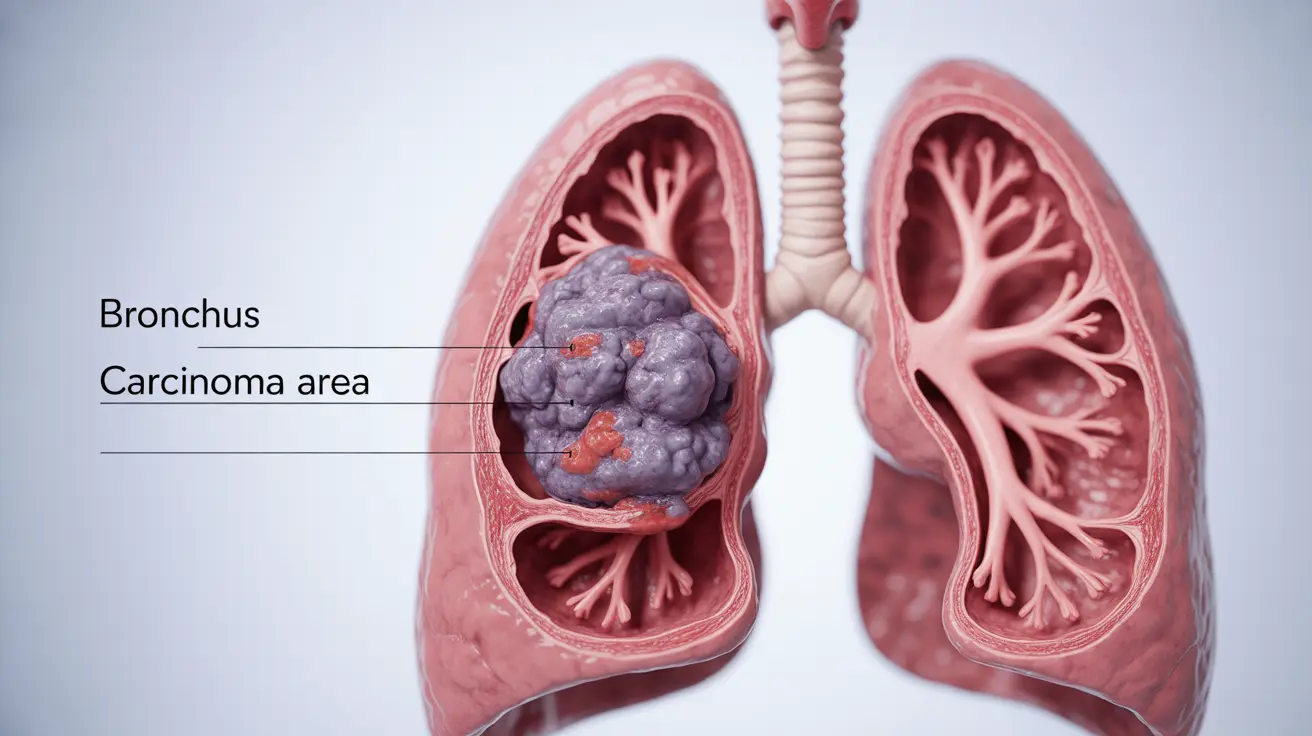
Bronchogenic carcinoma, a serious form of lung cancer that originates in the bronchi or airways of the lungs, requires early detection and proper medical intervention for the best possible outcomes. This comprehensive guide explores the essential aspects of bronchogenic carcinoma, from recognizing early warning signs to understanding treatment approaches.
Early Warning Signs and Symptoms
Recognizing the symptoms of bronchogenic carcinoma early can significantly impact treatment success. Common early indicators include:
- Persistent cough that worsens over time
- Chest pain or discomfort
- Unexplained weight loss
- Shortness of breath
- Hoarseness or changes in voice
- Coughing up blood (hemoptysis)
It's crucial to note that these symptoms may initially be subtle and can be mistaken for less serious conditions. However, when these signs persist for more than a few weeks, medical evaluation becomes essential.
Diagnostic Process and Staging
Diagnosing bronchogenic carcinoma involves several sophisticated medical procedures and imaging techniques:
Initial Assessment
- Chest X-rays
- CT scans
- PET scans
- Bronchoscopy
Staging Procedures
Once diagnosed, healthcare providers determine the cancer's stage through additional tests, which may include:
- Mediastinoscopy
- Bone scans
- Brain MRI
- Comprehensive blood work
Treatment Approaches
Small Cell Bronchogenic Carcinoma
Treatment for small cell type typically involves:
- Chemotherapy as the primary treatment
- Radiation therapy, often combined with chemotherapy
- Limited surgical options in specific cases
Non-Small Cell Bronchogenic Carcinoma
Treatment options may include:
- Surgery (when caught early)
- Targeted therapy
- Immunotherapy
- Combination approaches based on stage and overall health
Risk Factors and Prevention
Understanding risk factors is crucial for prevention and early detection:
- Smoking (primary risk factor)
- Exposure to secondhand smoke
- Occupational exposure to carcinogens
- Family history of lung cancer
- Environmental pollutants
Early Detection and Prognosis
Early detection significantly improves treatment outcomes. Regular screening may be recommended for high-risk individuals, particularly those with:
- Long-term smoking history
- Occupational exposure to lung carcinogens
- Family history of lung cancer
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the common symptoms of bronchogenic carcinoma to watch for early on?
Early symptoms include persistent cough, chest pain, unexplained weight loss, shortness of breath, and coughing up blood. Any unusual respiratory symptoms lasting more than a few weeks should be evaluated by a healthcare provider.
How is bronchogenic carcinoma diagnosed and staged?
Diagnosis involves imaging tests (X-rays, CT scans, PET scans), bronchoscopy, and tissue biopsies. Staging requires additional tests like mediastinoscopy, bone scans, and brain MRI to determine the extent of cancer spread.
What are the main treatment options for small cell and non-small cell bronchogenic carcinoma?
Small cell type typically requires chemotherapy and radiation therapy, while non-small cell type may be treated with surgery, targeted therapy, immunotherapy, or combinations depending on the stage and individual factors.
What are the primary risk factors that increase the chance of developing bronchogenic carcinoma?
The main risk factors include smoking, exposure to secondhand smoke, occupational exposure to carcinogens, family history of lung cancer, and environmental pollutants.
How can early detection of bronchogenic carcinoma improve prognosis and treatment outcomes?
Early detection allows for more treatment options, including potentially curative surgery for non-small cell types. It also typically results in better survival rates and quality of life outcomes compared to detection at later stages.