The COVID-19 incubation period - the time between exposure to the virus and the onset of symptoms - is a crucial factor in understanding how the disease spreads and implementing effective public health measures. As the virus continues to evolve, staying informed about this key characteristic helps individuals and healthcare providers make better decisions about testing, isolation, and prevention strategies.
This comprehensive guide explores the typical incubation period for COVID-19, how it varies among different variants, and its implications for public health guidelines. Understanding these aspects is essential for managing potential exposures and preventing transmission effectively.
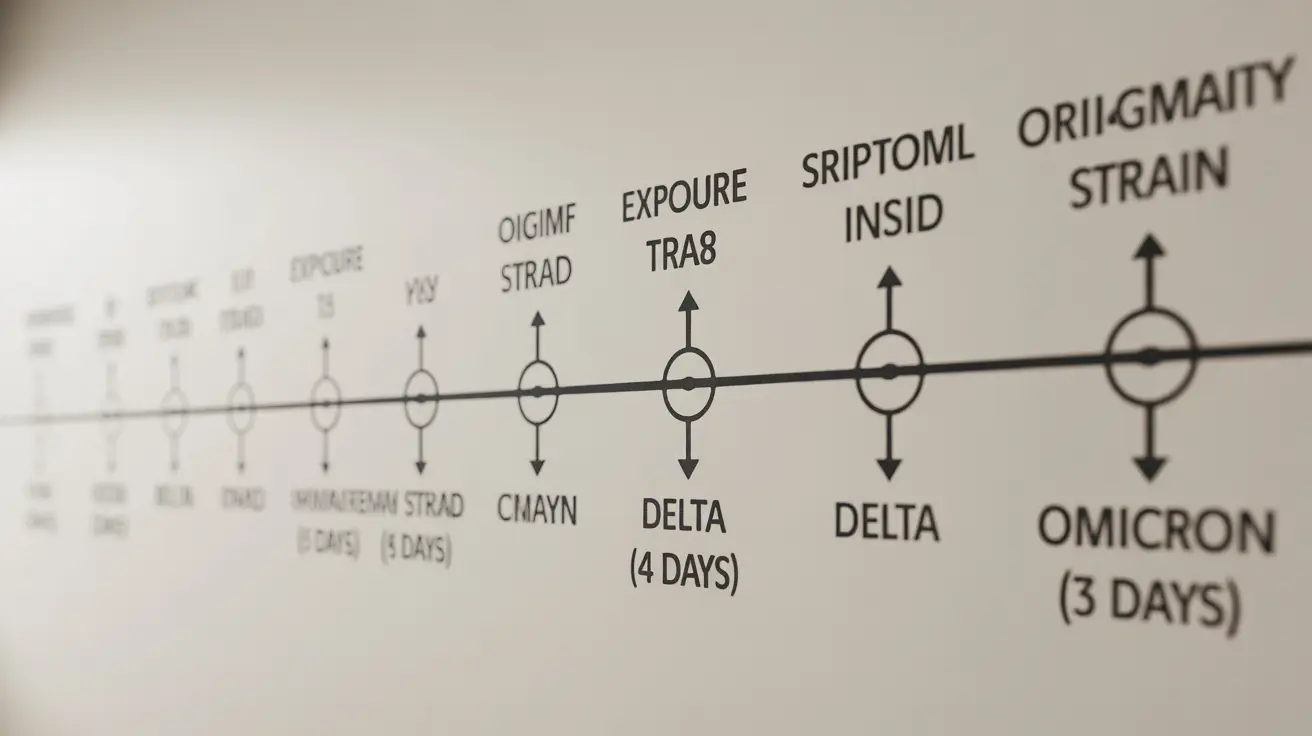
The Basic Timeline: COVID-19's Typical Incubation Period
The incubation period for COVID-19 has evolved throughout the pandemic, particularly as new variants have emerged. Current research indicates that symptoms typically develop within 2-14 days after exposure, with most people showing signs around day 3-5. This timeline can vary significantly between individuals and depends on several factors, including the specific variant involved.
Changes in Incubation Periods Across Variants
Different COVID-19 variants have demonstrated varying incubation periods:
- Original strain: 5-6 days average
- Delta variant: 4 days average
- Omicron variant: 3 days average
- Newer subvariants: Generally shorter periods
Transmission During the Incubation Period
One of the most challenging aspects of COVID-19 is that infected individuals can transmit the virus before developing symptoms. Studies have shown that pre-symptomatic transmission accounts for a significant portion of COVID-19 spread, making it crucial to understand this aspect of the disease.
Key Transmission Facts
Important points about viral transmission during the incubation period include:
- Viral load can peak before symptom onset
- Highest transmissibility often occurs 1-2 days before symptoms appear
- Asymptomatic carriers can spread the virus throughout the entire period
Impact on Public Health Guidelines
Understanding the incubation period has directly influenced public health recommendations and protocols. These guidelines are regularly updated based on new research and emerging variants to provide the most effective protection against virus spread.
Current Recommendations
Key guidelines related to the incubation period include:
- Testing timing after known exposure
- Isolation duration for positive cases
- Quarantine periods for exposed individuals
- Monitoring windows for potential symptoms
Factors Affecting Individual Incubation Periods
Several factors can influence how long it takes for symptoms to develop after exposure:
- Viral variant type
- Individual immune system status
- Vaccination status
- Age and overall health
- Exposure dose
- Underlying medical conditions
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the typical incubation period for COVID-19 and how long can it vary? The typical incubation period ranges from 2-14 days, with most people developing symptoms within 3-5 days after exposure. This period can vary based on individual factors and the specific variant involved.
How does the incubation period differ between COVID-19 variants like Delta and Omicron? The incubation period has generally become shorter with newer variants. While Delta typically showed symptoms around 4 days after exposure, Omicron and its subvariants tend to have even shorter incubation periods, often around 3 days.
Can a person spread COVID-19 during the incubation period before showing symptoms? Yes, individuals can transmit COVID-19 during the incubation period before developing symptoms. This pre-symptomatic transmission is a significant factor in the virus's spread.
How does the incubation period affect recommended quarantine and isolation guidelines? The incubation period directly influences isolation and quarantine recommendations. Current guidelines consider both the typical incubation window and the period of highest transmissibility to determine appropriate isolation durations.
What factors influence the length of the COVID-19 incubation period in individuals? Multiple factors affect the incubation period length, including the specific variant, individual immune status, vaccination history, age, overall health condition, and the initial exposure dose.