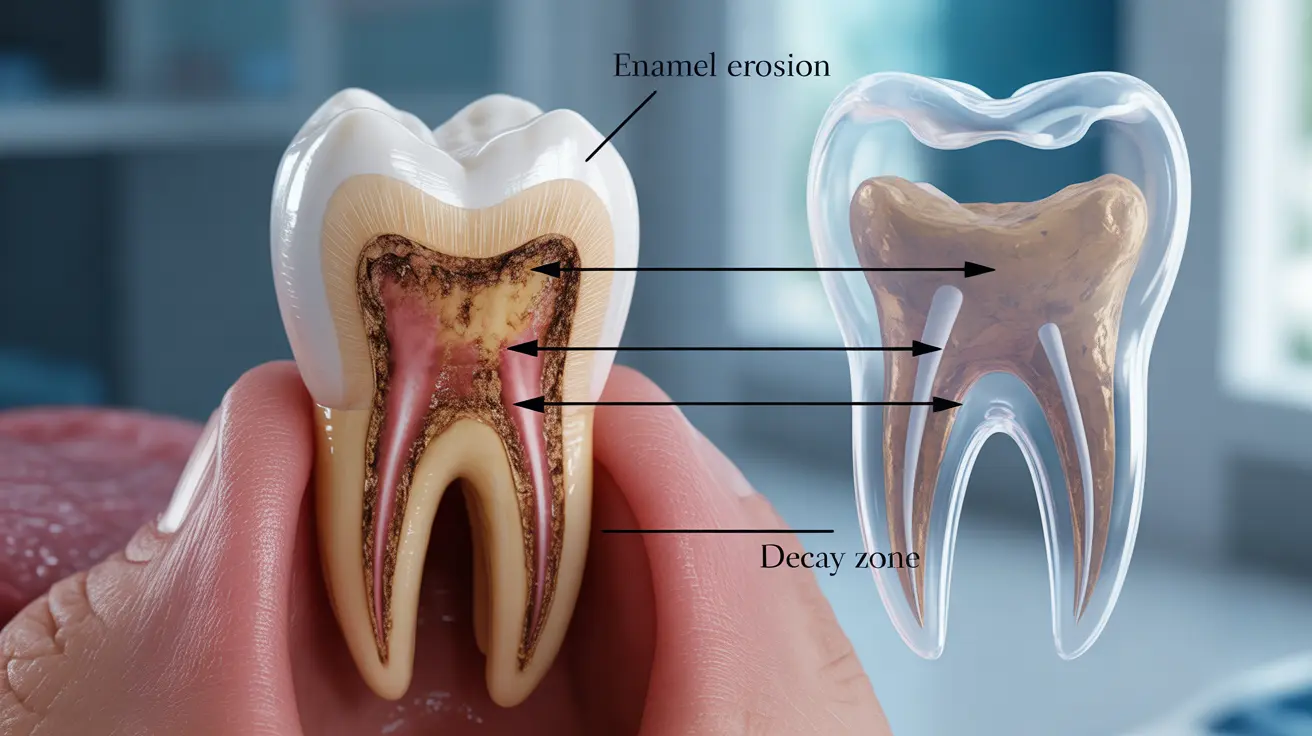
Calcium deficiency can significantly affect your dental health, potentially leading to serious oral health complications if left unaddressed. As one of the most crucial minerals for maintaining strong teeth and bones, inadequate calcium levels can compromise your dental structure and increase vulnerability to various oral health issues.
Understanding how calcium deficiency affects your teeth and knowing the warning signs can help you take proactive steps to protect your dental health. Let's explore the relationship between calcium levels and oral health, along with effective prevention and treatment strategies.
Signs and Symptoms of Calcium Deficiency in Teeth
When calcium levels are insufficient, several distinctive signs may appear in your dental health:
- Delayed tooth development in children
- Weakening of tooth enamel
- Increased sensitivity to hot and cold
- Brittle or easily chipped teeth
- Softening of teeth structure
- Increased vulnerability to decay
These symptoms often develop gradually, making it crucial to maintain regular dental check-ups for early detection and intervention.
The Connection Between Calcium and Tooth Decay
Calcium plays a vital role in maintaining tooth strength and integrity. When calcium levels are low, your teeth become more susceptible to decay through several mechanisms:
- Weakened enamel structure
- Reduced mineral density in teeth
- Compromised ability to remineralize tooth surfaces
- Increased acid vulnerability
The relationship between calcium deficiency and tooth decay is particularly concerning because the damage can be permanent if not addressed early.
Prevention and Dietary Solutions
Maintaining adequate calcium intake through diet is essential for protecting your dental health. Key dietary sources include:
- Dairy products (milk, yogurt, cheese)
- Leafy green vegetables (kale, spinach)
- Fortified plant-based milk alternatives
- Sardines and other calcium-rich fish
- Tofu made with calcium sulfate
- Almonds and other nuts
Aim for the recommended daily calcium intake, which varies by age and gender, typically ranging from 1,000 to 1,300 mg per day for adults.
Professional Diagnosis and Treatment
Healthcare professionals use several methods to diagnose calcium deficiency affecting teeth:
- Dental examinations
- Blood calcium level tests
- Bone density scans
- Medical history evaluation
- Assessment of dietary habits
Treatment typically involves a comprehensive approach combining dietary changes, supplements when necessary, and specific dental interventions to address existing damage.
The Role of Vitamin D
Vitamin D is essential for optimal calcium absorption and utilization. Without adequate vitamin D levels, even sufficient calcium intake may not effectively protect your teeth. Consider these sources of vitamin D:
- Sunlight exposure
- Fatty fish
- Egg yolks
- Fortified foods
- Supplements (when recommended by a healthcare provider)
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the common signs and symptoms of calcium deficiency that affect teeth? Common signs include weakened enamel, increased tooth sensitivity, delayed tooth development in children, and greater susceptibility to decay and chips.
How does calcium deficiency increase the risk of tooth decay and tooth loss? Calcium deficiency weakens tooth structure, reduces mineral density, and compromises the tooth's ability to resist acid attacks, making decay more likely. Over time, this can lead to tooth loss if untreated.
What foods or supplements can help prevent calcium deficiency to protect teeth? Dairy products, leafy greens, fortified plant-based milk, calcium-rich fish, and nuts are excellent dietary sources. Supplements may be recommended by healthcare providers when dietary intake is insufficient.
How is calcium deficiency in teeth diagnosed and treated by healthcare professionals? Professionals use dental examinations, blood tests, and medical history evaluation for diagnosis. Treatment typically involves dietary modifications, possible supplementation, and specific dental treatments as needed.
Can vitamin D improve calcium absorption and support dental health? Yes, vitamin D is crucial for calcium absorption and utilization in the body. Adequate vitamin D levels through sunlight exposure, diet, or supplements help ensure optimal calcium absorption for dental health.