Chronic laryngitis is a persistent inflammation of the voice box (larynx) that affects millions of people worldwide, causing ongoing voice problems and discomfort. Unlike the temporary hoarseness you might experience with a common cold, chronic laryngitis persists for weeks or months, significantly impacting daily communication and quality of life.
This long-lasting condition requires proper understanding and management to prevent complications and restore vocal health. By recognizing the symptoms early and seeking appropriate treatment, individuals can effectively manage chronic laryngitis and protect their voice for the long term.
What Is Chronic Laryngitis?
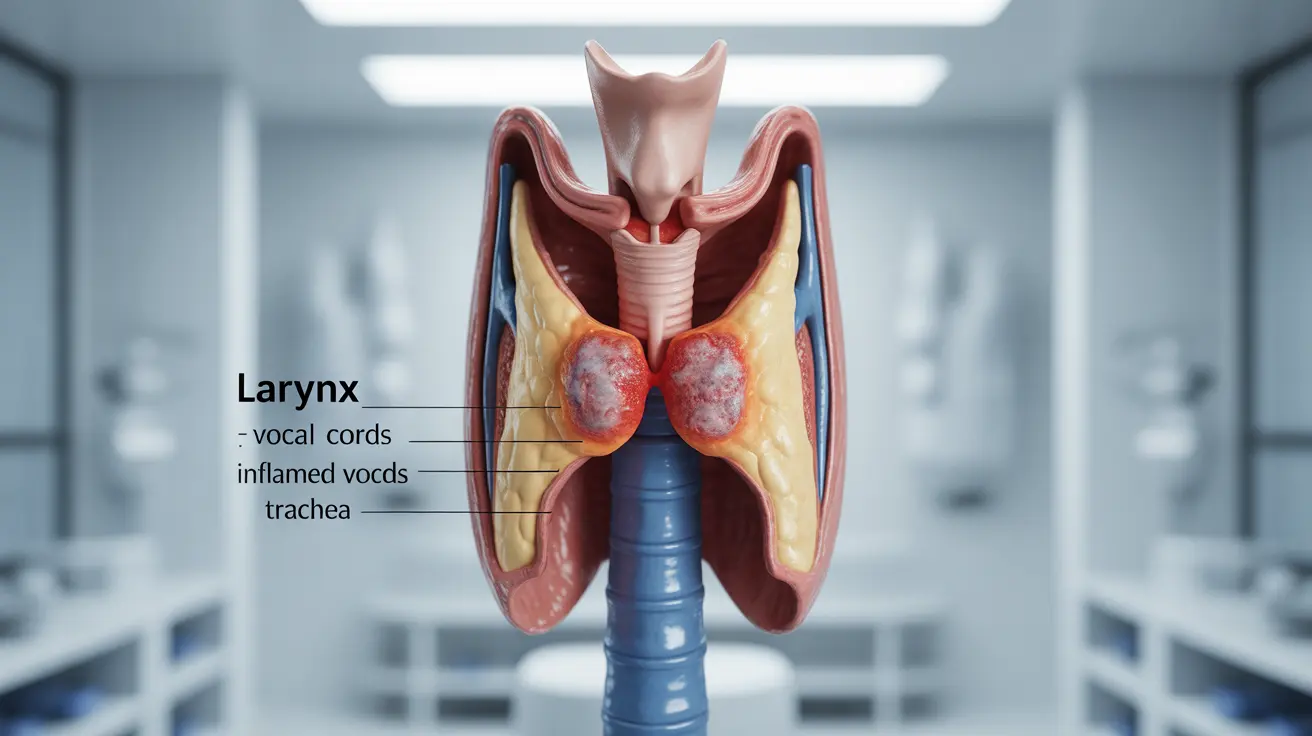
Chronic laryngitis occurs when the vocal cords and surrounding tissues in the larynx remain inflamed for an extended period, typically lasting more than three weeks. This prolonged inflammation can cause structural changes to the vocal cords, leading to persistent voice problems and throat discomfort.
The condition affects people of all ages but is particularly common among individuals who use their voice professionally, such as teachers, singers, and public speakers. Environmental factors, lifestyle choices, and underlying health conditions can all contribute to the development of this persistent throat condition.
Recognizing the Symptoms of Chronic Laryngitis
The hallmark symptom of chronic laryngitis is persistent hoarseness that doesn't resolve with rest or basic home remedies. Voice changes may range from mild roughness to complete voice loss, depending on the severity of inflammation.
Additional symptoms commonly experienced include:
- Persistent throat clearing and coughing
- A sensation of having something stuck in the throat
- Throat pain or discomfort, especially when speaking
- Reduced vocal range and difficulty projecting the voice
- Voice fatigue after minimal speaking
- A weak or breathy voice quality
These symptoms often worsen throughout the day with voice use and may be accompanied by general throat irritation or dryness. Unlike acute laryngitis, these symptoms persist despite rest and basic care measures.
Understanding the Causes and Risk Factors
Chronic laryngitis develops from various factors that cause ongoing irritation to the vocal cords and larynx. Identifying the underlying cause is crucial for effective treatment and prevention of recurrence.
Common Causes
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) represents one of the most frequent causes of chronic laryngitis. Stomach acid that reaches the throat can cause persistent inflammation of the vocal cords, leading to ongoing symptoms even without typical heartburn.
Chronic voice overuse or misuse, particularly among professional voice users, can lead to persistent inflammation. Shouting, speaking loudly for extended periods, or using improper vocal techniques can strain the vocal cords and cause chronic irritation.
Environmental irritants play a significant role in many cases. Regular exposure to cigarette smoke, air pollution, chemical fumes, or dry air can maintain chronic inflammation in the larynx.
Acute vs. Chronic Laryngitis
The primary difference between acute and chronic laryngitis lies in duration and underlying causes. Acute laryngitis typically results from viral infections, develops suddenly, and resolves within one to two weeks with proper rest and care.
Chronic laryngitis, conversely, persists for weeks to months and often stems from ongoing irritation rather than infection. While acute laryngitis usually improves with voice rest and supportive care, chronic cases require identification and management of underlying causes for effective resolution.
Professional Diagnosis and Evaluation
Diagnosing chronic laryngitis requires a comprehensive evaluation by a healthcare professional, typically an otolaryngologist (ENT specialist). The diagnostic process begins with a detailed medical history and physical examination.
During the evaluation, doctors will ask about symptom duration, voice use patterns, lifestyle factors, and potential exposures to irritants. They'll also review any medications that might contribute to throat dryness or irritation.
Diagnostic Procedures
Laryngoscopy represents the primary diagnostic tool for evaluating chronic laryngitis. This procedure allows direct visualization of the vocal cords using a flexible or rigid scope inserted through the nose or mouth. The examination reveals inflammation, structural changes, or other abnormalities affecting the larynx.
Additional testing may include pH monitoring to detect acid reflux, allergy testing if environmental triggers are suspected, or voice analysis to assess vocal function and identify harmful voice use patterns.
Comprehensive Treatment Approaches
Effective treatment of chronic laryngitis requires addressing underlying causes while managing symptoms and promoting vocal cord healing. Treatment plans are typically individualized based on the specific cause and severity of the condition.
Medical Treatments
For cases related to acid reflux, proton pump inhibitors or H2 blockers help reduce stomach acid production and prevent further irritation of the vocal cords. These medications often require several weeks to months of consistent use for optimal results.
Corticosteroids may be prescribed for severe inflammation, providing rapid reduction in swelling and irritation. These are typically used short-term due to potential side effects with prolonged use.
If allergies contribute to the condition, antihistamines or allergy medications can help reduce inflammation and symptoms.
Voice Therapy and Lifestyle Modifications
Voice therapy with a speech-language pathologist plays a crucial role in treatment, especially for individuals with voice overuse or misuse patterns. Therapy focuses on proper vocal techniques, breathing exercises, and strategies to reduce vocal strain.
Lifestyle modifications form an essential component of treatment. These include avoiding throat clearing, staying well-hydrated, using a humidifier to maintain adequate moisture in the air, and eliminating exposure to irritants like smoke and chemicals.
Prevention Strategies and Long-term Management
Preventing chronic laryngitis recurrence requires ongoing attention to vocal health and lifestyle factors. Understanding personal triggers and implementing protective measures can significantly reduce the risk of developing persistent voice problems.
Vocal Hygiene Practices
Maintaining good vocal hygiene involves staying adequately hydrated by drinking plenty of water throughout the day. Avoiding excessive caffeine and alcohol, which can contribute to dehydration, supports optimal vocal cord function.
Using proper voice techniques, including speaking at an appropriate volume and avoiding shouting or whispering, helps prevent vocal strain. Taking regular voice breaks during extended speaking periods allows the vocal cords to rest and recover.
Environmental and Lifestyle Factors
Creating a voice-friendly environment includes using humidifiers in dry conditions, avoiding exposure to smoke and chemical irritants, and managing underlying conditions like GERD or allergies that can contribute to laryngeal inflammation.
For individuals in voice-intensive professions, learning proper vocal techniques and incorporating regular voice rest periods into daily routines can prevent overuse injuries and chronic inflammation.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the most common symptoms of chronic laryngitis?
The most common symptoms include persistent hoarseness lasting more than three weeks, voice fatigue, throat discomfort, frequent throat clearing, and a sensation of something stuck in the throat. Unlike acute laryngitis, these symptoms don't improve with basic rest and continue for weeks or months.
What causes chronic laryngitis and how is it different from acute laryngitis?
Chronic laryngitis is typically caused by ongoing irritation from acid reflux, voice overuse, environmental irritants, or allergies, while acute laryngitis usually results from viral infections. The key difference is duration – chronic laryngitis persists for weeks to months, whereas acute laryngitis typically resolves within 1-2 weeks with proper care.
How is chronic laryngitis diagnosed by a doctor?
Diagnosis involves a comprehensive medical history, physical examination, and laryngoscopy to directly visualize the vocal cords. Additional tests may include pH monitoring for acid reflux detection, allergy testing, or voice analysis to identify contributing factors and assess vocal function.
What are the best treatment options for chronic laryngitis?
Treatment depends on the underlying cause but often includes medications for acid reflux or allergies, voice therapy with a speech-language pathologist, lifestyle modifications, and elimination of irritants. Severe cases may require short-term corticosteroids to reduce inflammation.
Can chronic laryngitis be prevented, and what lifestyle changes help?
Yes, chronic laryngitis can often be prevented through proper vocal hygiene, staying hydrated, avoiding irritants like smoke, managing acid reflux, using humidifiers in dry environments, and learning proper voice techniques. Regular voice rest and avoiding voice abuse are crucial for prevention.