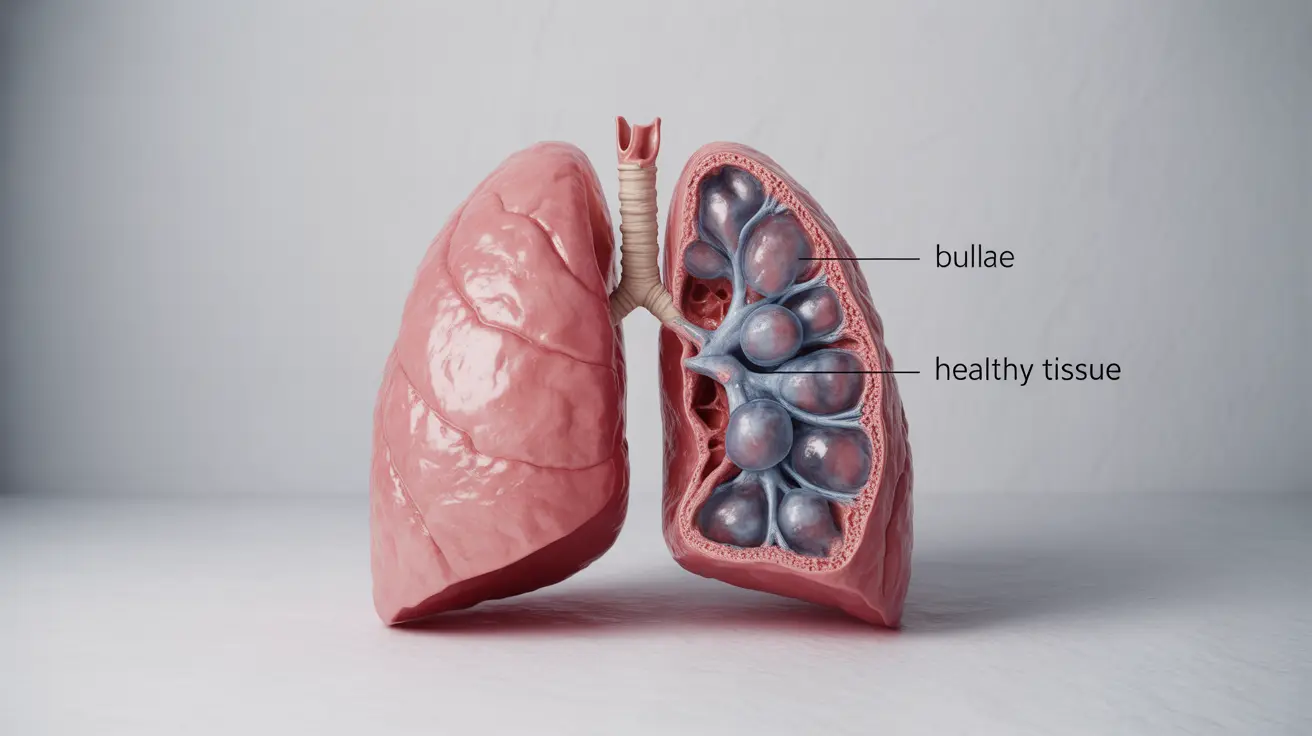
Bullous emphysema is a serious respiratory condition characterized by the formation of large air-filled sacs, or bullae, in the lungs. These bullae can significantly impact breathing capacity and overall lung function. Understanding this condition is crucial for those affected and their caregivers, as early recognition and proper management can help improve outcomes and quality of life.
This comprehensive guide explores the key aspects of bullous emphysema, including its symptoms, diagnostic approaches, treatment options, and essential lifestyle modifications that can help manage the condition effectively.
Understanding Bullous Emphysema
Bullous emphysema occurs when air spaces in the lungs become abnormally enlarged, forming bubble-like sacs that can compress surrounding healthy lung tissue. These bullae can vary in size and number, and they typically develop as a result of long-term damage to the lung tissue.
Common Signs and Symptoms
Recognition of symptoms is crucial for early diagnosis and treatment of bullous emphysema. Common indicators include:
- Progressive shortness of breath
- Chronic cough
- Chest tightness or discomfort
- Reduced exercise tolerance
- Fatigue
- Wheezing
- Frequent respiratory infections
Diagnostic Process and Testing
Healthcare providers use various diagnostic tools to confirm bullous emphysema and assess its severity:
Imaging Studies
Chest X-rays and CT scans are essential for visualizing bullae and evaluating their size, location, and impact on surrounding lung tissue. These imaging techniques help doctors plan the most appropriate treatment approach.
Pulmonary Function Tests
These tests measure lung capacity, airflow, and oxygen exchange efficiency, providing crucial information about the extent of lung damage and functional impairment.
Treatment Approaches
Conservative Management
Initial treatment often focuses on managing symptoms and preventing further lung damage through:
- Bronchodilators to improve breathing
- Anti-inflammatory medications
- Pulmonary rehabilitation programs
- Oxygen therapy when needed
Surgical Options
In severe cases, surgical intervention may be necessary. The main surgical approaches include:
- Bullectomy (removal of bullae)
- Lung volume reduction surgery
- Lung transplantation in extreme cases
Lifestyle Modifications and Prevention
Several lifestyle changes can help manage bullous emphysema and prevent complications:
- Immediate smoking cessation
- Regular exercise within personal limitations
- Maintaining proper nutrition
- Avoiding air pollution and irritants
- Following vaccination schedules
- Practicing good respiratory hygiene
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the common symptoms and signs of bullous emphysema to watch for?
Common symptoms include progressive shortness of breath, chronic cough, chest tightness, reduced exercise tolerance, and frequent respiratory infections. These symptoms typically develop gradually and may worsen over time.
How is bullous emphysema diagnosed and what tests are involved?
Diagnosis involves chest X-rays, CT scans, and pulmonary function tests. These diagnostic tools help visualize the bullae, assess lung function, and determine the extent of the condition.
What treatment options are available for bullous emphysema, including medications and surgery?
Treatment options range from conservative approaches like bronchodilators and pulmonary rehabilitation to surgical interventions such as bullectomy or lung volume reduction surgery in severe cases. The choice of treatment depends on the severity of the condition and individual patient factors.
How does smoking cause bullous emphysema and can quitting smoking improve the condition?
Smoking damages lung tissue and accelerates the formation of bullae. While quitting smoking cannot reverse existing damage, it can significantly slow disease progression and improve overall lung function and quality of life.
What lifestyle changes and preventive measures can help manage bullous emphysema and reduce complications?
Key lifestyle modifications include smoking cessation, regular exercise within limitations, maintaining good nutrition, avoiding air pollutants, getting recommended vaccinations, and following proper respiratory hygiene practices.