Chronic cholecystitis is a long-term condition characterized by recurring inflammation of the gallbladder, often leading to persistent discomfort and potential complications if left untreated. This condition typically develops after multiple episodes of acute cholecystitis or due to ongoing irritation from gallstones, affecting the gallbladder's normal function and structure over time.
Understanding this condition is crucial for those affected, as proper management can significantly improve quality of life and prevent serious complications. Let's explore the key aspects of chronic cholecystitis, from its symptoms to treatment options.
Common Symptoms and Warning Signs
Chronic cholecystitis often presents with a range of symptoms that can vary in intensity and frequency. The most common symptoms include:
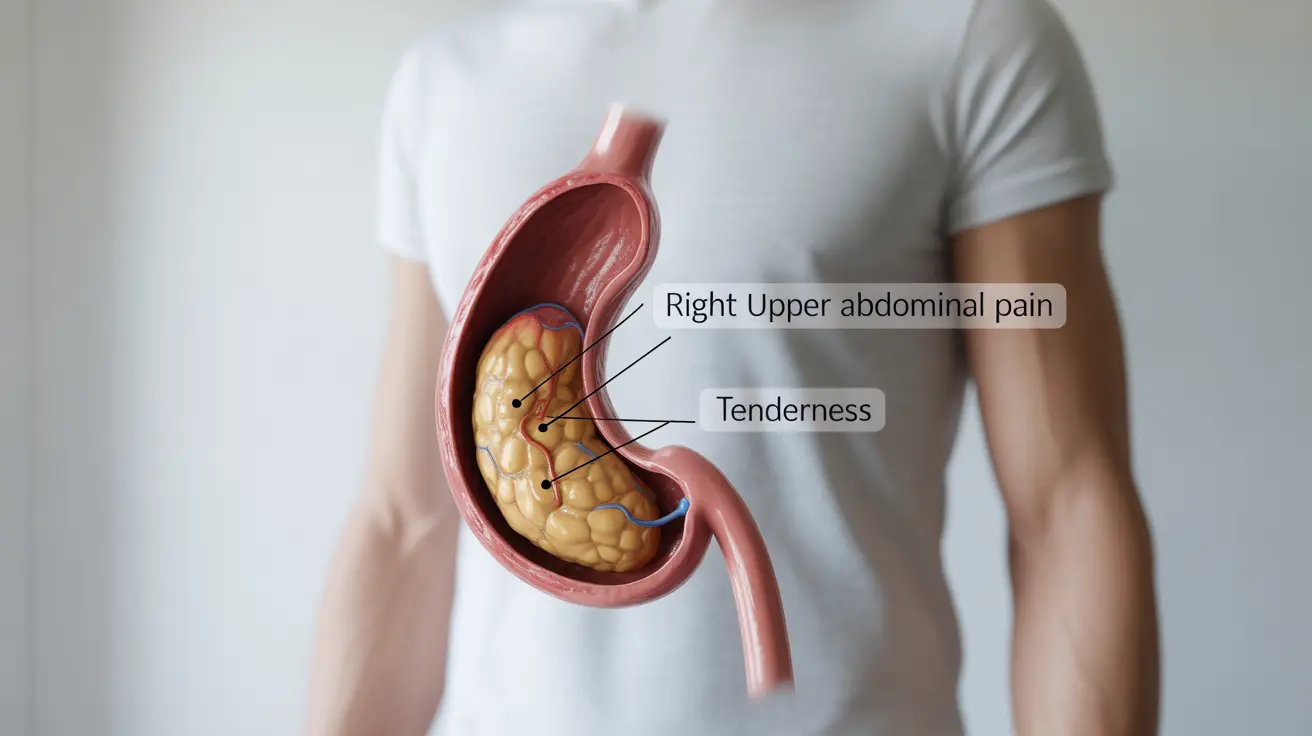
- Recurring right upper abdominal pain
- Tenderness in the right upper quadrant
- Nausea and occasional vomiting
- Bloating after meals
- Intolerance to fatty foods
- Mild fever during flare-ups
Unlike acute cholecystitis, the symptoms of chronic cholecystitis may be less severe but more persistent, often worsening after meals, particularly those high in fat.
Diagnostic Procedures and Tests
Accurate diagnosis of chronic cholecystitis requires a comprehensive medical evaluation. Healthcare providers typically use multiple diagnostic tools:
Imaging Studies
- Ultrasound examination
- HIDA scan (cholescintigraphy)
- CT scan when necessary
- MRI in complex cases
Laboratory Tests
- Complete blood count
- Liver function tests
- Lipase levels
- Blood chemistry panel
Treatment Approaches
Treatment for chronic cholecystitis typically involves several approaches, depending on the severity of symptoms and overall health status of the patient.
Conservative Management
Initial treatment may include:
- Pain management
- Dietary modifications
- Antibiotics when infection is present
- Regular monitoring of symptoms
Surgical Intervention
Laparoscopic cholecystectomy (gallbladder removal) is often the definitive treatment for chronic cholecystitis. This minimally invasive procedure is recommended when:
- Conservative treatment fails
- Symptoms significantly impact quality of life
- Complications develop or are likely to develop
Dietary Management and Lifestyle Changes
Proper dietary management plays a crucial role in controlling symptoms and preventing flare-ups. Key dietary recommendations include:
- Limiting fatty and fried foods
- Avoiding large meals
- Increasing fiber intake
- Maintaining healthy weight
- Staying well-hydrated
Potential Complications
Without proper treatment, chronic cholecystitis can lead to serious complications:
- Gallbladder perforation
- Gangrene
- Abscess formation
- Fistula development
- Chronic pain syndrome
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the symptoms of chronic cholecystitis and what does it feel like?
Chronic cholecystitis typically causes recurring right upper abdominal pain, tenderness, and discomfort that often worsen after meals. Patients may experience nausea, bloating, and intolerance to fatty foods. The pain is usually less severe than acute attacks but more persistent, described as a dull ache or pressure in the upper right abdomen.
How is chronic cholecystitis diagnosed and what tests will my doctor order?
Diagnosis typically involves imaging studies such as ultrasound, HIDA scan, or CT scan, combined with blood tests to check liver function and inflammation markers. Your doctor will also perform a physical examination and review your medical history. Additional tests may be ordered based on your specific symptoms and presentation.
What are the best treatment options for chronic cholecystitis, and is gall bladder removal always necessary?
While laparoscopic cholecystectomy (gallbladder removal) is often the definitive treatment, it's not always immediately necessary. Initial treatment may include dietary modifications, pain management, and antibiotics. However, surgery is typically recommended for recurring or severe symptoms to prevent complications.
Which foods should I avoid with chronic cholecystitis, and can changing my diet help my symptoms?
A low-fat diet can significantly help manage symptoms. Avoid fried foods, high-fat dairy products, and fatty meats. Focus on lean proteins, whole grains, fruits, and vegetables. Small, frequent meals are often better tolerated than large meals. Dietary changes can help reduce symptoms but may not prevent the need for eventual surgery.
What are the possible complications if chronic cholecystitis is left untreated?
Untreated chronic cholecystitis can lead to serious complications including gallbladder perforation, gangrene, abscess formation, and fistula development. It may also result in chronic pain syndrome and increase the risk of gallbladder cancer. Regular medical monitoring and appropriate treatment are essential to prevent these complications.