When doctors suspect a potentially dangerous blood clot in the lungs, a CT chest scan is often the go-to diagnostic tool. This advanced imaging procedure, specifically known as CT pulmonary angiography, provides detailed images that can reveal the presence and location of pulmonary emboli, helping healthcare providers make quick and accurate diagnoses.
Understanding what this vital diagnostic test involves and when it's needed can help patients feel more prepared and less anxious about the procedure. Let's explore the essential aspects of CT chest scans for pulmonary embolism detection.
Warning Signs That May Lead to a CT Chest Scan
Several critical symptoms may prompt your healthcare provider to order a CT chest scan to check for pulmonary embolism:
- Sudden shortness of breath
- Sharp chest pain, especially when breathing deeply
- Rapid heartbeat
- Coughing up blood
- Anxiety and sweating
- Lightheadedness or fainting
These symptoms, particularly when combined with risk factors like recent surgery, prolonged immobility, or a history of blood clots, often warrant immediate medical attention and diagnostic imaging.
The CT Pulmonary Angiogram Process
During a CT chest scan for pulmonary embolism, you'll undergo a carefully coordinated procedure:
Preparation Phase
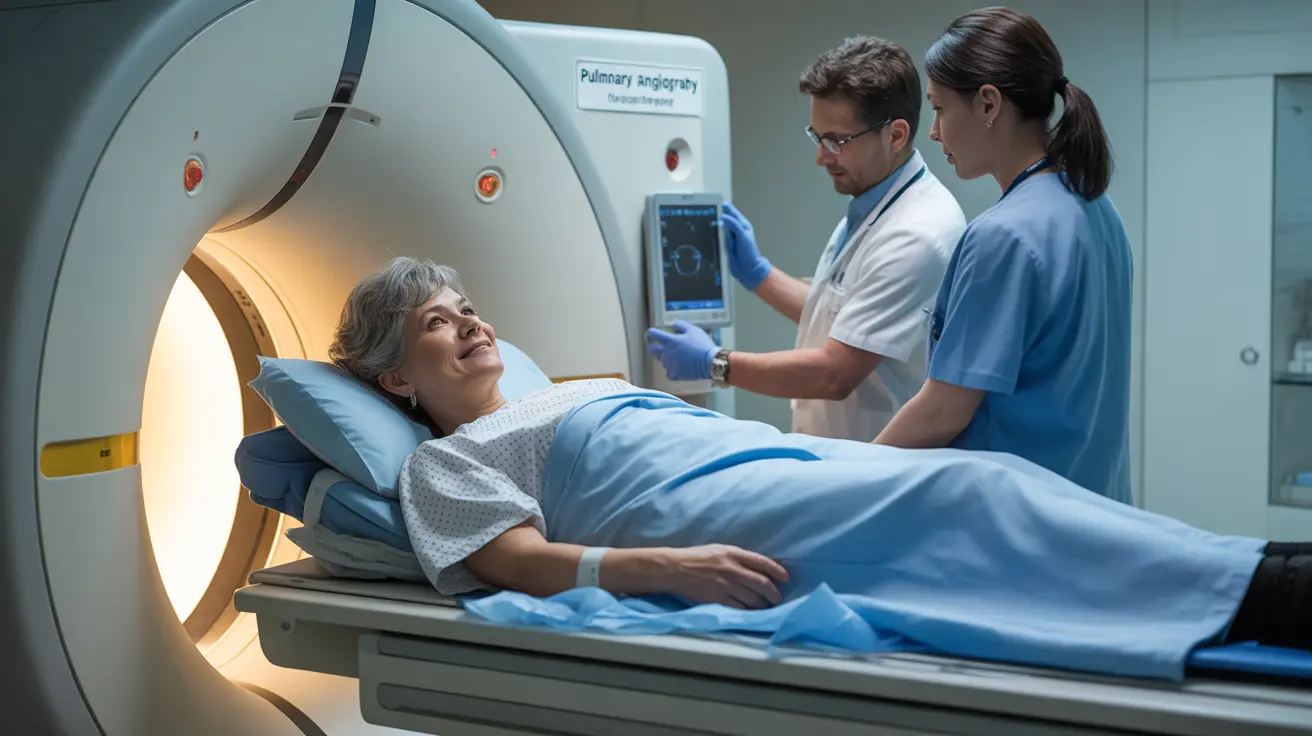
Before the scan begins, you'll need to change into a hospital gown and remove any metal objects. A healthcare professional will insert an IV line for contrast dye administration.
During the Scan
You'll lie on a movable table that slides into the CT scanner. The machine rotates around you, capturing detailed cross-sectional images of your chest. The contrast dye is injected during the scan to highlight blood vessels and potential clots.
Timing and Duration
The actual scanning process typically takes only a few minutes, though the entire procedure, including preparation, may last 15-30 minutes.
Understanding CT Scan Accuracy and Benefits
CT pulmonary angiography is highly effective at detecting blood clots in the lungs. The technology can identify both large and small pulmonary emboli with remarkable precision, offering several advantages:
- High sensitivity and specificity for detecting clots
- Ability to visualize surrounding lung tissue
- Quick results for emergency situations
- Non-invasive diagnostic method
- Capability to detect alternative causes of symptoms
Contrast Dye Considerations and Risks
While contrast dye is essential for clear imaging, patients should be aware of potential risks and side effects:
Common Side Effects
- Warm sensation during injection
- Metallic taste in mouth
- Brief nausea
- Mild itching
Serious Risks
Though rare, more serious reactions can occur, including:
- Allergic reactions
- Kidney problems in at-risk patients
- Contrast extravasation
Treatment Following Diagnosis
If a pulmonary embolism is confirmed through CT chest scanning, treatment typically begins immediately. Options may include:
- Anticoagulation medications
- Thrombolytic therapy for severe cases
- Placement of vena cava filters
- Ongoing monitoring and follow-up care
Frequently Asked Questions
What symptoms might indicate I need a CT chest pulmonary angiography to check for a pulmonary embolism?
Symptoms that may indicate the need for a CT chest scan include sudden shortness of breath, sharp chest pain, rapid heartbeat, coughing up blood, and dizziness, especially when combined with risk factors like recent surgery or prolonged immobility.
How is a CT pulmonary angiogram performed to diagnose blood clots in the lungs?
The procedure involves lying on a table that moves through a CT scanner while contrast dye is injected through an IV line. The scanner takes detailed cross-sectional images of your chest while the dye highlights blood vessels, allowing doctors to identify any clots.
What are the risks and side effects of receiving contrast dye during a CT chest scan for pulmonary embolism?
Common side effects include a warm sensation, metallic taste, and mild nausea. More serious risks, though rare, include allergic reactions and potential kidney problems in susceptible individuals.
Can CT chest scans detect small pulmonary emboli that other tests might miss?
Yes, CT pulmonary angiography is highly sensitive and can detect both large and small pulmonary emboli that might be missed by other diagnostic tests, making it the preferred imaging method for suspected PE.
What are the treatment options after a pulmonary embolism is diagnosed by CT pulmonary angiography?
Treatment typically includes blood-thinning medications (anticoagulants), and in severe cases, may involve thrombolytic therapy or placement of vena cava filters. The specific treatment plan depends on the size and location of the clot and the patient's overall health status.