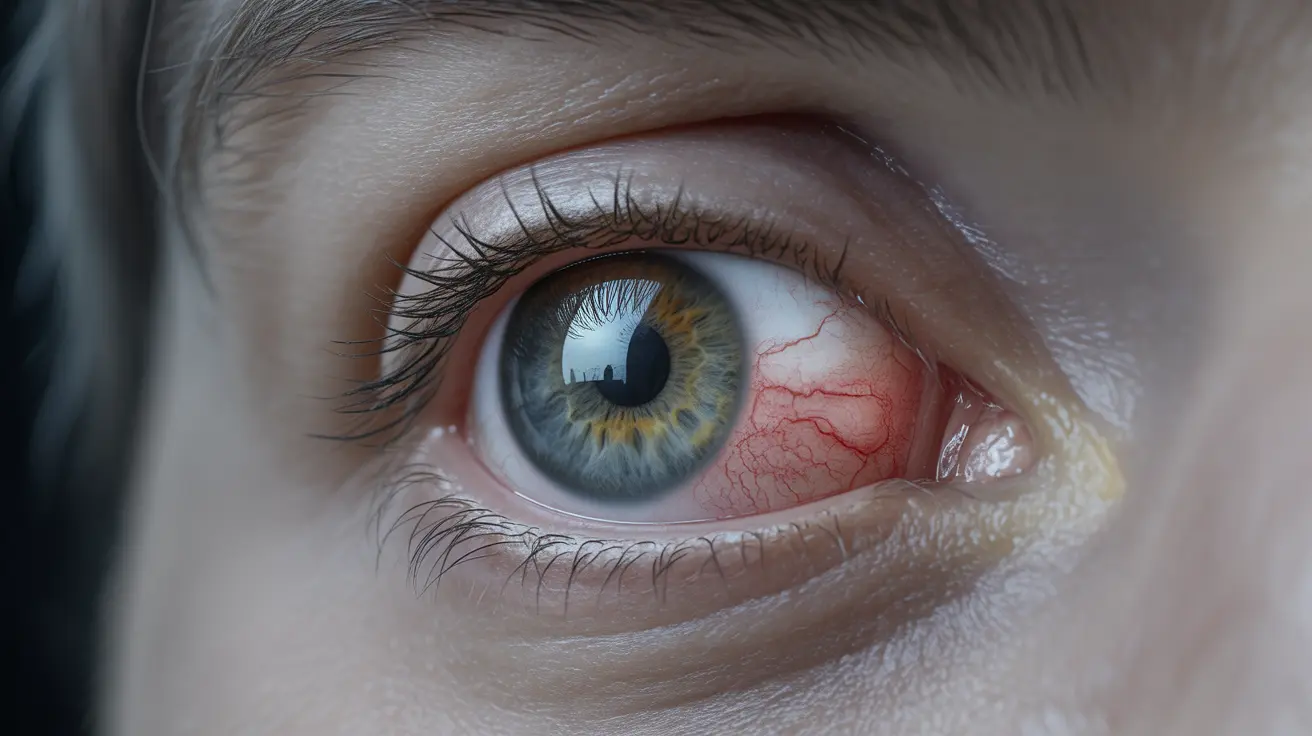
Chemosis is a concerning eye condition where the conjunctiva—the clear membrane covering the white part of the eye—becomes swollen and fills with fluid. This swelling can cause discomfort and affect vision, making it important to understand its causes and available treatments. While chemosis can be alarming when it occurs, the condition is often treatable with proper medical attention.
This comprehensive guide will explore the various aspects of chemosis, including its common triggers, diagnostic procedures, and effective treatment approaches. Whether you're experiencing symptoms or seeking to better understand this eye condition, we'll provide the essential information you need.
Understanding the Nature of Chemosis
Chemosis occurs when fluid accumulates in the conjunctiva, causing it to become swollen and sometimes appear as a blister-like formation on the eye's surface. This condition can affect one or both eyes and may range from mild to severe, depending on the underlying cause.
The swelling typically appears as a transparent or slightly yellowish elevation of the conjunctiva, which may be localized or extend across the entire visible surface of the eye. In severe cases, the swollen tissue might prevent the eyelids from closing properly.
Common Causes and Risk Factors
Several factors can contribute to the development of chemosis:
- Allergic reactions to environmental triggers
- Eye infections (bacterial or viral)
- Trauma or injury to the eye
- Systemic conditions affecting fluid balance
- Thyroid eye disease
- Post-surgical complications
Recognizing Symptoms
The symptoms of chemosis can vary but typically include:
- Visible swelling of the conjunctiva
- Watery or irritated eyes
- Sensation of pressure or fullness
- Blurred vision in some cases
- Difficulty closing the eyelids completely
- Increased tear production
Diagnostic Process
When diagnosing chemosis, eye care professionals typically perform a thorough examination that includes:
- Detailed medical history review
- Slit-lamp examination
- Assessment of eye movement and vision
- Evaluation of underlying systemic conditions
- Testing for allergies if suspected
Treatment Approaches
Medical Interventions
Treatment options often depend on the underlying cause and may include:
- Antihistamine eye drops for allergy-related cases
- Anti-inflammatory medications
- Artificial tears for lubrication
- Antibiotics if bacterial infection is present
- Treatment of underlying systemic conditions
Home Care Measures
Several self-care strategies can help manage symptoms:
- Cold compresses to reduce swelling
- Gentle eye massage when recommended
- Avoiding eye rubbing
- Maintaining proper eye hygiene
- Using protective eyewear when needed
Prevention Strategies
While not all cases of chemosis can be prevented, certain measures can help reduce risk:
- Regular eye checkups
- Prompt treatment of allergies
- Protection from eye trauma
- Proper contact lens care
- Management of underlying health conditions
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the common causes and symptoms of chemosis in the eye?
Chemosis commonly results from allergic reactions, infections, trauma, or systemic conditions. Key symptoms include visible swelling of the conjunctiva, eye irritation, pressure sensation, and sometimes blurred vision.
How is chemosis typically diagnosed and what should I expect during an eye exam?
Diagnosis involves a comprehensive eye examination using a slit lamp, review of medical history, and assessment of vision and eye movement. Your doctor may also perform tests to identify underlying causes such as allergies or infections.
What are effective treatments for chemosis caused by allergies or infections?
Treatment typically includes antihistamine eye drops for allergies, antibiotics for infections, and anti-inflammatory medications. The specific treatment plan depends on the underlying cause of chemosis.
How can I safely relieve the swelling and irritation caused by chemosis at home?
Safe home remedies include applying cold compresses, using artificial tears, avoiding eye rubbing, and maintaining good eye hygiene. Always follow your eye care professional's specific recommendations.
What steps can I take to prevent chemosis or reduce the risk of recurrence?
Prevention strategies include regular eye check-ups, prompt treatment of allergies, protecting eyes from injury, proper contact lens care, and managing any underlying health conditions that might contribute to chemosis.