After completing initial treatment for thyroid cancer, many patients wonder about the possibility of the cancer returning. Understanding the risk factors, warning signs, and monitoring procedures for thyroid cancer recurrence is crucial for maintaining long-term health and peace of mind.
While thyroid cancer generally has a favorable prognosis, some patients may experience recurrence months or years after their initial treatment. Being informed about the possibility of recurrence empowers patients to stay vigilant with their follow-up care and recognize potential warning signs early.
Understanding Thyroid Cancer Recurrence Rates
The likelihood of thyroid cancer returning varies significantly based on several factors, including the initial cancer type and stage. Papillary thyroid cancer, the most common type, has a relatively low recurrence rate when caught and treated early. However, some patients may experience recurrence within the first five years after treatment.
Statistics show that approximately 15-30% of patients may experience thyroid cancer recurrence, though this rate varies based on individual risk factors and the effectiveness of initial treatment.
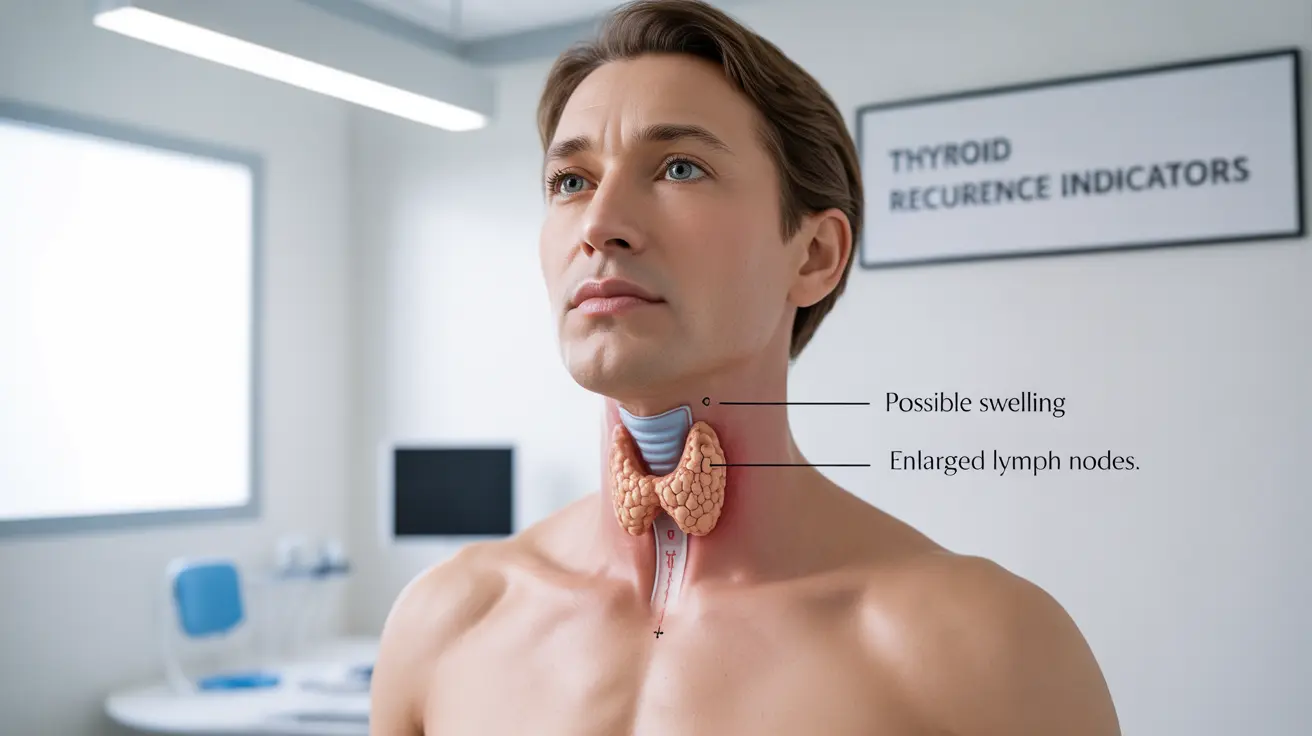
Warning Signs of Recurring Thyroid Cancer
Recognizing potential signs of recurrence is essential for early detection and intervention. Common symptoms may include:
- Neck swelling or new lumps
- Difficulty swallowing or breathing
- Hoarseness or voice changes
- Persistent neck pain
- Swollen lymph nodes
These symptoms don't necessarily indicate recurrence but should be promptly evaluated by a healthcare provider.
Risk Factors for Recurrence
Several factors can influence the likelihood of thyroid cancer returning:
- Initial tumor size and stage
- Type of thyroid cancer
- Presence of genetic mutations
- Incomplete initial treatment
- Age at diagnosis
- Gender
- Family history
Monitoring and Detection Methods
Healthcare providers use various tools and tests to monitor for potential recurrence:
Regular Blood Tests
Thyroglobulin levels are regularly monitored, as this protein can indicate the presence of thyroid tissue or cancer cells.
Imaging Studies
Periodic neck ultrasounds, radioiodine scans, and other imaging techniques help detect potential recurrence early.
Physical Examinations
Regular neck examinations by healthcare providers can identify concerning changes or new growths.
Treatment Approaches for Recurrent Thyroid Cancer
When thyroid cancer returns, treatment options may include:
- Additional surgery
- Radioactive iodine therapy
- Targeted drug therapy
- External beam radiation
- Clinical trials for advanced cases
Frequently Asked Questions
How likely is thyroid cancer to come back after initial treatment? The recurrence rate varies between 15-30%, depending on factors such as cancer type, stage, and initial treatment effectiveness.
What are the common signs and symptoms that thyroid cancer has recurred? Common signs include neck swelling, difficulty swallowing, voice changes, persistent neck pain, and swollen lymph nodes.
Which factors increase the risk of thyroid cancer recurrence? Risk factors include initial tumor size and stage, cancer type, genetic mutations, incomplete initial treatment, age at diagnosis, and family history.
How is recurrent thyroid cancer detected and monitored during follow-up? Detection methods include regular blood tests (particularly thyroglobulin levels), imaging studies like ultrasounds and radioiodine scans, and physical examinations.
What types of thyroid cancer have the highest chances of coming back? Aggressive variants such as tall cell papillary thyroid cancer, poorly differentiated thyroid cancer, and anaplastic thyroid cancer typically have higher recurrence rates compared to well-differentiated papillary thyroid cancer.