If you've been diagnosed with uterine fibroids and are trying to conceive, you likely have concerns about how these noncancerous growths might affect your fertility. While fibroids can impact pregnancy chances, many women with fibroids successfully conceive and carry healthy pregnancies to term. Understanding the relationship between fibroids and fertility can help you make informed decisions about your reproductive health.
The impact of fibroids on fertility varies significantly depending on several factors, including their size, location, and number. Let's explore how fibroids affect pregnancy chances and what you can do to optimize your fertility.
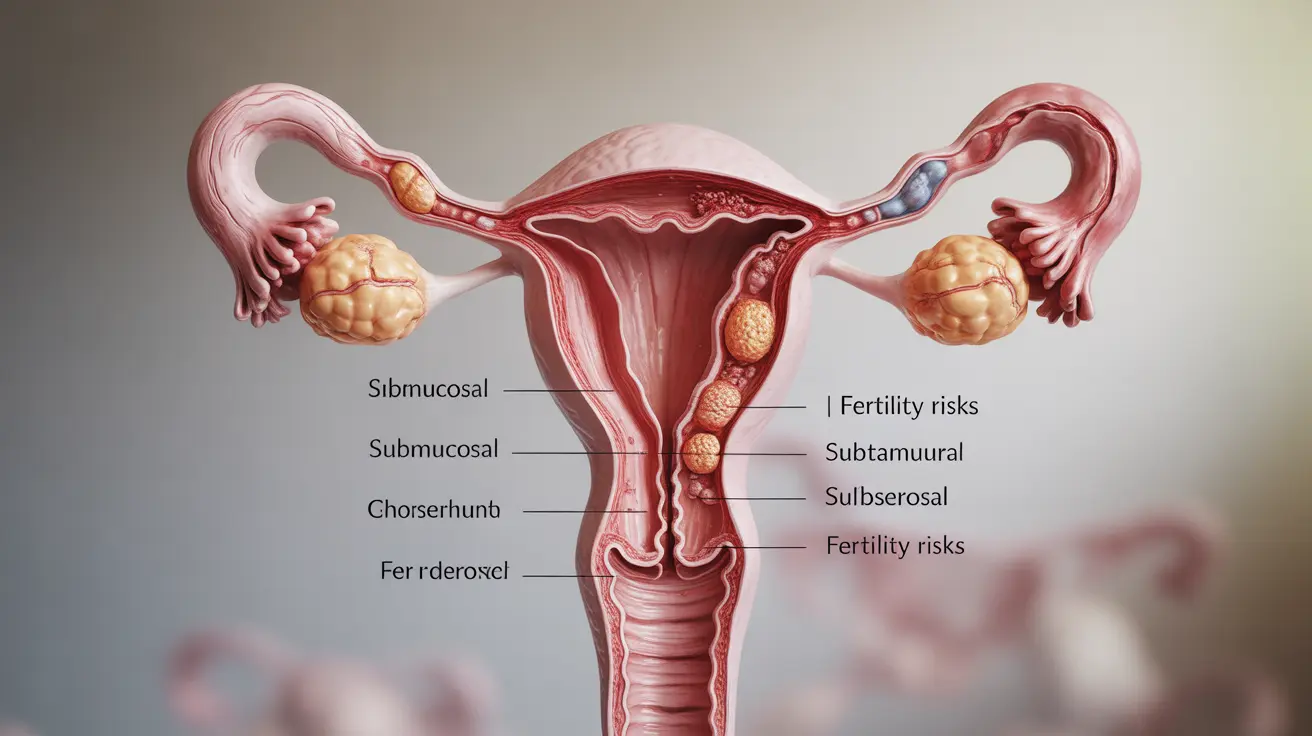
How Fibroids Impact Fertility
Fibroids can affect fertility in several ways, depending on their characteristics and location within the uterus:
Submucosal Fibroids
These fibroids, which grow into the uterine cavity, typically have the most significant impact on fertility. They can interfere with embryo implantation and reduce pregnancy rates by up to 70% in some cases.
Intramural Fibroids
Fibroids within the uterine wall may affect fertility if they're large enough to distort the uterine cavity or interfere with the fallopian tubes. Their impact varies based on size and exact location.
Subserosal Fibroids
These outer wall fibroids generally have the least impact on fertility unless they're very large or located near the fallopian tubes.
Pregnancy Success Rates with Fibroids
Your chances of getting pregnant with fibroids depend on several key factors:
- Size of fibroids (larger ones typically cause more fertility issues)
- Number of fibroids present
- Location within the uterus
- Age and overall fertility status
- Presence of other fertility factors
Research suggests that women with fibroids who have no other fertility issues may have pregnancy rates similar to those without fibroids, especially if the fibroids are small and don't affect the uterine cavity.
Treatment Options to Improve Fertility
If fibroids are affecting your fertility, several treatment options may help improve your chances of conception:
Myomectomy
This surgical procedure removes fibroids while preserving the uterus. It can significantly improve pregnancy rates for women with fibroids that are impacting fertility.
Minimally Invasive Procedures
Some women may be candidates for less invasive treatments, depending on their fibroid characteristics. However, not all procedures are recommended for women planning future pregnancies.
Monitoring and Timing
In cases of small fibroids that don't affect the uterine cavity, careful monitoring and optimal timing of conception attempts may be sufficient.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the chances of getting pregnant if I have uterine fibroids?
Your chances depend largely on the location and size of your fibroids. Women with fibroids that don't affect the uterine cavity often have normal fertility rates, while those with submucosal fibroids may have reduced chances without treatment.
How do fibroids affect fertility and the ability to conceive?
Fibroids can affect fertility by distorting the uterine cavity, blocking fallopian tubes, interfering with blood flow to the endometrium, and potentially affecting sperm movement or embryo implantation.
Can fibroids increase the risk of miscarriage or pregnancy complications?
Yes, certain types of fibroids can increase the risk of miscarriage and complications such as preterm labor, placental abruption, or cesarean delivery. The risk level depends on the fibroid characteristics.
Does the location or size of fibroids influence pregnancy outcomes?
Yes, location and size are crucial factors. Submucosal fibroids and large intramural fibroids tend to have the most significant impact on pregnancy outcomes, while small subserosal fibroids typically cause fewer issues.
Can removing fibroids improve my chances of becoming pregnant?
Yes, removing fibroids through myomectomy can improve fertility rates, particularly if the fibroids were affecting the uterine cavity or causing significant uterine distortion. Success rates vary based on individual circumstances.