Coughing after eating is a common yet concerning symptom that can significantly impact your quality of life and enjoyment of meals. This uncomfortable experience may signal various underlying conditions, from minor issues to more serious health concerns that require medical attention.
Understanding why you're coughing after eating is crucial for finding the right treatment and preventing future episodes. Let's explore the main causes, treatment options, and when you should consult a healthcare provider.
Common Causes of Post-Meal Coughing
Several conditions can trigger coughing after eating, with some being more common than others:
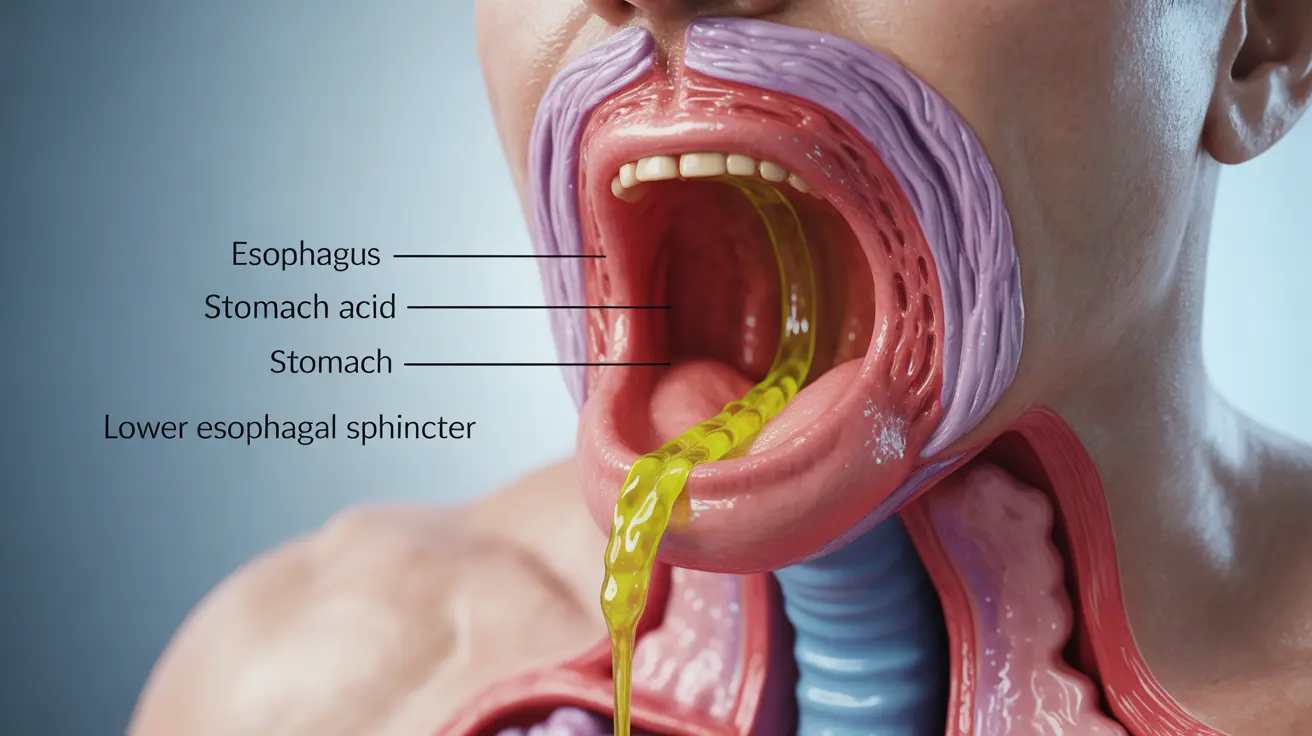
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD)
GERD is one of the most frequent causes of post-meal coughing. When stomach acid flows back into the esophagus, it can irritate the throat and trigger a cough reflex. This typically occurs within 30 minutes to an hour after eating.
Dysphagia
Difficulty swallowing, or dysphagia, can cause food or liquids to enter the airway instead of the esophagus, leading to coughing. This condition may be related to nerve problems, muscle disorders, or structural issues in the throat.
Food Allergies and Sensitivities
Allergic reactions to certain foods can cause inflammation in the throat and airways, resulting in coughing. Common food allergens include nuts, dairy, eggs, and shellfish.
Treatment Approaches
Managing GERD-Related Coughing
If acid reflux is causing your post-meal coughing, several treatment options are available:
- Over-the-counter antacids
- H2 blockers or proton pump inhibitors
- Dietary modifications
- Elevation of the head during sleep
Addressing Food Allergies
For allergy-related coughing, treatment typically involves:
- Identifying and avoiding trigger foods
- Taking antihistamines when needed
- Carrying emergency medication if prescribed
- Working with an allergist for proper management
Prevention Strategies
Several lifestyle changes can help prevent coughing after eating:
- Eat smaller, more frequent meals
- Avoid lying down for 2-3 hours after eating
- Chew food thoroughly and eat slowly
- Stay upright while eating
- Avoid known trigger foods
- Maintain a healthy weight
When to Seek Medical Help
Consult a healthcare provider if you experience:
- Persistent coughing that doesn't improve
- Difficulty breathing or swallowing
- Weight loss
- Chest pain
- Coughing up blood
- Frequent choking while eating
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the most common causes of coughing after eating?
The most common causes include GERD (acid reflux), dysphagia (swallowing difficulties), and food allergies or sensitivities. Other potential causes include aspiration during eating and postnasal drip.
How can acid reflux (GERD) lead to coughing after meals and how is it treated?
GERD causes stomach acid to flow back into the esophagus, irritating the throat and triggering coughs. Treatment includes lifestyle changes, dietary modifications, and medications like antacids or proton pump inhibitors.
Can food allergies cause coughing after eating and what symptoms should I watch for?
Yes, food allergies can cause coughing after eating. Watch for additional symptoms like throat tightness, wheezing, hives, difficulty breathing, and swelling of the face or throat. These symptoms may indicate a serious allergic reaction requiring immediate medical attention.
When should I see a doctor if I often cough after eating?
See a doctor if you experience persistent coughing after meals, difficulty breathing or swallowing, unexplained weight loss, chest pain, or if you're coughing up blood. These symptoms may indicate a serious underlying condition requiring medical evaluation.
What lifestyle changes can help prevent coughing after meals?
Effective lifestyle changes include eating smaller portions, avoiding trigger foods, staying upright after meals, eating slowly, thoroughly chewing food, and maintaining a healthy weight. For GERD-related coughing, avoiding late-night meals and elevating the head of your bed can also help.