While mastitis is commonly associated with breastfeeding, it can also occur during pregnancy. This inflammatory condition of the breast tissue requires prompt attention and proper medical care to ensure both maternal and fetal health. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options specific to pregnancy is crucial for expectant mothers.
This comprehensive guide will explore everything you need to know about mastitis during pregnancy, including risk factors, prevention strategies, and safe treatment approaches.
Understanding Mastitis in Pregnancy
Mastitis during pregnancy, though less common than postpartum mastitis, can develop when bacteria enter the breast tissue through small cuts or cracks. The condition causes inflammation and infection, leading to various uncomfortable symptoms that require medical attention.
Signs and Symptoms to Watch For
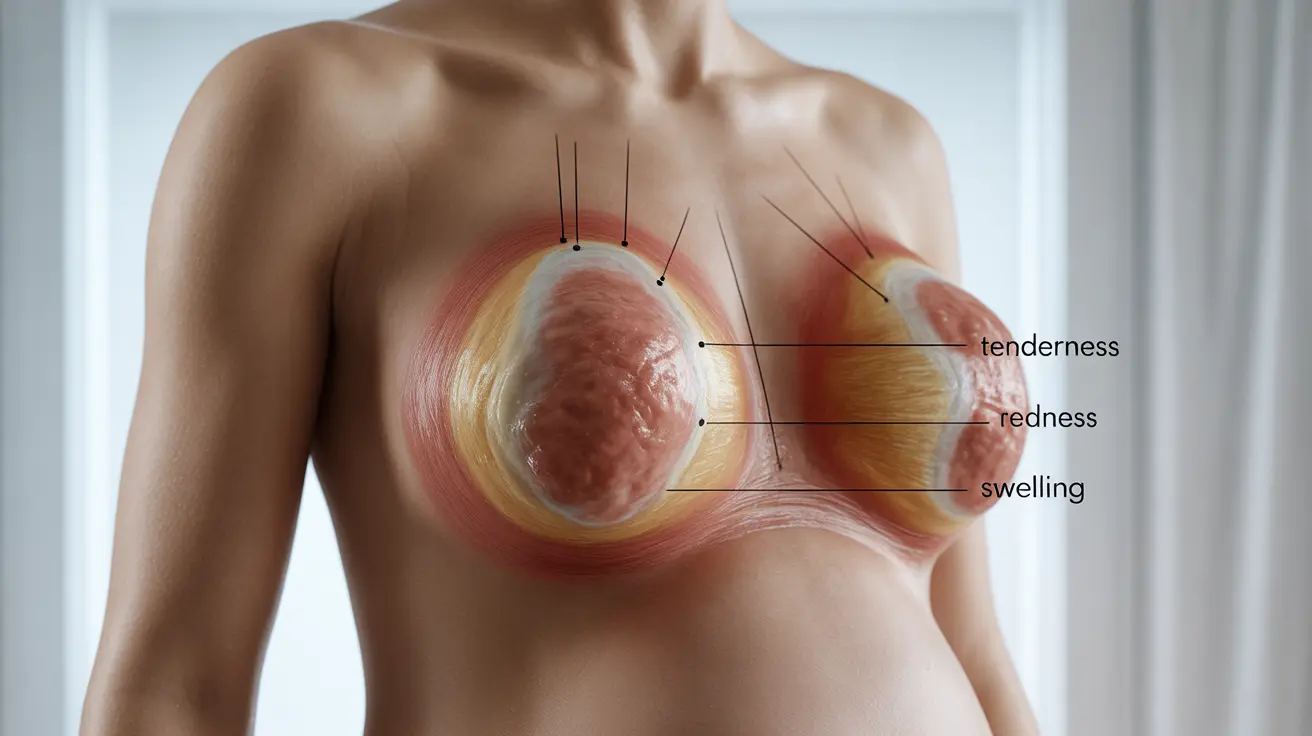
Recognizing the early signs of mastitis during pregnancy is crucial for timely treatment. Common symptoms include:
- Breast tenderness and swelling
- Redness in a specific area of the breast
- Warm or hot spots on the breast
- Flu-like symptoms, including fever and chills
- General fatigue and body aches
- Skin that appears stretched or shiny
Causes and Risk Factors
Several factors can contribute to developing mastitis during pregnancy:
Physical Changes
Hormonal fluctuations during pregnancy can cause changes in breast tissue and milk ducts, potentially increasing susceptibility to infection.
Skin Conditions
Cracked nipples or other breast skin conditions can create entry points for bacteria, leading to infection.
Previous History
Women who have experienced mastitis before may be at higher risk of developing it during pregnancy.
Treatment Options During Pregnancy
Treatment for mastitis during pregnancy must be carefully selected to ensure safety for both mother and baby. Common approaches include:
Medical Interventions
- Pregnancy-safe antibiotics prescribed by healthcare providers
- Over-the-counter pain relievers approved for pregnancy
- Warm compresses to reduce discomfort
Self-Care Measures
Several self-care strategies can help manage symptoms:
- Gentle breast massage
- Wearing loose-fitting, comfortable clothing
- Getting adequate rest
- Staying well-hydrated
Prevention Strategies
Taking preventive measures can help reduce the risk of developing mastitis during pregnancy:
- Maintain good breast hygiene
- Avoid tight-fitting bras
- Address any skin conditions promptly
- Report early symptoms to healthcare providers
- Keep the breast area clean and dry
When to Seek Medical Care
Immediate medical attention is necessary if you experience:
- Severe breast pain
- High fever (101°F or higher)
- Symptoms that worsen despite self-care
- Unusual breast discharge
- Increased breast swelling or redness
Frequently Asked Questions
Can you get mastitis while pregnant, and how common is it?
Yes, you can develop mastitis during pregnancy, although it's less common than postpartum mastitis. The exact prevalence isn't well-documented, but pregnant women should be aware of the possibility and monitor for symptoms.
What are the signs and symptoms of mastitis during pregnancy?
Key symptoms include breast tenderness, redness, warm areas on the breast, fever, fatigue, and flu-like symptoms. The affected breast may also appear swollen and feel painful to touch.
How is mastitis treated safely when you are pregnant?
Treatment typically involves pregnancy-safe antibiotics prescribed by a healthcare provider, along with pain management through approved medications and self-care measures like warm compresses and rest.
What causes mastitis in pregnant women if they are not breastfeeding?
Mastitis during pregnancy can occur due to hormonal changes affecting breast tissue, bacteria entering through small skin breaks, or previous breast conditions. The presence of natural colostrum can also create conditions favorable for infection.
How can pregnant women prevent mastitis and breast infections?
Prevention strategies include maintaining good breast hygiene, wearing properly fitting bras, promptly treating any skin conditions, and reporting early symptoms to healthcare providers. Regular monitoring of breast health is also important during pregnancy.