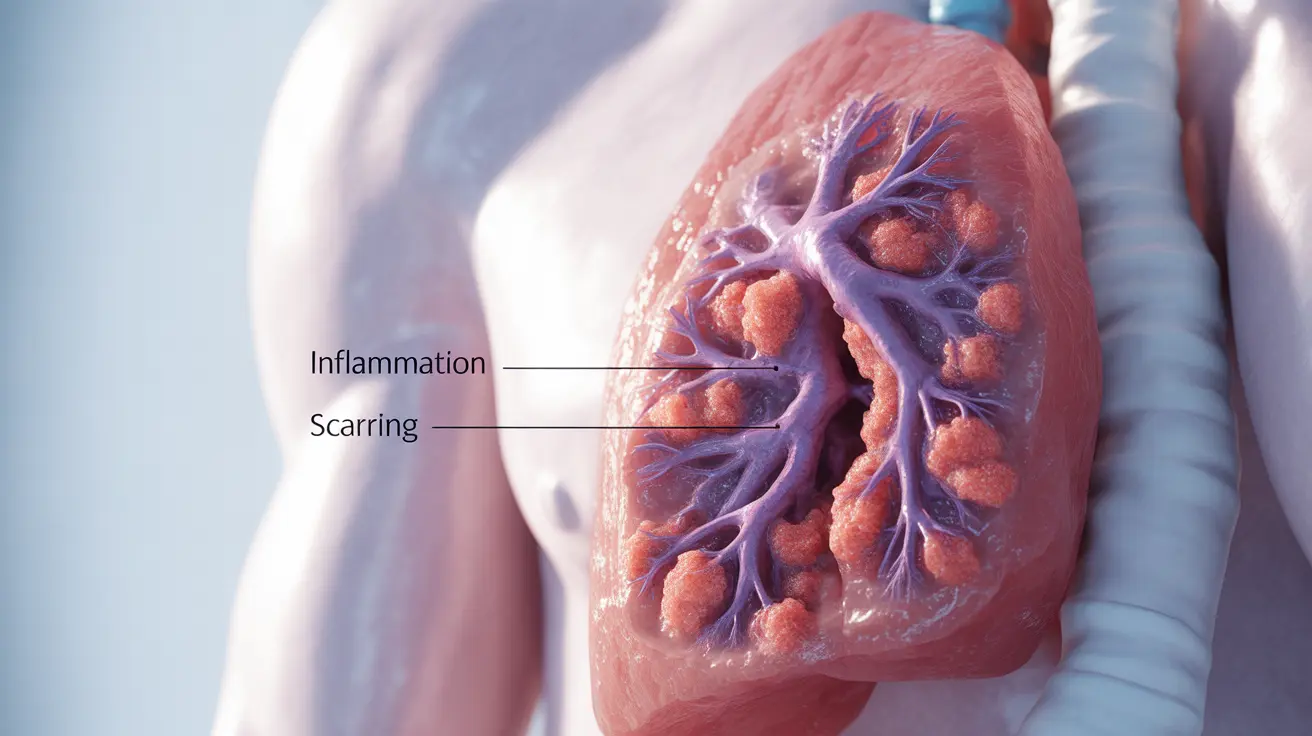
Bronchiolitis in adults is a serious respiratory condition that affects the bronchioles, the smallest airways in the lungs. While commonly associated with infants and young children, this condition can also develop in adults, often presenting as bronchiolitis obliterans, a more severe form that can cause permanent lung damage if left untreated.
Understanding this condition is crucial for early detection and proper management, as adult bronchiolitis can significantly impact quality of life and respiratory function. This comprehensive guide explores the key aspects of bronchiolitis in adults, including its symptoms, causes, diagnosis, and treatment options.
Understanding Adult Bronchiolitis
Adult bronchiolitis differs from the more common childhood version, typically presenting as bronchiolitis obliterans, also known as constrictive bronchiolitis. This condition involves inflammation and scarring of the small airways, leading to permanent narrowing and potential respiratory complications.
Common Symptoms and Progression
The symptoms of bronchiolitis in adults typically develop gradually and may include:
- Persistent dry cough
- Shortness of breath, especially during physical activity
- Wheezing
- Fatigue
- Chest discomfort or tightness
- Difficulty breathing that worsens over time
These symptoms often progress slowly, making early recognition challenging. Many patients initially mistake their symptoms for other respiratory conditions, potentially delaying crucial treatment.
Causes and Risk Factors
Several factors can contribute to the development of bronchiolitis in adults:
- Exposure to toxic chemicals or fumes
- Viral or bacterial infections
- Autoimmune conditions
- Organ transplant complications
- Certain medications
- Occupational exposures
Understanding these risk factors is essential for prevention and early intervention, particularly for individuals working in high-risk environments.
Diagnostic Process
Diagnosing bronchiolitis in adults typically involves multiple approaches:
- Pulmonary function tests
- High-resolution CT scans
- Chest X-rays
- Bronchoscopy
- Surgical lung biopsy in some cases
Early diagnosis is crucial for implementing effective treatment strategies and preventing further lung damage.
Treatment Approaches
Treatment for adult bronchiolitis focuses on managing symptoms and preventing disease progression. Common treatment options include:
- Corticosteroids to reduce inflammation
- Bronchodilators for breathing improvement
- Immunosuppressive medications in certain cases
- Oxygen therapy when necessary
- Pulmonary rehabilitation programs
The specific treatment plan depends on the underlying cause and severity of the condition.
Prevention Strategies
Preventing bronchiolitis in adults involves several key measures:
- Using appropriate protective equipment in hazardous work environments
- Avoiding exposure to toxic chemicals and fumes
- Regular medical check-ups for high-risk individuals
- Maintaining good respiratory hygiene
- Quitting smoking and avoiding secondhand smoke
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the common symptoms of bronchiolitis in adults and how do they develop over time? Common symptoms include persistent dry cough, progressive shortness of breath, wheezing, and fatigue. These symptoms typically develop gradually over weeks or months, often becoming more severe with physical activity.
What causes bronchiolitis obliterans in adults and which exposures or conditions increase the risk? Bronchiolitis obliterans can be caused by exposure to toxic chemicals, viral infections, autoimmune conditions, and organ transplant complications. High-risk exposures include industrial chemicals, diacetyl (found in some flavorings), and certain medication reactions.
How is bronchiolitis in adults diagnosed and what tests are typically used? Diagnosis involves a combination of pulmonary function tests, high-resolution CT scans, chest X-rays, and sometimes bronchoscopy or surgical lung biopsy. Doctors will also review the patient's medical history and exposure history.
What treatment options are available for managing bronchiolitis obliterans in adults? Treatment options include corticosteroids, bronchodilators, immunosuppressive medications, oxygen therapy, and pulmonary rehabilitation. The treatment plan is tailored to each patient's specific condition and needs.
How can exposure to harmful chemicals be prevented to reduce the risk of developing bronchiolitis in adults? Prevention involves using appropriate personal protective equipment, ensuring proper ventilation in work environments, following safety protocols when handling chemicals, and regular workplace safety assessments. Regular medical monitoring for high-risk individuals is also important.