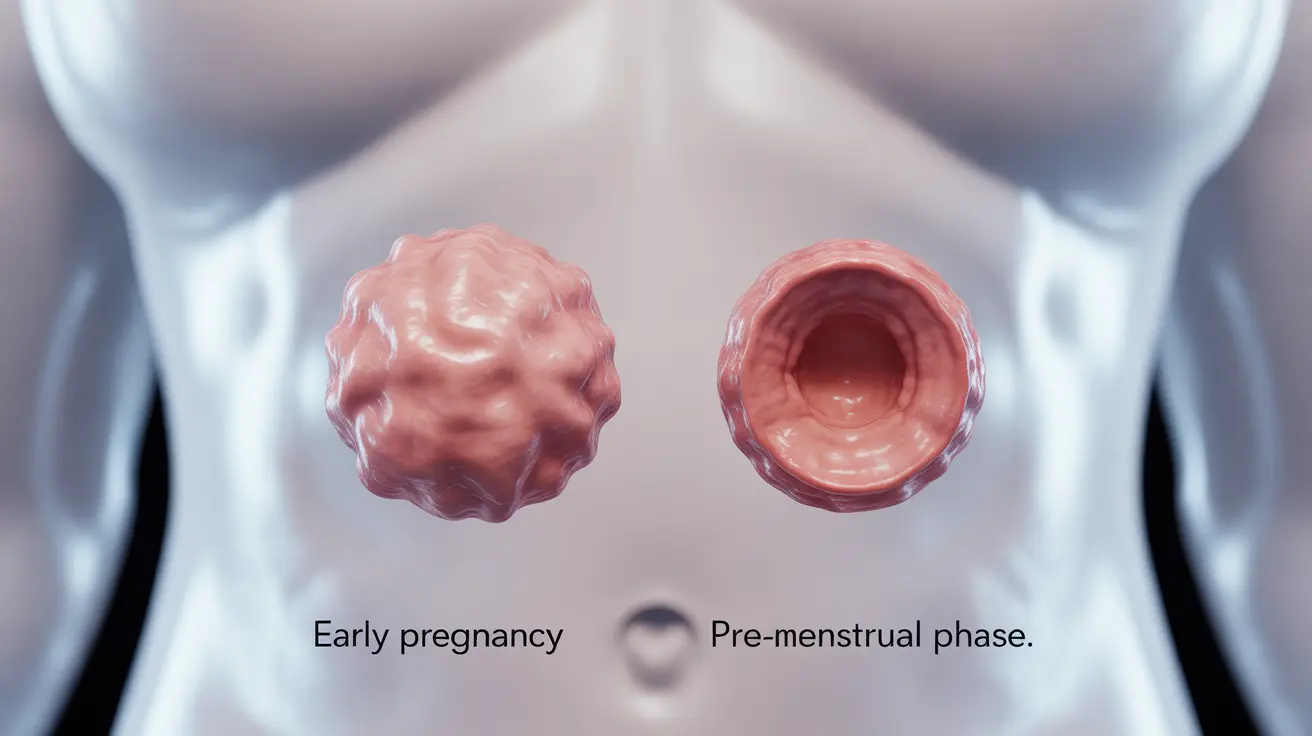
Understanding the differences between cervical changes during early pregnancy versus before a period can provide valuable insights into your body's current state. While these changes alone cannot definitively confirm pregnancy, knowing what to look for can help you better understand your reproductive health.
In this comprehensive guide, we'll explore the key differences in cervical position, texture, and other characteristics that distinguish early pregnancy from pre-menstrual changes. We'll also discuss proper examination techniques and additional symptoms to watch for.
Understanding Your Cervix
The cervix is the lower part of the uterus that connects to the vaginal canal. This remarkable organ undergoes various changes throughout your menstrual cycle and during pregnancy, serving as a potential indicator of your reproductive status.
Cervical Changes Before Period
During the pre-menstrual phase, your cervix exhibits specific characteristics:
- Low position in the vaginal canal
- Firm texture (similar to touching the tip of your nose)
- Slightly open to allow menstrual flow
- Less cervical mucus production
- Generally feels dry to the touch
Cervical Changes in Early Pregnancy
Early pregnancy brings distinct cervical changes:
- Higher position in the vaginal canal
- Notably softer texture (more like touching your lips)
- Tightly closed to protect the developing pregnancy
- Increased cervical mucus production
- Generally feels more moist
Why the Cervix Softens During Pregnancy
During early pregnancy, increased blood flow and hormonal changes, particularly rising levels of estrogen and progesterone, cause the cervix to become softer and more pliable. This process, known as cervical softening or "ripening," helps prepare the cervix for its important role during pregnancy and childbirth.
How to Check Your Cervix
If you choose to check your cervical position, follow these important steps:
- Wash your hands thoroughly with soap and water
- Find a comfortable position (squatting or with one leg elevated)
- Use your middle finger to reach the cervix
- Note the position, texture, and moisture level
- Always maintain proper hygiene to prevent infection
Important Precautions
When checking your cervix, keep these safety considerations in mind:
- Never check your cervix if you suspect you might be pregnant
- Avoid checking during active infection or bleeding
- Stop if you experience any discomfort
- Consult your healthcare provider if you're unsure about what you're feeling
Additional Early Pregnancy Signs
While cervical changes can be informative, look for these additional early pregnancy symptoms:
- Missed period
- Breast tenderness
- Mild cramping or spotting
- Nausea or food aversions
- Increased urination frequency
- Fatigue
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the main differences in the cervix's position and texture before a period versus early pregnancy?
Before a period, the cervix is typically low, firm, and slightly open. During early pregnancy, it becomes higher, softer, and tightly closed. The texture changes from firm (like a nose tip) to soft (like lips) due to increased blood flow and hormonal changes.
How can I check my cervix to determine if I'm pregnant, and what specific changes should I look for?
To check your cervix, ensure clean hands, find a comfortable position, and gently feel for position, texture, and moisture. Look for a high, soft, closed cervix with increased moisture. However, these checks should not replace proper pregnancy testing.
Why does the cervix feel softer in early pregnancy compared to before a menstrual period?
The cervix becomes softer in early pregnancy due to increased blood flow and hormonal changes, particularly rising estrogen and progesterone levels. This softening, known as cervical ripening, is a natural preparation for pregnancy and childbirth.
Can cervical changes alone confirm pregnancy, or is a pregnancy test still necessary?
Cervical changes alone cannot definitively confirm pregnancy. While they can be indicative, a pregnancy test is always necessary for confirmation. Home pregnancy tests and follow-up with healthcare providers remain the most reliable methods.
What are some other signs or symptoms that might accompany changes in the cervix during early pregnancy?
Additional early pregnancy signs include missed periods, breast tenderness, mild cramping, spotting, nausea, food aversions, frequent urination, and fatigue. These symptoms, combined with cervical changes, may suggest pregnancy, but testing is still necessary for confirmation.