A cerebellar stroke occurs when blood flow to the cerebellum - the part of the brain responsible for balance, coordination, and fine motor control - is disrupted. This serious medical condition requires immediate attention, as early intervention can significantly improve outcomes and prevent long-term complications.
Understanding cerebellar strokes is crucial because their symptoms can sometimes be subtle or mistaken for other conditions, potentially delaying critical treatment. This comprehensive guide will explore the key aspects of cerebellar strokes, from recognition to recovery.
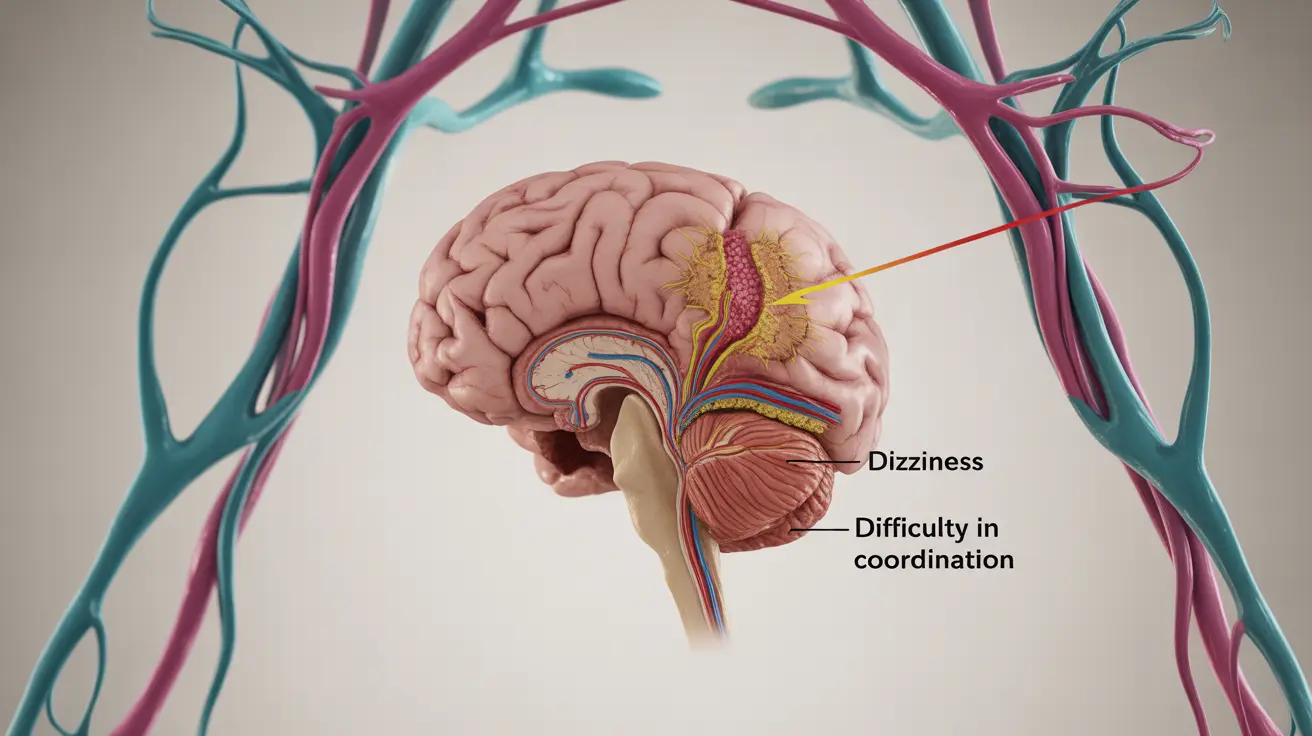
Recognizing the Signs and Symptoms
Cerebellar strokes present with distinct symptoms that differ from other types of strokes due to the cerebellum's specific functions. Common indicators include:
- Severe dizziness or vertigo
- Difficulty maintaining balance while walking
- Sudden onset of coordination problems
- Severe headache
- Nausea and vomiting
- Slurred speech
- Vision problems
Unlike typical strokes affecting other brain regions, facial drooping and arm weakness may be less prominent in cerebellar strokes. The combination of severe dizziness, balance problems, and headache should prompt immediate medical attention.
Diagnostic Approach and Imaging
When a cerebellar stroke is suspected, healthcare providers employ various diagnostic tools to confirm the condition and determine its extent:
- CT (Computed Tomography) scans
- MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging)
- MRA (Magnetic Resonance Angiography)
- Physical examination
- Neurological assessment
Time is critical in stroke diagnosis, as early detection can lead to more effective treatment options and better outcomes.
Understanding Causes and Risk Factors
Cerebellar strokes can occur through two main mechanisms:
Ischemic Cerebellar Stroke
Caused by blood clots or blockages in vessels supplying the cerebellum, accounting for approximately 80% of cases.
Hemorrhagic Cerebellar Stroke
Results from bleeding in the cerebellum, often due to high blood pressure or weakened blood vessels.
Common risk factors include:
- High blood pressure
- Diabetes
- Smoking
- High cholesterol
- Heart disease
- Advanced age
- Family history of stroke
Treatment and Recovery Options
Treatment approaches for cerebellar stroke depend on the type, severity, and timing of diagnosis. Initial interventions may include:
- Emergency medications to dissolve clots
- Blood pressure management
- Surgical intervention when necessary
- Supportive care to prevent complications
Rehabilitation typically involves:
- Physical therapy for balance and coordination
- Occupational therapy for daily activities
- Speech therapy if needed
- Cognitive rehabilitation
Prevention and Lifestyle Modifications
Preventing cerebellar strokes involves managing risk factors through lifestyle changes:
- Regular blood pressure monitoring
- Healthy diet rich in fruits and vegetables
- Regular exercise
- Smoking cessation
- Limited alcohol consumption
- Stress management
- Regular medical check-ups
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the common signs and symptoms of a cerebellar stroke to watch for?
The most common signs include severe dizziness, balance problems, coordination difficulties, headache, nausea, vomiting, and vision problems. Unlike typical strokes, facial drooping may be less common.
How is a cerebellar stroke diagnosed and what imaging tests are used?
Diagnosis typically involves CT scans, MRI, and MRA imaging, along with comprehensive neurological examinations. These tests help determine the type, location, and extent of the stroke.
What are the main causes and risk factors of a cerebellar stroke?
Main causes include blood clots, vessel blockages, or bleeding in the cerebellum. Risk factors include high blood pressure, diabetes, smoking, high cholesterol, heart disease, and advanced age.
What treatment options and rehabilitation therapies are available for cerebellar stroke recovery?
Treatment options include emergency medications, surgery when necessary, and comprehensive rehabilitation including physical, occupational, and speech therapy. The specific approach depends on the stroke type and severity.
How can I reduce my risk of having a cerebellar stroke through lifestyle changes?
Risk reduction involves maintaining healthy blood pressure, eating a balanced diet, exercising regularly, quitting smoking, limiting alcohol consumption, managing stress, and having regular medical check-ups.