For men struggling with fertility issues or low testosterone levels, Clomid (clomiphene citrate) has emerged as a valuable treatment option. While traditionally known as a fertility medication for women, Clomid's use in men has shown promising results for improving reproductive health and hormone balance. This comprehensive guide explores how Clomid works for men and what to expect from treatment.
Understanding How Clomid Works in Men
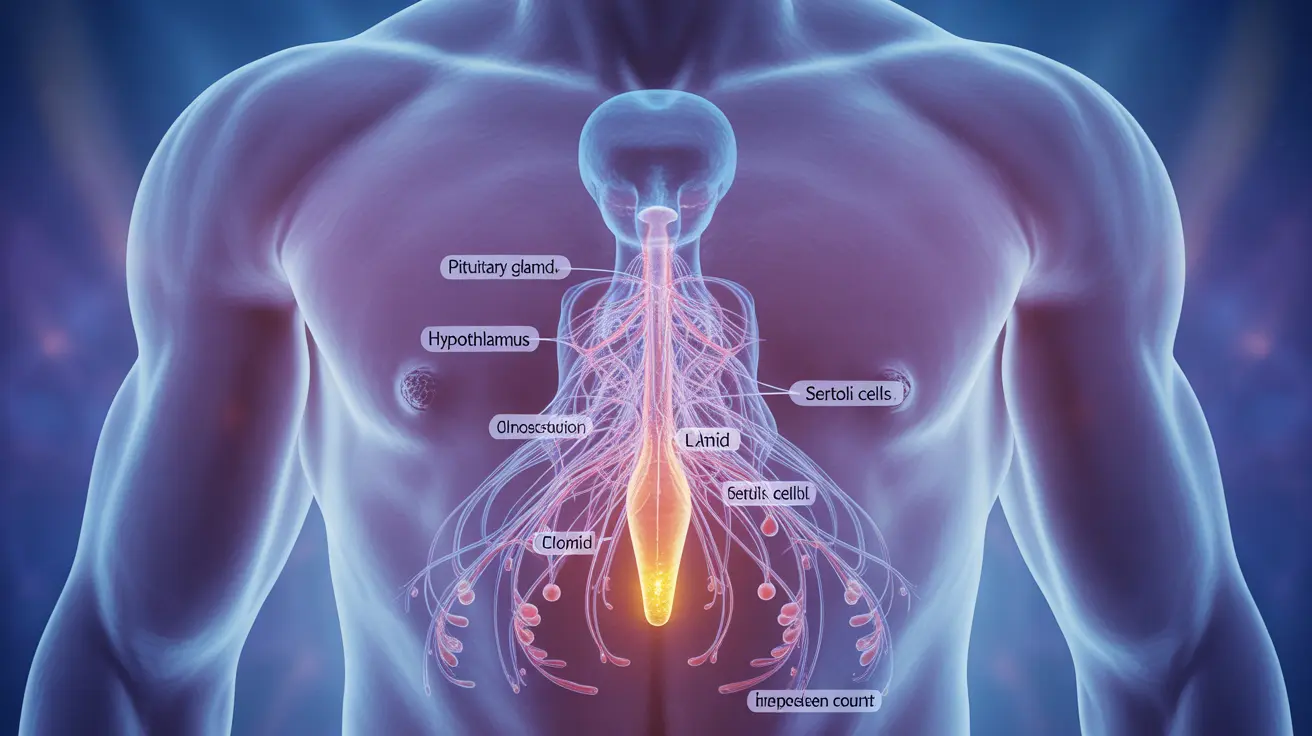
Clomid functions by blocking estrogen receptors in the brain, which triggers the body to produce more testosterone and sperm naturally. This mechanism helps restore hormone balance and can improve fertility outcomes in men experiencing low testosterone or reduced sperm production.
The medication stimulates the pituitary gland to release more follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH), which in turn promotes testosterone production and healthy sperm development.
Dosage and Treatment Protocol
The typical Clomid treatment protocol for men differs from that prescribed for women. Most healthcare providers start with a lower dose and adjust based on individual response and hormone levels.
Standard Dosing Guidelines
Common dosing protocols include:
- 25-50 mg daily
- 25-50 mg every other day
- Treatment courses typically lasting 3-6 months
Regular monitoring through blood tests helps healthcare providers adjust dosage and track progress throughout treatment.
Expected Results and Success Rates
Clinical studies have shown encouraging results for men taking Clomid, particularly those with specific fertility challenges:
- Increased testosterone levels within 4-6 weeks of treatment
- Improved sperm count and quality in many cases
- Enhanced fertility potential when used as part of a comprehensive treatment plan
Potential Side Effects and Risks
While generally well-tolerated, men should be aware of possible side effects when taking Clomid:
- Visual disturbances or blurred vision
- Mood changes
- Breast tenderness
- Headaches
- Weight gain
- Gastrointestinal discomfort
Alternative Treatment Options
For men who may not respond to Clomid or prefer different approaches, several alternatives exist:
- Testosterone replacement therapy
- Human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) injections
- Lifestyle modifications
- Natural supplements and vitamins
- Other fertility medications
Frequently Asked Questions
How does Clomid work to improve testosterone and sperm production in men?
Clomid works by blocking estrogen receptors in the brain, which stimulates the production of FSH and LH hormones. These hormones naturally increase testosterone production and support healthy sperm development in the testes.
What is the typical Clomid dosage and treatment length for male infertility?
Most men are prescribed 25-50 mg of Clomid daily or every other day. Treatment typically continues for 3-6 months, with regular monitoring to assess effectiveness and adjust dosage as needed.
What are the potential side effects of taking Clomid as a man?
Common side effects may include visual changes, mood alterations, breast tenderness, headaches, and gastrointestinal issues. Most side effects are mild and resolve on their own or with dosage adjustment.
How effective is Clomid in increasing sperm count and improving pregnancy chances for men?
Studies show that Clomid can significantly improve sperm count and quality in many men, particularly those with specific fertility issues. Success rates vary, but many couples see improved pregnancy chances when male partners respond well to treatment.
Are there alternative treatments to Clomid for men with low testosterone or infertility?
Yes, alternatives include testosterone replacement therapy, hCG injections, lifestyle changes, nutritional supplements, and other fertility medications. The best treatment choice depends on individual factors and should be discussed with a healthcare provider.