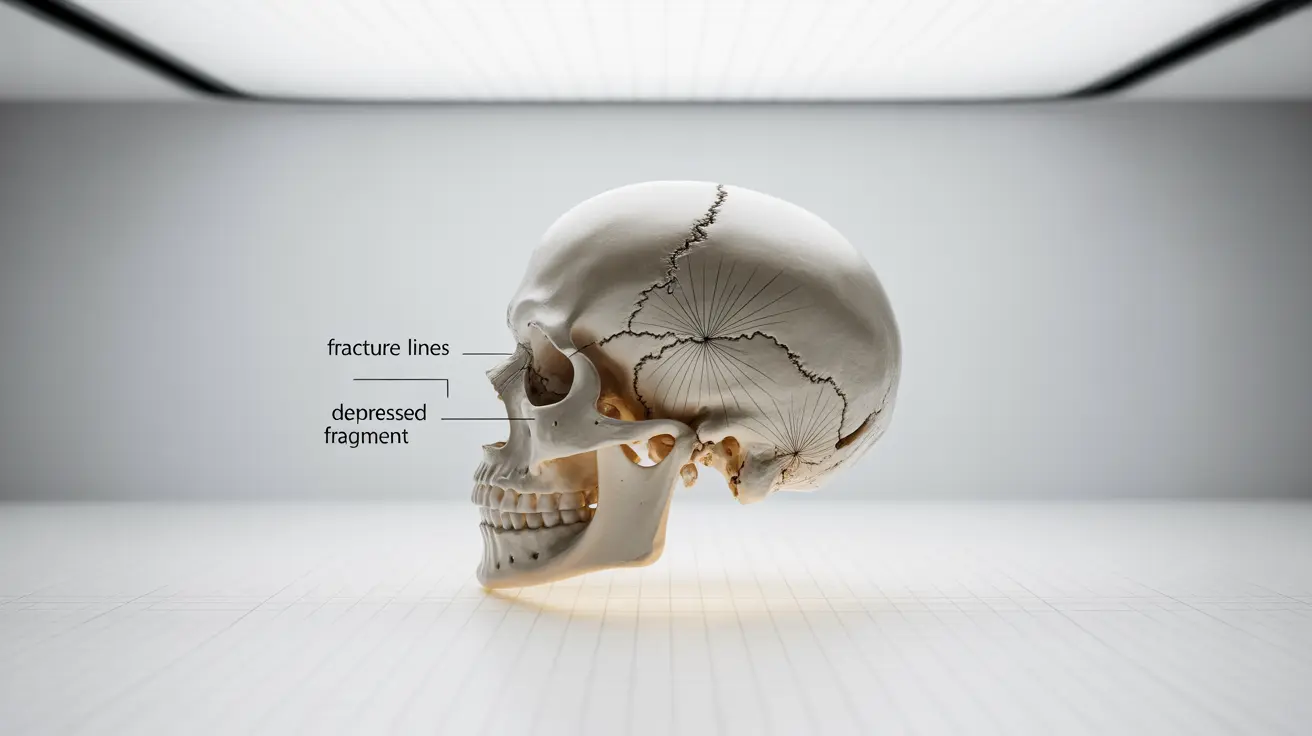
A calvarial fracture is a serious injury involving a break in the skull's upper portion, which protects the brain. These fractures require immediate medical attention and can range from simple, linear breaks to more complex patterns that may need surgical intervention. Understanding the signs, diagnosis process, and treatment options is crucial for both medical professionals and those affected by this condition.
This comprehensive guide explores the essential aspects of calvarial fractures, including recognition of symptoms, diagnostic procedures, treatment approaches, and potential complications. Whether you're a healthcare provider or seeking information about this condition, this article provides valuable insights into managing these critical injuries.
Understanding Calvarial Fractures
Calvarial fractures occur in the dome-shaped portion of the skull that houses and protects the brain. These injuries typically result from significant trauma, such as car accidents, falls from height, or severe sports injuries. The nature and severity of the fracture can vary considerably, from hairline cracks to complex, depressed fractures that may affect brain tissue.
Recognizing the Signs and Symptoms
Identifying a calvarial fracture early is crucial for proper treatment and preventing complications. Common indicators include:
- Visible deformity or depression in the skull
- Severe head pain or headache
- Bruising around the eyes or behind the ears
- Clear fluid leaking from the nose or ears
- Nausea and vomiting
- Changes in consciousness or confusion
- Seizures
Diagnostic Procedures and Imaging
Medical professionals use various imaging techniques to confirm and assess calvarial fractures. The primary diagnostic tools include:
- CT (Computed Tomography) scans
- X-rays of the skull
- MRI in certain cases to evaluate soft tissue damage
These imaging studies help determine the fracture's location, pattern, and severity, which guides treatment decisions.
Treatment Approaches
Conservative Management
Not all calvarial fractures require surgery. Simple, non-displaced fractures may heal with conservative treatment, including:
- Close monitoring
- Pain management
- Rest and activity modification
- Regular follow-up imaging
- Prevention of further injury
Surgical Intervention
Surgery becomes necessary when the fracture:
- Is significantly displaced
- Creates pressure on the brain
- Causes cosmetic deformity
- Results in cerebrospinal fluid leakage
- Involves multiple bone fragments
Preventing Complications
Careful monitoring and appropriate treatment are essential to prevent potential complications such as:
- Infection
- Brain tissue damage
- Cerebrospinal fluid leaks
- Post-traumatic seizures
- Chronic headaches
Recovery and Rehabilitation
Recovery from a calvarial fracture varies depending on severity but typically involves:
- Regular medical follow-up
- Gradual return to activities
- Physical therapy when needed
- Cognitive rehabilitation if brain injury occurred
- Prevention strategies to avoid future injury
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the common symptoms that indicate a possible calvarial fracture after head trauma? Common symptoms include severe headache, visible skull deformation, bruising around the eyes or behind the ears, clear fluid leakage from nose or ears, confusion, and sometimes loss of consciousness.
How is a calvarial fracture diagnosed and what imaging tests are typically used? Diagnosis primarily relies on CT scans, which provide detailed images of the skull and brain. X-rays may be used for initial screening, and MRI might be needed to assess soft tissue damage.
When is surgery required to treat a calvarial fracture compared to conservative management? Surgery is necessary for displaced fractures, those causing brain pressure, significant cosmetic deformity, CSF leakage, or when multiple bone fragments are present. Simple, non-displaced fractures often heal with conservative management.
What complications can arise from a calvarial fracture and how can they be prevented? Potential complications include infection, brain tissue damage, CSF leaks, seizures, and chronic headaches. Prevention involves proper initial treatment, careful monitoring, and following medical advice regarding activity restrictions.
What are the immediate steps to take if a calvarial fracture is suspected? Seek emergency medical care immediately, avoid moving the person unless absolutely necessary, and stabilize the head and neck. Do not apply direct pressure to a visible skull depression, and wait for professional medical evaluation.