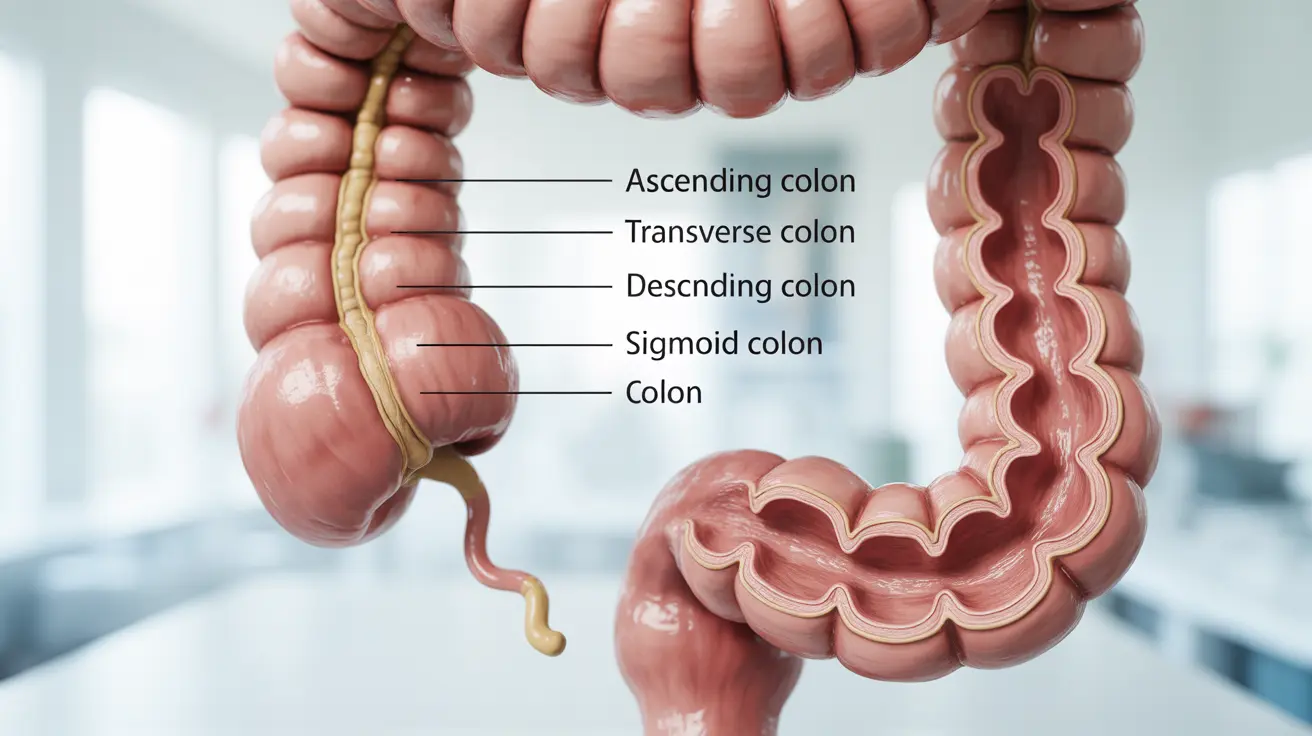
Colon pain can be an uncomfortable and concerning symptom that affects many people. This discomfort, which occurs in the large intestine, can range from mild cramping to severe abdominal pain. Understanding the underlying causes and knowing when to seek medical attention is crucial for proper management and treatment.
While occasional colon discomfort might be related to temporary factors like diet or stress, persistent or severe pain could indicate more serious conditions that require medical evaluation. Let's explore the various aspects of colon pain and learn how to address this common health concern effectively.
Common Causes of Colon Pain
Colon pain can stem from various conditions, ranging from minor digestive issues to more serious medical conditions:
- Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS)
- Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD)
- Diverticulitis
- Constipation
- Gas and bloating
- Food intolerances
- Infections
- Colon polyps or cancer
Warning Signs and Symptoms
Certain symptoms accompanying colon pain warrant immediate medical attention:
- Severe abdominal pain
- Blood in stool
- Persistent changes in bowel habits
- Unexplained weight loss
- Fever
- Nausea and vomiting
- Night sweats
- Chronic fatigue
Diagnostic Process
Healthcare providers use various methods to diagnose the cause of colon pain:
Physical Examination
Your doctor will perform a thorough physical examination and discuss your medical history, including the nature, duration, and severity of your symptoms.
Diagnostic Tests
Common diagnostic procedures may include:
- Blood tests
- Stool analysis
- Colonoscopy
- CT scan
- X-rays
- Ultrasound
Managing Colon Pain Through Lifestyle Changes
Several lifestyle modifications can help alleviate colon pain:
Dietary Adjustments
- Increasing fiber intake gradually
- Staying well-hydrated
- Avoiding trigger foods
- Eating regular, balanced meals
- Limiting caffeine and alcohol
Stress Management
Stress can exacerbate colon pain. Consider incorporating these stress-reduction techniques:
- Regular exercise
- Meditation or deep breathing exercises
- Adequate sleep
- Yoga or gentle stretching
- Professional counseling when needed
Treatment Options
Treatment approaches vary depending on the underlying cause:
Medical Treatments
- Anti-spasmodic medications
- Anti-inflammatory drugs
- Antibiotics (if infection is present)
- Probiotics
- Prescription medications for specific conditions
Alternative Therapies
Some people find relief through complementary treatments:
- Acupuncture
- Herbal remedies
- Heat therapy
- Gentle massage
- Mind-body techniques
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the most common causes of colon pain and how can I tell which one I might have? The most common causes include IBS, IBD, diverticulitis, and constipation. The nature, location, and timing of pain, along with accompanying symptoms, can help determine the cause. However, accurate diagnosis requires professional medical evaluation.
What symptoms should prompt me to see a doctor for colon pain? Seek immediate medical attention if you experience severe abdominal pain, blood in stool, persistent changes in bowel habits, unexplained weight loss, fever, or prolonged nausea and vomiting.
How is colon pain diagnosed and what tests might be needed? Diagnosis typically involves physical examination, medical history review, and various tests such as blood work, stool analysis, colonoscopy, CT scans, or other imaging studies depending on your symptoms and risk factors.
What dietary and lifestyle changes can help reduce colon pain? Key changes include increasing fiber intake gradually, staying hydrated, identifying and avoiding trigger foods, managing stress, maintaining regular exercise, and establishing consistent eating patterns.
What treatment options are available for chronic colon pain conditions like IBS or inflammatory bowel disease? Treatment options include medications (anti-spasmodics, anti-inflammatories, or condition-specific drugs), dietary modifications, stress management techniques, and sometimes alternative therapies. The specific treatment plan depends on the underlying condition and its severity.