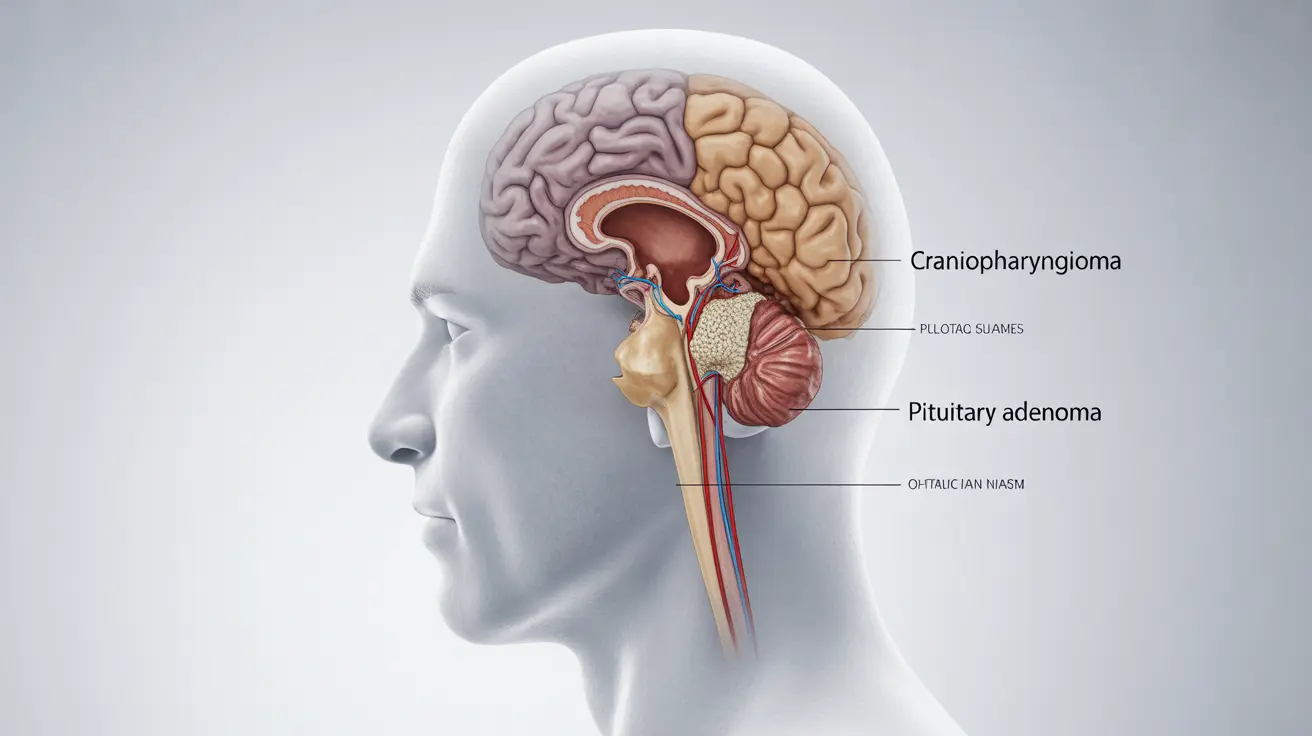
Understanding the distinctions between craniopharyngioma and pituitary adenoma is crucial for proper diagnosis and treatment. While both are brain tumors that affect the pituitary region, they have different characteristics, affect different age groups, and may require distinct treatment approaches. This comprehensive guide explores the key differences between these two conditions to help patients and caregivers better understand their unique features.
Understanding Craniopharyngioma and Pituitary Adenoma
Craniopharyngiomas are rare, benign tumors that develop near the pituitary gland, typically originating from embryonic tissue. In contrast, pituitary adenomas are more common tumors that develop directly from the pituitary gland tissue. Understanding these fundamental differences is essential for proper medical management.
Age and Occurrence Patterns
Craniopharyngiomas most commonly affect children between 5 and 14 years old, though they can occur in adults. These tumors account for approximately 5-10% of brain tumors in children. Pituitary adenomas, however, are more prevalent in adults, typically appearing between 30 and 60 years of age, and represent about 15% of all brain tumors.
Clinical Symptoms and Presentation
Visual Disturbances
Both conditions can cause vision problems due to their proximity to the optic chiasm. Patients may experience:
- Double vision
- Peripheral vision loss
- Progressive vision deterioration
Hormonal Symptoms
The impact on hormone production differs between the two conditions:
- Craniopharyngiomas often affect multiple hormone systems simultaneously
- Pituitary adenomas may cause specific hormonal overproduction or underproduction depending on the tumor type
Diagnostic Approaches
Doctors use various imaging techniques to distinguish between these tumors:
- MRI with contrast
- CT scans
- Visual field testing
- Hormone level assessment
Treatment Strategies
Surgical Options
Treatment approaches vary based on the tumor type:
- Craniopharyngiomas often require more aggressive surgical removal
- Pituitary adenomas may be treated with less invasive techniques, such as transsphenoidal surgery
Additional Therapies
Post-surgical treatments may include:
- Radiation therapy
- Hormone replacement therapy
- Regular monitoring and follow-up care
Long-term Outlook and Management
The prognosis differs between the two conditions. Pituitary adenomas generally have a more favorable outlook with proper treatment, while craniopharyngiomas may require more intensive long-term management due to their location and tendency to recur.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the main differences between craniopharyngioma and pituitary adenoma in symptoms and age affected?
Craniopharyngiomas primarily affect children (5-14 years) and cause multiple hormonal deficiencies, while pituitary adenomas typically occur in adults (30-60 years) and may cause specific hormonal imbalances. Both can affect vision, but craniopharyngiomas often present with more severe symptoms earlier.
How do doctors diagnose and distinguish craniopharyngioma from pituitary adenoma using imaging tests?
Doctors use MRI with contrast and CT scans to identify characteristic features of each tumor. Craniopharyngiomas often show calcification and cystic components, while pituitary adenomas typically appear as solid masses within the pituitary gland.
What treatment options are available for craniopharyngioma compared to pituitary adenoma?
Craniopharyngiomas usually require more extensive surgery and may need radiation therapy. Pituitary adenomas can often be treated with less invasive surgical approaches or, in some cases, medication alone.
Can craniopharyngioma or pituitary adenoma cause hormonal imbalances, and what symptoms might this lead to?
Both conditions can cause hormonal imbalances. Craniopharyngiomas typically affect multiple hormone systems, causing growth problems, diabetes insipidus, and thyroid issues. Pituitary adenomas may cause either overproduction or underproduction of specific hormones, leading to targeted symptoms.
What is the typical prognosis and potential complications for patients with craniopharyngioma versus pituitary adenoma?
Pituitary adenomas generally have a better prognosis with proper treatment. Craniopharyngiomas have a higher recurrence rate and may require lifelong hormone replacement therapy. Both conditions require ongoing monitoring, but craniopharyngiomas typically need more intensive long-term management.